Fluprostenol
Prostanoid pathway activator; Activates prostaglandin F2α receptor
概要
Fluprostenol is a metabolically stable analog of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) with potent PGF2α receptor agonist activity (Abramovitz et al.). Fluprostenol competitively binds to human and rat PGF2α receptors with IC₅₀ values of 3.5 and 7.5 nM, respectively (Abramovitz et al.; Lake et al.).
DIFFERENTIATION
· Inhibits adipose differentiation of newborn rat adipocyte precursors in primary culture (Serrero & Lepak)
DISEASE MODELING
· Inhibits endothelin–induced contraction of the trabecular meshwork in bovine ocular tissue in vitro, a model of intraocular pressure in glaucoma (Thieme et al.).
DIFFERENTIATION
· Inhibits adipose differentiation of newborn rat adipocyte precursors in primary culture (Serrero & Lepak)
DISEASE MODELING
· Inhibits endothelin–induced contraction of the trabecular meshwork in bovine ocular tissue in vitro, a model of intraocular pressure in glaucoma (Thieme et al.).
Alternative Names
16-m-trifluoromethylphenoxy tetranor Prostaglandin F2α
Cell Type
Adipocytes
Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Other
Application
Differentiation
Area of Interest
Disease Modeling, Stem Cell Biology
CAS Number
54276-17-4
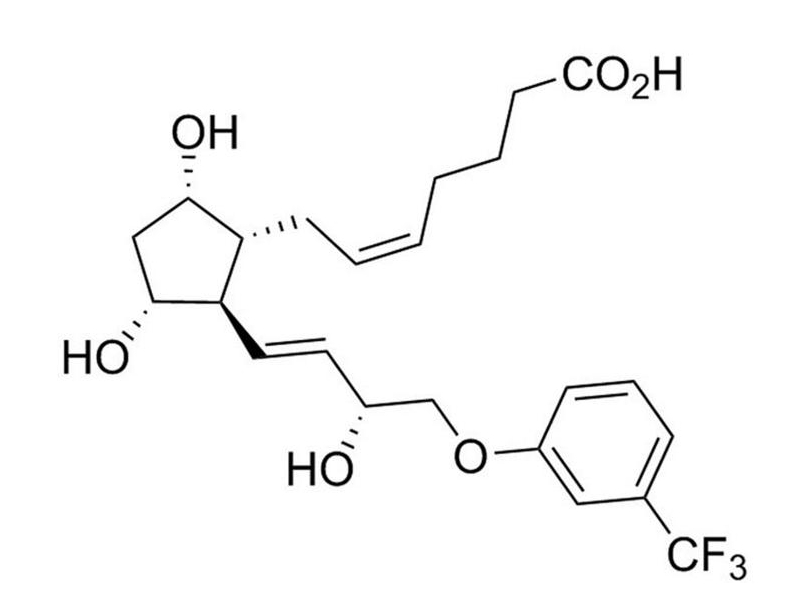
Chemical Formula
C₂₃H₂₉F₃O₆
Molecular Weight
458.5 g/mol
Purity
≥ 95%
Pathway
Prostanoid
Target
Prostaglandin Receptor
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Fluprostenol | 73672, 73674 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | Fluprostenol | 73672, 73674 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (4)
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2006 MAR
Endothelin antagonism: effects of FP receptor agonists prostaglandin F2alpha and fluprostenol on trabecular meshwork contractility.
