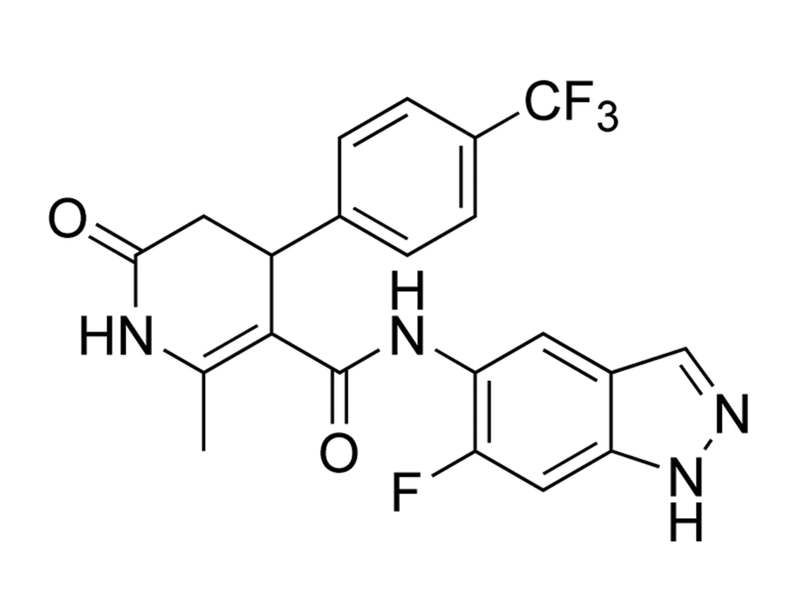
GSK429286A
RHO/ROCK pathway inhibitor; Inhibits ROCK1 and ROCK2
概要
GSK429286A is a cell-permeable inhibitor of Rho-associated kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2 with IC₅₀ values of 14 and 63 nM, respectively. It has improved oral bioavailability compared to closely related inhibitors. It also shows some selectivity towards p90 and p70 ribosomal S6 kinases (RSK) and leucine-rich repeat protein kinase-2 (LRRK2), with IC₅₀ values in the high nanomolar range (Goodman et al.; Nichols et al.).
MAINTENANCE
· Induces senescence-resistant proliferation of keratinocytes (Chapman et al.).
· ROCK inhibitors such as Y-27632 enhance the survival and cloning efficiency of human pluripotent stem cells when they are dissociated to single cells (Watanabe et al.)
DISEASE MODELING
· Reverses adrenalin-induced contraction of rat aortic tissue and decreases mean arterial pressure in spontaneously-hypertensive rats (Goodman et al.).
MAINTENANCE
· Induces senescence-resistant proliferation of keratinocytes (Chapman et al.).
· ROCK inhibitors such as Y-27632 enhance the survival and cloning efficiency of human pluripotent stem cells when they are dissociated to single cells (Watanabe et al.)
DISEASE MODELING
· Reverses adrenalin-induced contraction of rat aortic tissue and decreases mean arterial pressure in spontaneously-hypertensive rats (Goodman et al.).
Alternative Names
GSK 429286
Cell Type
Endothelial Cells, Pluripotent Stem Cells
Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Other
Application
Expansion, Maintenance
Area of Interest
Disease Modeling, Stem Cell Biology
CAS Number
864082-47-3
Chemical Formula
C₂₁H₁₆F₄N₄O₂
Molecular Weight
432.4 g/mol
Purity
≥ 98%
Pathway
RHO/ROCK
Target
ROCK
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | GSK429286A | 73182 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | GSK429286A | 73182 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (4)
Stem cell research & therapy 2014
The effect of Rho kinase inhibition on long-term keratinocyte proliferation is rapid and conditional.
