Human Recombinant Noggin
Noggin
概要
Noggin binds to and antagonizes bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) ligands of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) family. Noggin supports maintenance of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells in vitro, and can be used to prevent spontaneous differentiation in the short term (Chaturvedi et al.). Noggin is essential for development of structures derived from ectoderm embryonic somite, skeletal patterning, and neurogenesis in vivo. It also influences chondrogenesis, osteogenesis, and joint formation (Krause et al.), and promotes dopaminergic differentiation of embryonic stem cells and subsequent survival of dopamine neurons (Chiba et al.).
Subtype
Cytokines
Alternative Names
NOG, SYM1, SYNS1, Symphalangism 1 (proximal), Synostoses (multiple) syndrome
Cell Type
Neural Cells, PSC-Derived, Neurons, Pluripotent Stem Cells
Species
Human
Area of Interest
Neuroscience, Stem Cell Biology
Molecular Weight
30 kDa
Purity
≥ 95%
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Human Recombinant Noggin | 78060, 78060.1, 78060.2 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | Human Recombinant Noggin | 78060, 78060.1, 78060.2 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
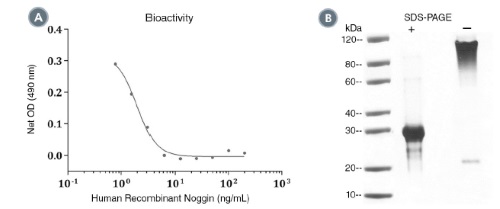
(A) The biological activity of Human Recombinant Noggin was tested by its ability to inhibit BMP-4 induced alkaline phosphatase
production of ATDC-5 cells. Inhibitition of BMP-4 induced alkaline phosphatase production was measured using a fluorometric assay
method. The EC50 is defined as the effective concentration of the growth factor at which inhibition of alkaline phosphatase production is
at 50% of maximum. The EC50 in the above example is 1.9 ng/mL.
(B) 2 μg of Human Recombinant Noggin was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (+) and non-reducing (-) conditions and visualized
by Coomassie Blue staining. Human Recombinant Noggin has a predicted molecular mass of 30 kDa.