Fasudil
RHO/ROCK pathway inhibitor; Inhibits ROCK2
概要
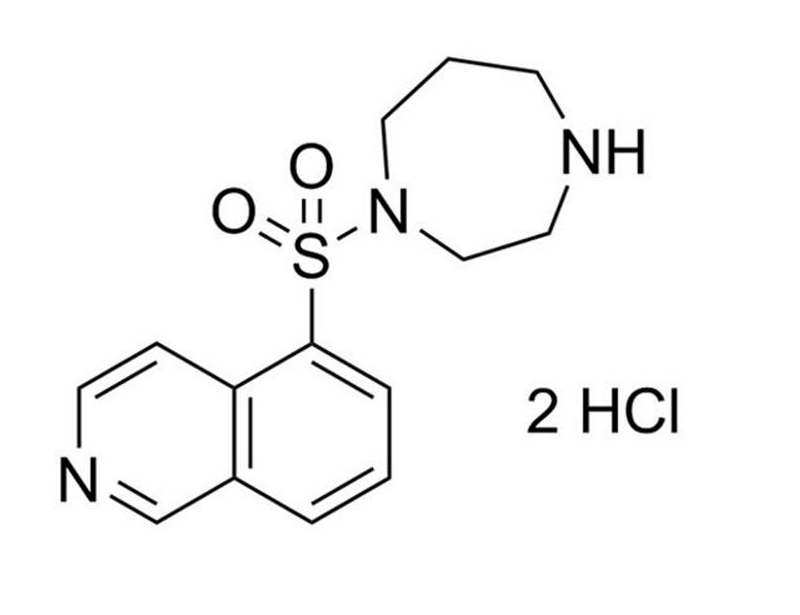
Fasudil (also known as HA-1077) is a potent inhibitor of Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 (ROCK2; IC₅₀ = 1.9 µM). Additionally, it inhibits protein kinase C-related kinase 2 (PRK2), mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase (MSK1), and mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 1b (MAPKAP-K1b) with IC₅₀ values of 4, 5, and 15 µM, respectively (Davies et al.). This product is supplied as the dihydrochloride salt of the molecule.
DIFFERENTIATION
· Suppresses proliferation and collagen production but also increases collagenase activity of hepatic stellate cells (Fukushima et al..
· Inhibits endothelial cell migration, viability, and tube formation in vitro in HUVECs (Yin et al.)
· Improves adipocyte differentiation, preventing development of diabetes and nephropathy in insulin-resistant diabetic rats (Kikuchi et al.).
DISEASE MODELING
· Reduces pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats (Oka et al.).
· Enhances neurological recovery after traumatic spinal cord injury (Hara et al.).
· Inhibits corneal neovascularization after alkali burns and promotes the healing of corneal epithelial defects in mice (Zeng et al.).
DIFFERENTIATION
· Suppresses proliferation and collagen production but also increases collagenase activity of hepatic stellate cells (Fukushima et al..
· Inhibits endothelial cell migration, viability, and tube formation in vitro in HUVECs (Yin et al.)
· Improves adipocyte differentiation, preventing development of diabetes and nephropathy in insulin-resistant diabetic rats (Kikuchi et al.).
DISEASE MODELING
· Reduces pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats (Oka et al.).
· Enhances neurological recovery after traumatic spinal cord injury (Hara et al.).
· Inhibits corneal neovascularization after alkali burns and promotes the healing of corneal epithelial defects in mice (Zeng et al.).
Alternative Names
HA-1077
Cell Type
Adipocytes, Endothelial Cells, HUVECs, Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells
Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Other
Application
Differentiation
Area of Interest
Angiogenic Cell Research, Disease Modeling
CAS Number
203911-27-7
Chemical Formula
C₁₄H₁₇N₃O₂S · 2HCl
Molecular Weight
364.3 g/mol
Purity
≥ 98%
Pathway
RHO/ROCK
Target
ROCK2
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Fasudil (Dihydrochloride) | 73662, 73664 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | Fasudil (Dihydrochloride) | 73662, 73664 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (7)
Molecular vision 2015 JAN
Fasudil hydrochloride, a potent ROCK inhibitor, inhibits corneal neovascularization after alkali burns in mice.
