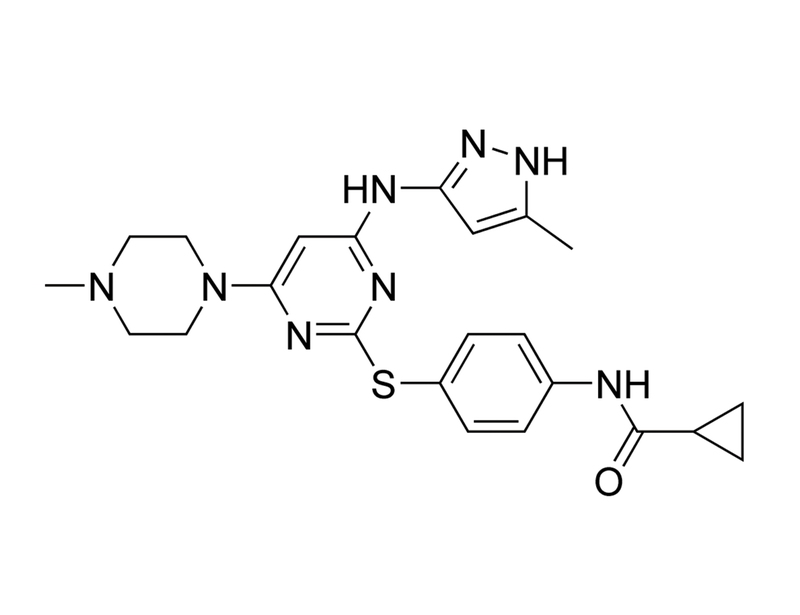
MK0457
Aurora kinase pathway inhibitor; Inhibits aurora kinase A
概要
MK0457 is a pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor with a preference for Aurora A (Ki = 0.6 nM) over Aurora B (Ki = 18 nM) or Aurora C (Ki = 4.6 nM; Pollard & Mortimore; Harrington et al.). It is selective in a protein kinase screen (190 kinases tested) with the closest hit being Fms-related tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT-3; Ki = 30 nM; Pollard & Mortimore; Harrington et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits proliferation of a wide variety of tumor cell lines in vitro (Harrington et al.; Li et al.; Arlot-Bonnemains et al.).
· Blocks the growth of tumors in xenograft models of cancer, inhibits histone H3 phosphorylation, and increases apoptosis (Harrington et al.; Li et al.; Lin et al.).
· Disrupts bipolar spindle formation during mitosis, arresting cell cycle progression at the G2/M phase (Li et al.).
CANCER RESEARCH
· Inhibits proliferation of a wide variety of tumor cell lines in vitro (Harrington et al.; Li et al.; Arlot-Bonnemains et al.).
· Blocks the growth of tumors in xenograft models of cancer, inhibits histone H3 phosphorylation, and increases apoptosis (Harrington et al.; Li et al.; Lin et al.).
· Disrupts bipolar spindle formation during mitosis, arresting cell cycle progression at the G2/M phase (Li et al.).
Alternative Names
Tozasertib; VX 680
Cell Type
Cancer Cells and Cell Lines
Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Non-Human Primate, Other
Area of Interest
Cancer Research
CAS Number
639089-54-6
Chemical Formula
C₂₃H₂₈N₈OS
Molecular Weight
464.6 g/mol
Purity
≥ 98%
Pathway
Aurora Kinase
Target
Aurora Kinase A
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | MK0457 | 73282, 73284 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MK0457 | 73282, 73284 | All | English |
数据及文献
Publications (5)
American journal of translational research 2010
VX680/MK-0457, a potent and selective Aurora kinase inhibitor, targets both tumor and endothelial cells in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Abstract
Abstract
Aurora kinases are key regulators of cell mitosis and have been implicated in the process of tumorigenesis. In recent years, the Aurora kinases have attracted much interest as promising targets for cancer treatment. Here we report on the roles of Aurora A and Aurora B kinases in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Using genomewide expression array analysis of 174 patient samples of ccRCC, we found that expression levels of Aurora A and B were significantly elevated in ccRCC compared to normal kidney samples. High expression levels of Aurora A and Aurora B were significantly associated with advanced tumor stage and poor patient survival. Inhibition of Aurora kinase activity with the drug VX680 (also referred to as MK-0457) inhibited ccRCC cell growth in vitro and led to ccRCC cell accumulation in the G2/M phase and apoptosis. Growth of ccRCC xenograft tumors was also inhibited by VX680 treatment, accompanied by a reduction of tumor microvessel density. Analysis of endothelial cell lines demonstrated that VX680 inhibits endothelial cell growth with effects similar to that seen in ccRCC cells. Our findings suggest that VX680 inhibits the growth of ccRCC tumors by targeting the proliferation of both ccRCC tumor cells and tumor-associated endothelial cells. Aurora kinases and their downstream cell cycle proteins have an important role in ccRCC and may be potent prognostic markers and therapy targets for this disease.