Abstract
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: We previously demonstrated that the lifespan of primary human keratinocytes could be extended indefinitely by culture in the presence of the Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y-27632. This technique has proven to be very useful in diverse areas of basic and clinical research. METHODS: In this follow-up study we determine whether the continual presence of Y-27632 is required for sustained proliferation. We also test whether different ROCK inhibitors can be used for this technique and whether it can also promote indefinite proliferation of animal keratinocytes. We measure keratinocyte gene expression, proliferation, behaviour and lifespan in the presence and absence of Y-27632. RESULTS: We demonstrate that the extension of lifespan observed by culture of keratinocytes in the presence of fibroblast feeders and a ROCK inhibitor is reversible and that cells senesce gradually when the inhibitor is removed from the medium. Conversely, keratinocytes that are close to the end of their replicative life span can be revived by ROCK inhibition. We demonstrate that different inhibitors of ROCK can also efficiently extend the lifespan of human keratinocytes and that ROCK inhibition extends the lifespan of animal keratinocytes derived from mouse and bovine epithelia. Gene expression analysis of human epidermal keratinocytes cells grown in the presence of Y-27632 demonstrates that ROCK inhibition primarily inhibits keratinocyte differentiation. Live-imaging of keratinocytes cultured with ROCK inhibitors show that the effect of ROCK inhibition on cellular proliferation is immediate and ROCK inhibited cells proliferate rapidly without differentiation or stratification. CONCLUSIONS: ROCK inhibition rapidly and conditionally induces indefinite proliferation of keratinocytes. This method has far-reaching applications for basic research, as well as for regenerative and personalized medicine.
ACS chemical biology 2013 MAY
A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of dissociated human embryonic stem cells.
Abstract
Abstract
Poor survival of human embryonic stem (hES) cells after cell dissociation is an obstacle to research, hindering manipulations such as subcloning. Here we show that application of a selective Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, Y-27632, to hES cells markedly diminishes dissociation-induced apoptosis, increases cloning efficiency (from approximately 1% to approximately 27%) and facilitates subcloning after gene transfer. Furthermore, dissociated hES cells treated with Y-27632 are protected from apoptosis even in serum-free suspension (SFEB) culture and form floating aggregates. We demonstrate that the protective ability of Y-27632 enables SFEB-cultured hES cells to survive and differentiate into Bf1(+) cortical and basal telencephalic progenitors, as do SFEB-cultured mouse ES cells.
The Biochemical journal 2009
Substrate specificity and inhibitors of LRRK2, a protein kinase mutated in Parkinson's disease.
Abstract
Abstract
The LRRK2 (leucine-rich repeat protein kinase-2) is mutated in a significant number of Parkinson's disease patients, but little is known about its regulation and function. A common mutation changing Gly2019 to serine enhances catalytic activity, suggesting that small-molecule inhibitors might have utility in treating Parkinson's disease. We employed various approaches to explore the substrate-specificity requirements of LRRK2 and elaborated a peptide substrate termed Nictide, that had 20-fold lower Km and nearly 2-fold higher Vmax than the widely deployed LRRKtide substrate. We demonstrate that LRRK2 has marked preference for phosphorylating threonine over serine. We also observed that several ROCK (Rho kinase) inhibitors such as Y-27632 and H-1152, suppressed LRRK2 with similar potency to which they inhibited ROCK2. In contrast, GSK429286A, a selective ROCK inhibitor, did not significantly inhibit LRRK2. We also identified a mutant LRRK2[A2016T] that was normally active, but resistant to H-1152 and Y-27632, as well as sunitinib, a structurally unrelated multikinase inhibitor that, in contrast with other compounds, suppresses LRRK2, but not ROCK. We have also developed the first sensitive antibody that enables measurement of endogenous LRRK2 protein levels and kinase activity as well as shRNA (short hairpin RNA) methods to reduce LRRK2 expression. Finally, we describe a pharmacological approach to validate whether substrates are phosphorylated by LRRK2 and use this to provide evidence that LRRK2 may not be rate-limiting for the phosphorylation of the proposed substrate moesin. The findings of the present study will aid with the investigation of LRRK2.
Journal of medicinal chemistry 2007
Development of dihydropyridone indazole amides as selective Rho-kinase inhibitors.
Abstract
Abstract
Rho kinase (ROCK1) mediates vascular smooth muscle contraction and is a potential target for the treatment of hypertension and related disorders. Indazole amide 3 was identified as a potent and selective ROCK1 inhibitor but possessed poor oral bioavailability. Optimization of this lead resulted in the discovery of a series of dihydropyridones, exemplified by 13, with improved pharmacokinetic parameters relative to the initial lead. Indazole substitution played a critical role in decreasing clearance and improving oral bioavailability.