BI-D1870
90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) inhibitor
概要
BI-D1870 inhibits the 90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinases (RSKs), which are serine/threonine kinases involved in diverse cellular processes including growth, survival, and motility (Romeo et al.).
MAINTENANCE AND SELF-RENEWAL
· Reduces neural stem cell proliferation and self-renewal in vitro (Karelina et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits growth of breast cancer cell lines (Stratford et al., Dhillon et al.).
MAINTENANCE AND SELF-RENEWAL
· Reduces neural stem cell proliferation and self-renewal in vitro (Karelina et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits growth of breast cancer cell lines (Stratford et al., Dhillon et al.).
Alternative Names
Not applicable
Cell Type
Cancer Cells and Cell Lines, Mammary Cells, Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells
Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Other
Area of Interest
Cancer Research, Epithelial Cell Biology, Stem Cell Biology
CAS Number
501437-28-1
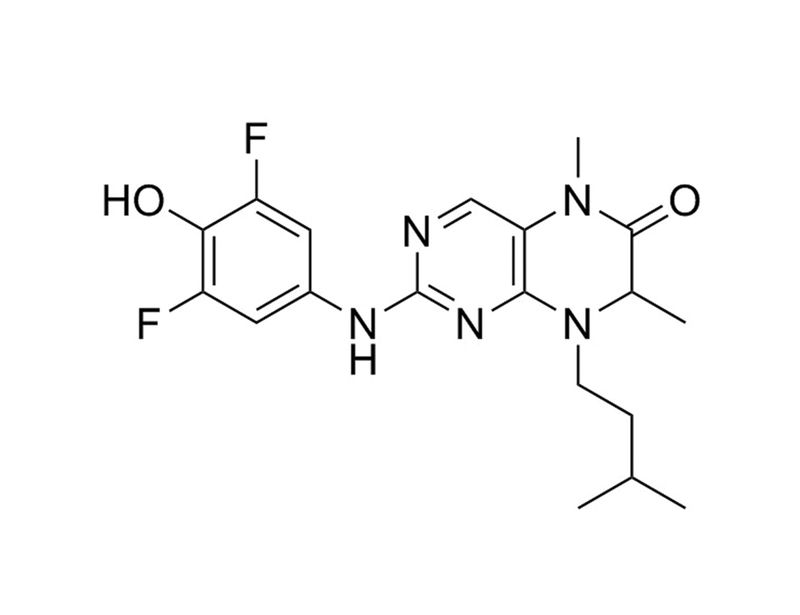
Chemical Formula
C₁₉H₂₃F₂N₅O₂
Molecular Weight
391.4 g/mol
Purity
≥ 95%
Target
RSK
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | BI-D1870 | 72712, 72714 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | BI-D1870 | 72712, 72714 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (5)
Experimental neurology 2014 MAR
Ribosomal S6 kinase regulates ischemia-induced progenitor cell proliferation in the adult mouse hippocampus.
Abstract
Abstract
Ischemia-induced progenitor cell proliferation is a prominent example of the adult mammalian brain's ability to regenerate injured tissue resulting from pathophysiological processes. In order to better understand and exploit the cell signaling mechanisms that regulate ischemia-induced proliferation, we examined the role of the p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade effector ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in this process. Here, using the endothelin-1 ischemia model in wild type mice, we show that the activated form of RSK is expressed in the progenitor cells of the subgranular zone (SGZ) after intrahippocampal cerebral ischemia. Further, RSK inhibition significantly reduces ischemia-induced SGZ progenitor cell proliferation. Using the neurosphere assay, we also show that both SGZ- and subventricular zone (SVZ)-derived adult neural stem cells (NSC) exhibit a significant reduction in proliferation in the presence of RSK and MAPK inhibitors. Taken together, these data reveal RSK as a regulator of ischemia-induced progenitor cell proliferation, and as such, suggest potential therapeutic value may be gained by specifically targeting the regulation of RSK in the progenitor cell population of the SGZ.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2012 JUL
Targeting p90 ribosomal S6 kinase eliminates tumor-initiating cells by inactivating Y-box binding protein-1 in triple-negative breast cancers.
Abstract
Abstract
Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) is the first reported oncogenic transcription factor to induce the tumor-initiating cell (TIC) surface marker CD44 in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. In order for CD44 to be induced, YB-1 must be phosphorylated at S102 by p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK). We therefore questioned whether RSK might be a tractable molecular target to eliminate TICs. In support of this idea, injection of MDA-MB-231 cells expressing Flag-YB-1 into mice increased tumor growth as well as enhanced CD44 expression. Despite enrichment for TICs, these cells were sensitive to RSK inhibition when treated ex vivo with BI-D1870. Targeting RSK2 with small interfering RNA (siRNA) or small molecule RSK kinase inhibitors (SL0101 and BI-D1870) blocked TNBC monolayer cell growth by ∼100%. In a diverse panel of breast tumor cell line models RSK2 siRNA predominantly targeted models of TNBC. RSK2 inhibition decreased CD44 promoter activity, CD44 mRNA, protein expression, and mammosphere formation. CD44(+) cells had higher P-RSK(S221/227) , P-YB-1(S102) , and mitotic activity relative to CD44(-) cells. Importantly, RSK2 inhibition specifically suppressed the growth of TICs and triggered cell death. Moreover, silencing RSK2 delayed tumor initiation in mice. In patients, RSK2 mRNA was associated with poor disease-free survival in a cohort of 244 women with breast cancer that had not received adjuvant treatment, and its expression was highest in the basal-like breast cancer subtype. Taking this further, we report that P-RSK(S221/227) is present in primary TNBCs and correlates with P-YB-1(S102) as well as CD44. In conclusion, RSK2 inhibition provides a novel therapeutic avenue for TNBC and holds the promise of eliminating TICs.