Journal of medicinal chemistry 2009
Discovery and development of aurora kinase inhibitors as anticancer agents.
Abstract
Abstract
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2008
Targeting aurora kinase with MK-0457 inhibits ovarian cancer growth.
Abstract
Abstract
PURPOSE: The Aurora kinase family plays pivotal roles in mitotic integrity and cell cycle. We sought to determine the effects of inhibiting Aurora kinase on ovarian cancer growth in an orthotopic mouse model using a small molecule pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor, MK-0457. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: We examined cell cycle regulatory effects and ascertained the therapeutic efficacy of Aurora kinase inhibition both alone and combined with docetaxel using both in vitro and in vivo ovarian cancer models. RESULTS: In vitro cytotoxicity assays with HeyA8 and SKOV3ip1 cells revealed textgreater10-fold greater docetaxel cytotoxicity in combination with MK-0457. After in vivo dose kinetics were determined using phospho-histone H3 status, therapy experiments with the chemosensitive HeyA8 and SKOV3ip1 as well as the chemoresistant HeyA8-MDR and A2780-CP20 models showed that Aurora kinase inhibition alone significantly reduced tumor burden compared with controls (P valuestextless0.01). Combination treatment with docetaxel resulted in significantly improved reduction in tumor growth beyond that afforded by docetaxel alone (P textlessor= 0.03). Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunohistochemistry revealed that MK-0457 alone and in combination with docetaxel significantly reduced cellular proliferation (P valuestextless0.001). Compared with controls, treatment with MK-0457 alone and in combination with docetaxel also significantly increased tumor cell apoptosis by approximately 3-fold (Ptextless0.01). Remarkably, compared with docetaxel monotherapy, MK-0457 combined with docetaxel resulted in significantly increased tumor cell apoptosis. CONCLUSIONS: Aurora kinase inhibition significantly reduces tumor burden and cell proliferation and increases tumor cell apoptosis in this preclinical orthotopic model of ovarian cancer. The role of Aurora kinase inhibition in ovarian cancer merits further investigation in clinical trials.
Endocrine-related cancer 2008
Effects of the Aurora kinase inhibitor VX-680 on anaplastic thyroid cancer-derived cell lines.
Abstract
Abstract
Anaplastic thyroid cancers (ATC) are aggressive tumors, which exhibit cell cycle misregulations leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation and genomic instability. They fail to respond to chemotherapeutic agents and radiation therapy, and most patients die within a few months of diagnosis. In the present study, we evaluated the in vitro effects on ATC cells of VX-680, an inhibitor of the Aurora serine/threonine kinases involved in the regulation of multiple aspects of chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. The effects of VX-680 on proliferation, apoptosis, soft agar colony formation, cell cycle, and ploidy were tested on the ATC-derived cell lines CAL-62, 8305C, 8505C, and BHT-101. Treatment of the different ATC cells with VX-680 inhibited proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner, with the IC50 between 25 and 150 nM. The VX-680 significantly impaired the ability of the different cell lines to form colonies in soft agar. Analysis of caspase-3 activity showed that VX-680 induced apoptosis in the different cell lines. CAL-62 cells exposed for 12 h to VX-680 showed an accumulation of cells with textgreater or =4N DNA content. Time-lapse analysis demonstrated that VX-680-treated CAL-62 cells exit metaphase without dividing. Moreover, histone H3 phosphorylation was abrogated following VX-680 treatment. In conclusion, our data demonstrated that VX-680 is effective in reducing cell growth of different ATC-derived cell lines and warrant further investigation to exploit its potential therapeutic value for ATC treatment.
Nature medicine 2004
VX-680, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the Aurora kinases, suppresses tumor growth in vivo.
Abstract
Abstract
The Aurora kinases are essential for the regulation of chromosome segregation and cytokinesis during mitosis. Aberrant expression and activity of these kinases occur in a wide range of human tumors, and lead to aneuploidy and tumorigenesis. Here we report the discovery of a highly potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of Aurora kinases, VX-680, that blocks cell-cycle progression and induces apoptosis in a diverse range of human tumor types. This compound causes profound inhibition of tumor growth in a variety of in vivo xenograft models, leading to regression of leukemia, colon and pancreatic tumors at well-tolerated doses. Our data indicate that Aurora kinase inhibition provides a new approach for the treatment of multiple human malignancies.