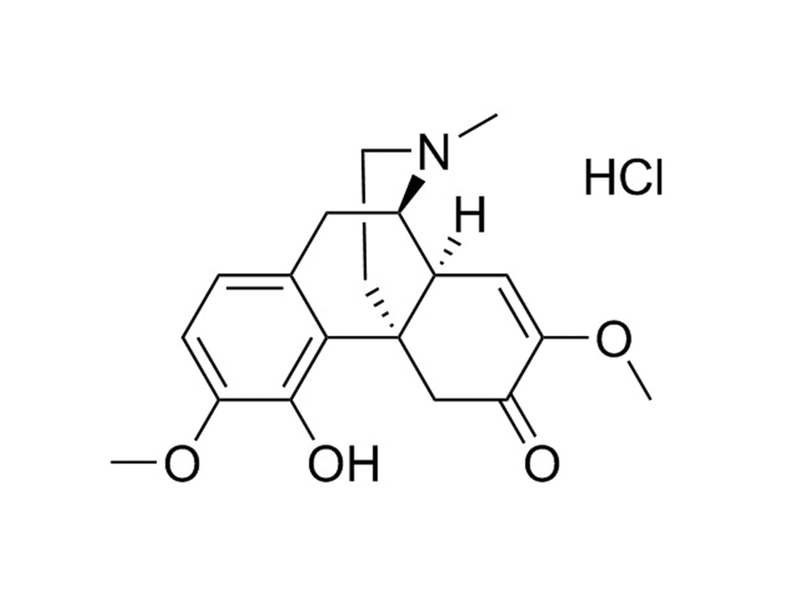
Sinomenine
Anti-inflammatory
概要
Sinomenine is a natural plant alkaloid commonly used to alleviate inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis (Wang and Li). It impairs signaling through Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB; Sun et al.; Wang and Li) and enhances the bioavailability of some compounds, at least in part through an inhibition of drug export by transporters like P-glycoprotein (Kesarwani et al.; Liu et al.).
MAINTENANCE AND SELF-RENEWAL
· Promotes self-renewal in cultured human and mouse embryonic stem cells (Desbordes et al.).
MAINTENANCE AND SELF-RENEWAL
· Promotes self-renewal in cultured human and mouse embryonic stem cells (Desbordes et al.).
Alternative Names
Cocculine; Cucoline; NSC 76021
Cell Type
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Other
Application
Expansion, Maintenance
Area of Interest
Stem Cell Biology
CAS Number
6080-33-7
Chemical Formula
C₁₉H₂₃NO₄ · HCl
Molecular Weight
365.9 g/mol
Purity
≥ 98%
Pathway
NF-κB
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Sinomenine (Hydrochloride) | 72882, 72884 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | Sinomenine (Hydrochloride) | 72882, 72884 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (5)
International immunopharmacology 2014 JAN
A combination of sinomenine and methotrexate reduces joint damage of collagen induced arthritis in rats by modulating osteoclast-related cytokines.
Abstract
Abstract
OBJECTIVE To analyze the combination therapy of Sinomenine (SIN) and Methotrexate (MTX) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), we herein demonstrated the combination effect of SIN and MTX on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in rats through their modulation on osteoclast-related cytokines. METHODS CIA was induced by the immunization of type II collagen (CII) in SD rats. SIN and MTX were administrated alone or in combination after the onset of arthritis. Arthritis index and histological analysis were used to evaluate the effect of treatments. Effects of SIN and MTX on expression of receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) and osteopontin (OPN) in synovial tissues were assayed by immunohistochemistry. RANKL, osteoprotegerin (OPG), IL-6, IL-17 and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in rat serum were measured by ELISA. The expression of osteoclast-related cytokines in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) from RA patients was assayed by RT-PCR. RESULTS SIN and MTX combination additively reduced the inflammatory symptoms and joint damage in CIA. Combination of SIN and MTX significantly repressed synovial RANKL and OPN production. SIN and MTX exhibited complementary and synergistic effect upon down-regulating RANKL, IL-6, IL-17 and MMPs in rat serum. SIN and MTX also modulated the expression of RANKL and OPG in RA-FLS. CONCLUSION SIN and MTX have additive effects, decreasing inflammation and joint damage in CIA rats by modulating osteoclast-related cytokines. These results are indicative of the combined effect of SIN and MTX for anti-arthritic treatment in RA.
