JIB-04
Epigenetic modifier; Inhibits Jumonji histone demethylases
概要
JIB-04 is an epigenetic modifier that is a pan-selective inhibitor of Jumonji histone demethylase enzymes. It inhibits members of the family in the high nanomolar range with IC₅₀ values of 230, 340, 435, 445, 855 and 1100 nM for JARID1A, JMJD2E, JMJD2B, JMJD2A, JMJD3, and JMJD2C, respectively. It shows no activity against histone deacetylases and minimal effects against iron-containing enzymes methylcytosine dioxygenase TET1 and prolyl hydroxylases (Wang et al.; Easmon et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits proliferation in a variety of human tumor cell lines (Easmon et al.).
· Selectively toxic to lung or prostate cancer cells in vitro, and not to normal cells of the same cell type or to normal control lines isolated from the same patient (Wang et al.).
· Reduces tumor burden and prolongs survival in a mouse model of breast cancer (Wang et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits proliferation in a variety of human tumor cell lines (Easmon et al.).
· Selectively toxic to lung or prostate cancer cells in vitro, and not to normal cells of the same cell type or to normal control lines isolated from the same patient (Wang et al.).
· Reduces tumor burden and prolongs survival in a mouse model of breast cancer (Wang et al.).
Alternative Names
JHDM Inhibitor VII; NSC 693627
Cell Type
Cancer Cells and Cell Lines
Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Other
Area of Interest
Cancer Research
CAS Number
199596-05-9
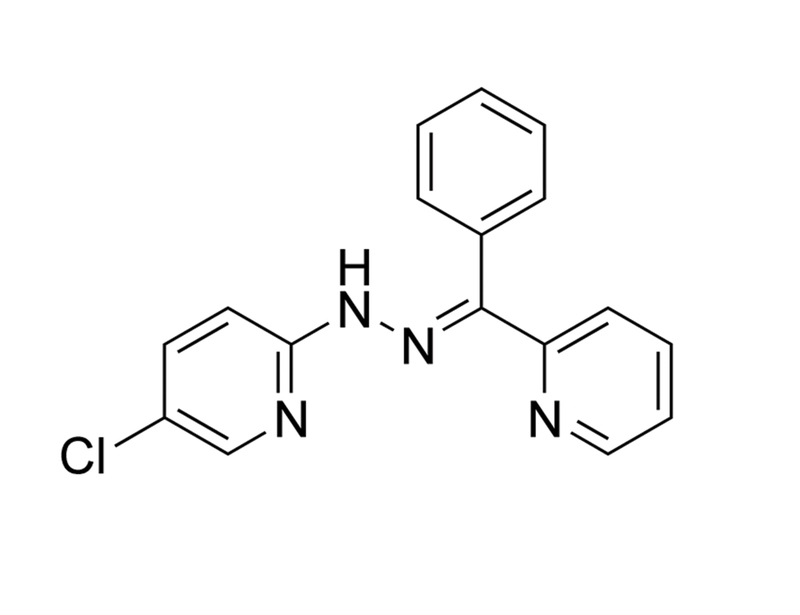
Chemical Formula
C₁₇H₁₃ClN₄
Molecular Weight
308.8 g/mol
Purity
≥ 95%
Pathway
Epigenetic
Target
Jumonji
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | JIB-04 | 73212 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | JIB-04 | 73212 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (2)
Nature Communications 2013
A small molecule modulates Jumonji histone demethylase activity and selectively inhibits cancer growth
Abstract
Abstract
The pharmacological inhibition of general transcriptional regulators has the potential to block growth through targeting multiple tumorigenic signalling pathways simultaneously. Here, using an innovative cell-based screen, we identify a structurally unique small molecule (named JIB-04) that specifically inhibits the activity of the Jumonji family of histone demethylases in vitro, in cancer cells, and in tumours in vivo. Unlike known inhibitors, JIB-04 is not a competitive inhibitor of α-ketoglutarate. In cancer, but not in patient-matched normal cells, JIB-04 alters a subset of transcriptional pathways and blocks viability. In mice, JIB-04 reduces tumour burden and prolongs survival. Importantly, we find that patients with breast tumours that overexpress Jumonji demethylases have significantly lower survival. Thus, JIB-04, a novel inhibitor of Jumonji demethylases in vitro and in vivo, constitutes a unique potential therapeutic and research tool against cancer, and validates the use of unbiased cellular screens to discover chemical modulators with disease relevance.
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 1997
Azinyl and Diazinyl Hydrazones Derived from Aryl N -Heteroaryl Ketones: Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity † , ‡
Abstract
Abstract
A series of N-heteroaryl hydrazones derived from aryl N-heteroaryl or bis-N-heteroaryl methanones was prepared in search for potential novel antitumor agents. The stereochemistry of these compounds was established by means of NMR spectroscopy. Antiproliferative activity was determined in a panel of human tumor cell lines (CCRF-CEM, Burkitt's lymphoma, HeLa, ZR-75-1, HT-29, and MEXF 276L) in vitro. Generally, the new compounds were found to be more potent (IC50 = 0.011-0.436 microM) than the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor hydroxyurea (IC50 = 140 microM). Most of the compounds exhibited the highest activity against Burkitt's lymphoma with an IC50 of 0.011-0.035 microM. [14C]Cytidine incorporation into DNA was quantitated for selected hydrazones (Z-A, E-1, Z-3, Z-4, E-5, Z-5, E-13, E-18, Z-19, Z-24, and E-26) as a measure of the inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. The E-configurated compounds were found to inhibit [14C]cytidine incorporation to a greater extent (IC50 = 0.67-5.05 microM) than the Z-isomers (IC50 = 7.20 to textgreater 10 microM). Principal component analysis of the IC50 values obtained for inhibition of cell proliferation revealed that the cell lines tested can be grouped into three main families showing different sensitivities toward the compounds in our series [(i) CCRF-CEM, Burkitt's lymphoma, and Hela; (ii) HT-29; and (iii) MEXF 276 L].