The Biochemical journal 2012 JAN
Regulation and function of the RSK family of protein kinases.
Abstract
Abstract
The RSK (90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase) family comprises a group of highly related serine/threonine kinases that regulate diverse cellular processes, including cell growth, proliferation, survival and motility. This family includes four vertebrate isoforms (RSK1, RSK2, RSK3 and RSK4), and single family member orthologues are also present in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans. The RSK isoforms are downstream effectors of the Ras/ERK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase) signalling pathway. Significant advances in the field of RSK signalling have occurred in the past few years, including several new functions ascribed to the RSK isoforms, the discovery of novel protein substrates and the implication of different RSK isoforms in cancer. Collectively, these new findings increase the diversity of biological functions regulated by RSK, and highlight potential new directions of research. In the present paper, we review the structure, expression and activation mechanisms of the RSK isoforms, and discuss their physiological roles on the basis of established substrates and recent discoveries.
Oncogene 2010 NOV
The expression of activated Y-box binding protein-1 serine 102 mediates trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer cells by increasing CD44+ cells.
Abstract
Abstract
The development of acquired resistance to trastuzumab remains a prevalent challenge in the treatment of patients whose tumors express human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2). We previously reported that HER2 overexpressing breast cancers are dependent on Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) for growth and survival. As YB-1 is also linked to drug resistance in other types of cancer, we address its possible role in trastuzumab insensitivity. Employing an in vivo model of acquired resistance, we demonstrate that resistant cell lines have elevated levels of P-YB-1(S102) and its activating kinase P-RSK and these levels are sustained following trastuzumab treatment. Further, to demonstrate the importance of YB-1 in mediating drug resistance, the expression of the active mutant YB-1(S102D) rendered the BT474 cell line insensitive to trastuzumab. Questioning the role of tumor-initiating cells (TIC) and their ability to escape cancer therapies, we investigate YB-1's role in inducing the cancer stem cell marker CD44. Notably, the resistant cells express more CD44 mRNA and protein compared with BT474 cells, which correlated with increased mammosphere formation. Expression of YB-1(S102D) in the BT474 cells increase CD44 protein levels, resulting in enhanced mammosphere formation. Further, exposing BT474 cells to trastuzumab selected for a resistant sub-population enriched for CD44. Conversely, small intefering RNA inhibition of CD44 restored trastuzumab sensitivity in the resistant cell lines. Our findings provide insight on a novel mechanism employed by tumor cells to acquire the ability to escape the effects of trastuzumab and suggest that targeting YB-1 may overcome resistance by eliminating the unresponsive TIC population, rendering the cancer sensitive to therapy.
The Biochemical journal 2007 DEC
The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update.
Abstract
Abstract
The specificities of 65 compounds reported to be relatively specific inhibitors of protein kinases have been profiled against a panel of 70-80 protein kinases. On the basis of this information, the effects of compounds that we have studied in cells and other data in the literature, we recommend the use of the following small-molecule inhibitors: SB 203580/SB202190 and BIRB 0796 to be used in parallel to assess the physiological roles of p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) isoforms, PI-103 and wortmannin to be used in parallel to inhibit phosphatidylinositol (phosphoinositide) 3-kinases, PP1 or PP2 to be used in parallel with Src-I1 (Src inhibitor-1) to inhibit Src family members; PD 184352 or PD 0325901 to inhibit MKK1 (MAPK kinase-1) or MKK1 plus MKK5, Akt-I-1/2 to inhibit the activation of PKB (protein kinase B/Akt), rapamycin to inhibit TORC1 [mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin)-raptor (regulatory associated protein of mTOR) complex], CT 99021 to inhibit GSK3 (glycogen synthase kinase 3), BI-D1870 and SL0101 or FMK (fluoromethylketone) to be used in parallel to inhibit RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase), D4476 to inhibit CK1 (casein kinase 1), VX680 to inhibit Aurora kinases, and roscovitine as a pan-CDK (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor. We have also identified harmine as a potent and specific inhibitor of DYRK1A (dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylated and -regulated kinase 1A) in vitro. The results have further emphasized the need for considerable caution in using small-molecule inhibitors of protein kinases to assess the physiological roles of these enzymes. Despite being used widely, many of the compounds that we analysed were too non-specific for useful conclusions to be made, other than to exclude the involvement of particular protein kinases in cellular processes.