Abstract
Abstract
PURPOSE To investigate the effects and mechanisms of fasudil hydrochloride (fasudil) on and in alkali burn-induced corneal neovascularization (CNV) in mice. METHODS To observe the effect of fasudil, mice with alkali-burned corneas were treated with either fasudil eye drops or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) four times per day for 14 consecutive days. After injury, CNV and corneal epithelial defects were measured. The production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and heme oxygenase-1(HO-1) was measured. The infiltration of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and the mRNA expressions of CNV-related genes were analyzed on day 14. RESULTS The incidence of CNV was significantly lower after treatment with 100 μM and 300 μM fasudil than with PBS, especially with 100 μM fasudil. Meanwhile, the incidences of corneal epithelial defects was lower (n=15, all ptextless0.01). After treatment with 100 μM fasudil, the intensity of DHE fluorescence was reduced in the corneal epithelium and stroma than with PBS treatment (n=5, all ptextless0.01), and the number of filtrated PMNs decreased. There were significant differences between the expressions of VEGF, TNF-a, MMP-8, and MMP-9 in the 100 μM fasudil group and the PBS group (n=8, all ptextless0.05). The production of HO-1 protein in the 100 μM fasudil group was 1.52±0.34 times more than in the PBS group (n=5 sample, ptextless0.05). CONCLUSIONS 100 μM fasudil eye drops administered four times daily can significantly inhibit alkali burn-induced CNV and promote the healing of corneal epithelial defects in mice. These effects are attributed to a decrease in inflammatory cell infiltration, reduction of ROS, and upregulation of HO-1 protein after fasudil treatment.
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2007 MAY
Fasudil inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
Abstract
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced endothelial cell migration is an important component of tumor angiogenesis. Rho and Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) are key regulators of focal adhesion, stress fiber formation, and thus cell motility. Inhibitors of this pathway have been shown to inhibit endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis. In this study, we investigated the antiangiogenic effect of fasudil, one of the ROCK inhibitors. Fasudil inhibited VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration, viability, and tube formation in vitro in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration was reduced by fasudil associated with loss of stress fiber formation, focal adhesion assembly, and with the suppression of tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion proteins. Furthermore, fasudil inhibited VEGF-induced phosphorylation of myosin light chain, which is one of the main substrates of ROCK. Therefore, the effect of fasudil was suggested to be ROCK dependent. Fasudil not only inhibited VEGF-induced cell proliferation but also reversed the protective effect of VEGF on apoptosis, which resulted in the decrease of cell viability. Moreover, fasudil inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis in a directed in vivo angiogenesis assay. These data are the first demonstration that fasudil has antiangiogenic properties. Therefore, fasudil might be useful for the treatment of angiogenesis-related diseases, especially cancer.
Circulation research 2007 MAR
Rho kinase-mediated vasoconstriction is important in severe occlusive pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats.
Abstract
Abstract
Vascular remodeling, rather than vasoconstriction, is believed to account for high vascular resistance in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). We have found previously that acute Rho kinase inhibition nearly normalizes PAH in chronically hypoxic rats that have no occlusive neointimal lesions. Here we examined whether Rho kinase-mediated vasoconstriction was also important in a rat model of severe occlusive PAH. Adult rats were exposed to chronic hypoxia ( approximately 10% O(2)) after subcutaneous injection of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor SUGEN 5416. Hemodynamic measurements were made in anesthetized rats after 2 weeks of hypoxia (early group) and 3 weeks of hypoxia plus 2 weeks of normoxia (late group). Both groups developed PAH, with greater severity in the late group. In the early group, intravenous fasudil was more effective than intravenous bradykinin, inhaled NO, or intravenous iloprost in reducing right ventricular systolic pressure. Despite more occlusive vascular lesions, fasudil also markedly reduced right ventricular systolic pressure in late-stage rats. Blood-perfused lungs from late-stage rats showed spontaneous vasoconstriction, which was reversed partially by the endothelin A receptor blocker BQ123 and completely by fasudil or Y-27632. Phosphorylation of MYPT1, a downstream target of Rho kinase, was increased in lungs from both groups of rats, and fasudil (intravenous) reversed the increased phosphorylation in the late group. Thus, in addition to structural occlusion, Rho kinase-mediated vasoconstriction is an important component of severe PAH in SUGEN 5416/hypoxia-exposed rats, and PAH can be significantly reduced in the setting of a severely remodeled lung circulation if an unconventional vasodilator is used.
