Human Recombinant IGF-II
Insulin-like growth factor 2
概要
Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF-II) is a polypeptide that belongs to the family of insulin-like growth factors that are similar in molecular structure to proinsulin. IGF-II binding to IGF-I receptor activates a signaling cascade via the MAPK and PI3K pathways. IGF-II affects growth, differentiation, and survival of cells in a variety of tissues during embryonic development. It stimulates proliferation and migration of primary lymphatic endothelial cells, and induces lymphangiogenesis (Guvakova).
Subtype
Cytokines, Growth Factors
Alternative Names
Insulin-like growth factor type 2, Insulin-like growth factor II, Somatomedin A, T3M-11-derived growth factor
Cell Type
Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells, Neural Cells, PSC-Derived, Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells, Neurons, Prostate Cells
Species
Human
Area of Interest
Epithelial Cell Biology, Neuroscience, Stem Cell Biology
Molecular Weight
7.5 kDa
Purity
≥ 95%
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Human Recombinant IGF-II | 78023, 78023.1, 78023.2 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | Human Recombinant IGF-II | 78023, 78023.1, 78023.2 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
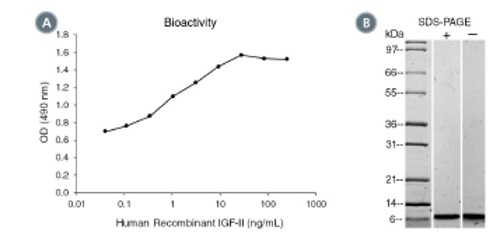
(A) The biological activity of Human Recombinant IGF-II was tested by its ability to promote the proliferation of FDC-P1 cells. Cell
proliferation was measured after 48 hours of culture using a fluorometric assay method. The EC50 is defined as the effective
concentration of the growth factor at which cell proliferation is at 50% of maximum. The EC50 in the above example is 1.1 - 1.6 ng/mL.
(B) 1 μg of Human Recombinant IGF-II was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (+) and non-reducing (-) conditions and visualized
by Coomassie Blue staining. Human Recombinant IGF-II has a predicted molecular mass of 7.5 kDa.