PloS one 2014 JAN
Sinomenine sensitizes multidrug-resistant colon cancer cells (Caco-2) to doxorubicin by downregulation of MDR-1 expression.
Abstract
Abstract
Chemoresistance in multidrug-resistant (MDR) cells over expressing P-glycoprotein (P-gp) encoded by the MDR1 gene, is a major obstacle to successful chemotherapy for colorectal cancer. Previous studies have indicated that sinomenine can enhance the absorption of various P-gp substrates. In the present study, we investigated the effect of sinomenine on the chemoresistance in colon cancer cells and explored the underlying mechanism. We developed multidrug-resistant Caco-2 (MDR-Caco-2) cells by exposure of Caco-2 cells to increasing concentrations of doxorubicin. We identified overexpression of COX-2 and MDR-1 genes as well as activation of the NF-κB signal pathway in MDR-Caco-2 cells. Importantly, we found that sinomenine enhances the sensitivity of MDR-Caco-2 cells towards doxorubicin by downregulating MDR-1 and COX-2 expression through inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. These findings provide a new potential strategy for the reversal of P-gp-mediated anticancer drug resistance.
Asian Pacific journal of tropical biomedicine 2013 APR
Bioavailability enhancers of herbal origin: an overview.
Abstract
Abstract
Recently, the use of herbal medicines has been increased all over the world due to their therapeutic effects and fewer adverse effects as compared to the modern medicines. However, many herbal drugs and herbal extracts despite of their impressive in-vitro findings demonstrates less or negligible in-vivo activity due to their poor lipid solubility or improper molecular size, resulting in poor absorption and hence poor bioavailability. Nowadays with the advancement in the technology, novel drug delivery systems open the door towards the development of enhancing bioavailability of herbal drug delivery systems. For last one decade many novel carriers such as liposomes, microspheres, nanoparticles, transferosomes, ethosomes, lipid based systems etc. have been reported for successful modified delivery of various herbal drugs. Many herbal compounds including quercetin, genistein, naringin, sinomenine, piperine, glycyrrhizin and nitrile glycoside have demonstrated capability to enhance the bioavailability. The objective of this review is to summarize various available novel drug delivery technologies which have been developed for delivery of drugs (herbal), and to achieve better therapeutic response. An attempt has also been made to compile a profile on bioavailability enhancers of herbal origin with the mechanism of action (wherever reported) and studies on improvement in drug bioavailability, exhibited particularly by natural compounds.
International immunopharmacology 2011 MAR
Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine.
Abstract
Abstract
Sinomenine (SN), a pure compound extracted from the Sinomenium acutum plant, has been found to inhibit T- and B-lymphocyte activation, proliferation and function and to interfere with the differentiation, recruitment and function of several other cell types, such as dendritic cells (DC). SN has demonstrated its potential anti-inflammatory role for treating immune-related disorders in experimental animal models and in some clinical applications. This review will summarize its potential effects, mechanisms and applications.
Cell stem cell 2008 JUN
High-throughput screening assay for the identification of compounds regulating self-renewal and differentiation in human embryonic stem cells.
Abstract
Abstract
High-throughput screening (HTS) of chemical libraries has become a critical tool in basic biology and drug discovery. However, its implementation and the adaptation of high-content assays to human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) have been hampered by multiple technical challenges. Here we present a strategy to adapt hESCs to HTS conditions, resulting in an assay suitable for the discovery of small molecules that drive hESC self-renewal or differentiation. Use of this new assay has led to the identification of several marketed drugs and natural compounds promoting short-term hESC maintenance and compounds directing early lineage choice during differentiation. Global gene expression analysis upon drug treatment defines known and novel pathways correlated to hESC self-renewal and differentiation. Our results demonstrate feasibility of hESC-based HTS and enhance the repertoire of chemical compounds for manipulating hESC fate. The availability of high-content assays should accelerate progress in basic and translational hESC biology.