Abstract
Abstract
PURPOSE This study analyzes additional mechanisms behind the ocular hypotensive effect of prostaglandin F (PGF) receptor (FP receptor) agonists PGF2alpha and fluprostenol (fluprostenol-isopropyl ester [travoprost]), which reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with glaucoma probably by enhancing uveoscleral flow. The trabecular meshwork (TM) is actively involved in IOP regulation through contractile mechanisms. Contractility of TM is induced by endothelin (ET)-1, a possible pathogenic factor in glaucoma. The involvement of FP receptor agonists in the ET-1 effects on TM function was studied. METHODS The effects of FP receptor agonists on contractility of bovine TM (BTM) were investigated using a force-length transducer. The effects of PGF2alpha on intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) mobilization in cultured cells were measured using fura-2AM. The expression of the FP receptor protein was examined using Western blot analysis. RESULTS The ET-1-induced (10(-8) M) contraction in isolated BTM was inhibited by PGF2alpha (10(-6) M) and fluprostenol (10(-6) M). This effect was blocked by FP receptor antagonists. Carbachol-induced contraction or baseline tension was not affected by PGF2alpha or fluprostenol. In cultured TM cells, ET-1 caused a transient increase in [Ca2+]i that was reduced by PGF2alpha. No reduction occurred in the presence of the FP receptor antagonist Al-8810. Western blot analysis revealed the expression of the FP receptor in native and cultured TM. CONCLUSIONS FP receptor agonists operate by direct interaction with ET-1-induced contractility of TM. This effect is mediated by the FP receptor. Thus, FP receptor agonists may decrease IOP by enhancing aqueous humor outflow through the TM by inhibiting ET-1-dependent mechanisms.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 1997 APR
Prostaglandin F2alpha receptor (FP receptor) agonists are potent adipose differentiation inhibitors for primary culture of adipocyte precursors in defined medium.
Abstract
Abstract
Prostaglandin F2alpha inhibits adipose differentiation of primary culture of adipocyte precursors and of the adipogenic cell line 1246 in defined medium. In the present paper, we investigated the effect of FP receptor agonists cloprostenol and fluprostenol on the differentiation of newborn rat adipocyte precursors in primary culture. The results show that cloprostenol and fluprostenol are very potent inhibitors of adipose differentiation. Dose response studies indicate that both agonists are more potent than PGF2alpha in inhibiting adipocyte precursors differentiation. 50% inhibition of adipose differentiation was observed at a concentration of 3 x 10(-12) M for cloprostenol and 3 to 10 x 10(-11) M for fluprostenol respectively whereas the PGF2alpha concentration required to elicit the same effect was 10(-8) M. In contrast compounds structurally related to PGE2 such as 17-phenyl trinor PGE2 had no effect on adipose differentiation except when added at a 10,000-fold higher concentration.
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 JAN
Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the human prostanoid FP receptor.
Abstract
Abstract
A cDNA clone coding for a functional human prostanoid FP receptor has been isolated from a uterus cDNA library. The human FP receptor consists of 359 amino acid residues with a predicted molecular mass of 40,060, and has the seven putative transmembrane domains characteristic of G-protein-coupled receptors. Challenge of Xenopus oocytes expressing the FP receptor with 10 nM of either prostaglandin (PG) F2 alpha or the selective FP-receptor agonist fluprostenol resulted in an elevation in intracellular Ca2+. Radioreceptor binding studies using membranes prepared from mammalian COS cells transfected with the FP receptor cDNA showed that the rank order of potency for prostaglandins and prostaglandin analogs in competition for [3H]PGF2 alpha specific binding sites was as predicted for the FP receptor, with PGF2 alpha approximately fluprostenol textgreater PGD2 textgreater PGE2 textgreater U46619 textgreater iloprost. In summary, we have cloned the human prostanoid FP receptor which is functionally coupled to the Ca2+ signalling pathway.
FEBS letters 1994 DEC
Cloning of the rat and human prostaglandin F2 alpha receptors and the expression of the rat prostaglandin F2 alpha receptor.
Abstract
Abstract
We have cloned the FP receptor from rat corpus luteum and human uterus cDNA libraries, respectively. The coding DNA sequence in the rat cDNA is 1101 bp and is similar to the mouse cDNA coding for a receptor protein of 366 amino acids. The human sequence shows a 5 bp deficiency in the 3' region, truncating the coding sequence to 359 amino acids. Northern blot analysis indicates highest expression in the ovary. Cell lines have been established giving stable expression of the FP receptor. Activation of the cloned FP receptor gave an increase in intracellular calcium, indicating signaling via phospholipase C-mediated phosphoinositide turnover. Using [3H]PGF2 alpha, binding of PGs showed the rank order of fluprostenol textgreater PhXA70 textgreater PGF2 alpha textgreater or = PhXA85 textgreater PGD2 textgreater PGE2.