The Journal of endocrinology 2007 MAR
A Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, prevents development of diabetes and nephropathy in insulin-resistant diabetic rats.
Abstract
Abstract
Fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, may improve insulin signaling. However, its long-term effect on metabolic abnormalities and its preventive effect on diabetic nephropathy are still unknown. We assessed these effects of fasudil in insulin-resistant diabetic rats, comparing them with those of an angiotensin II receptor blocker, olmesartan. Male Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty (OLETF) and Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka, non-diabetic control, rats at 15 weeks of age were used. OLETF rats were randomized to receive a low or a high dose of fasudil or olmesartan for 25 weeks. To examine the therapeutic effects after the development of diabetes, OLETF rats at 30 weeks of age were given fasudil for 10 weeks. Administration of high-dose fasudil completely suppressed the development of diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia and increased serum adiponectin levels in OLETF rats. High-dose olmesartan also decreased hemoglobin A1c and increased serum adiponectin. There was a significant correlation between hemoglobin A1c and serum adiponectin or free fatty acid levels. The treatment with high-dose fasudil ameliorated proteinuria, glomerulosclerosis, renal interstitial fibrosis, and macrophage infiltration in OLETF rats. Olmesartan, even at the low dose, suppressed renal complications. The treatment with fasudil after the development of diabetes improved the metabolic abnormalities in OLETF rats, but could not suppress the progression of nephropathy. We conclude that the long-term treatment with fasudil prevents the development of diabetes, at least in part, by improving adipocyte differentiation in insulin-resistant diabetic rats. Early use of fasudil may prevent diabetic nephropathy.
Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver 2005 AUG
Fasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, suppresses collagen production and enhances collagenase activity in hepatic stellate cells.
Abstract
Abstract
BACKGROUND/AIMS The Rho-ROCK signaling pathways play an important role in the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). We investigated the effects of fasudil hydrochloride hydrate (fasudil), a Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, on cell growth, collagen production, and collagenase activity in HSCs. METHODS Rat HSCs and human HSC-derived TWNT-4 cells were cultured for studies on stress fiber formation and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) expression. Proliferation was measured by BrdU incorporation, and apoptosis by TUNEL assay. The phosphorylation states of the MAP kinases (MAPKs), extra cellular signal -regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), c-jun kinase (JNK), and p38 were evaluated by western blot analysis. Type I collagen, matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) production and gene expression were evaluated by ELISA and real-time PCR, respectively. Collagenase activity (active MMP-1) was also evaluated. RESULTS Fasudil (100 microM) inhibited cell spreading, the formation of stress fibers, and expression of alpha-SMA with concomitant suppression of cell growth, although it did not induce apoptosis. Fasudil inhibited phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK, and p38. Treatment with fasudil suppressed the production and transcription of collagen and TIMP, stimulated the production and transcription of MMP-1, and enhanced collagenase activity. CONCLUSION These findings demonstrated that fasudil not only suppresses proliferation and collagen production but also increases collagenase activity.
The Biochemical journal 2000 OCT
Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors.
Abstract
Abstract
The specificities of 28 commercially available compounds reported to be relatively selective inhibitors of particular serine/threonine-specific protein kinases have been examined against a large panel of protein kinases. The compounds KT 5720, Rottlerin and quercetin were found to inhibit many protein kinases, sometimes much more potently than their presumed targets, and conclusions drawn from their use in cell-based experiments are likely to be erroneous. Ro 318220 and related bisindoylmaleimides, as well as H89, HA1077 and Y 27632, were more selective inhibitors, but still inhibited two or more protein kinases with similar potency. LY 294002 was found to inhibit casein kinase-2 with similar potency to phosphoinositide (phosphatidylinositol) 3-kinase. The compounds with the most impressive selectivity profiles were KN62, PD 98059, U0126, PD 184352, rapamycin, wortmannin, SB 203580 and SB 202190. U0126 and PD 184352, like PD 98059, were found to block the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade in cell-based assays by preventing the activation of MAPK kinase (MKK1), and not by inhibiting MKK1 activity directly. Apart from rapamycin and PD 184352, even the most selective inhibitors affected at least one additional protein kinase. Our results demonstrate that the specificities of protein kinase inhibitors cannot be assessed simply by studying their effect on kinases that are closely related in primary structure. We propose guidelines for the use of protein kinase inhibitors in cell-based assays.