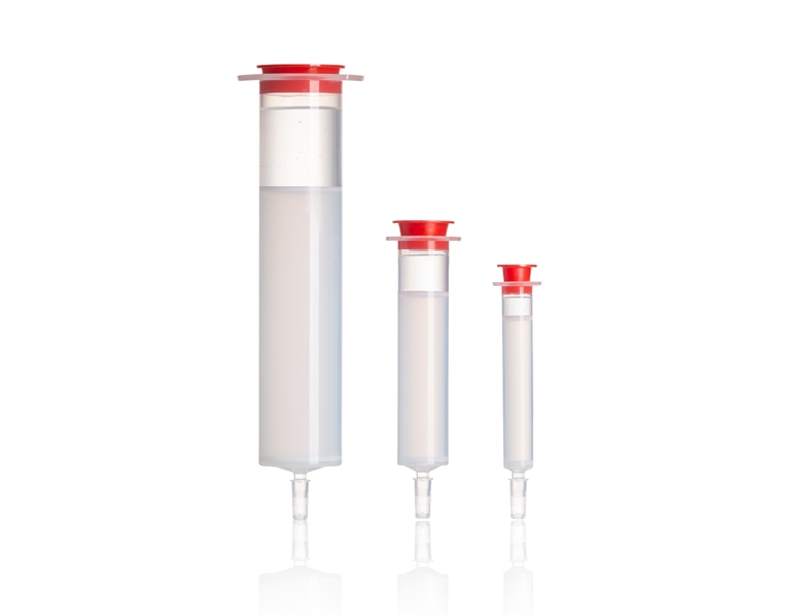
Extracellular Vesicle SEC Columns
The EV isolation protocol using the SEC columns is easy and takes approximately 15 minutes. The columns are available in three sizes for different sample volume ranges and can be used up to five times.
• Reusable (up to five times)
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
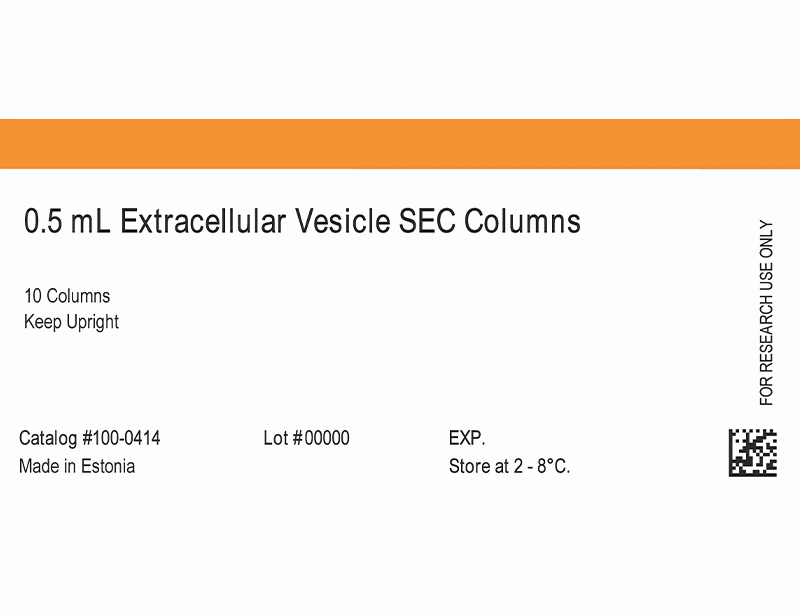
| Product Information Sheet | 0.5 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Columns | 100-0414 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | 2 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Columns | 100-0415 | All | English |
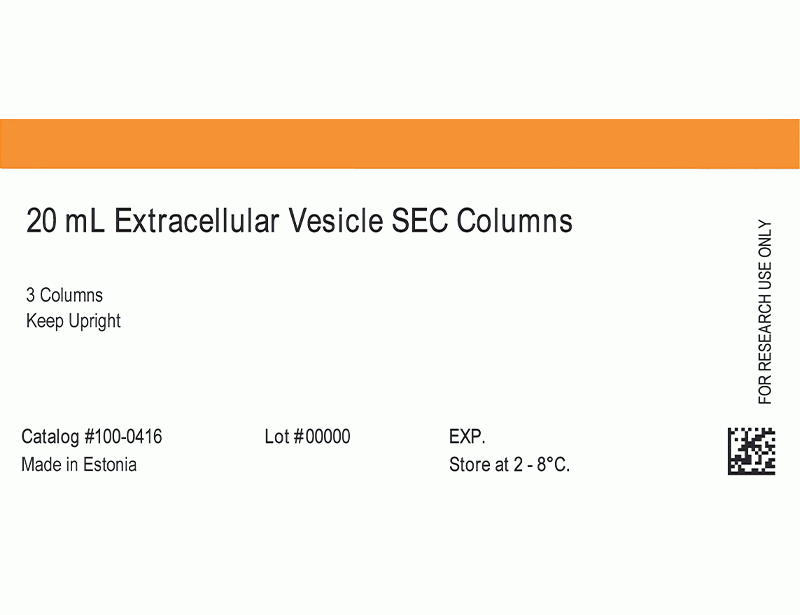
| Product Information Sheet | 20 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Columns | 100-0416 | All | English |
Data
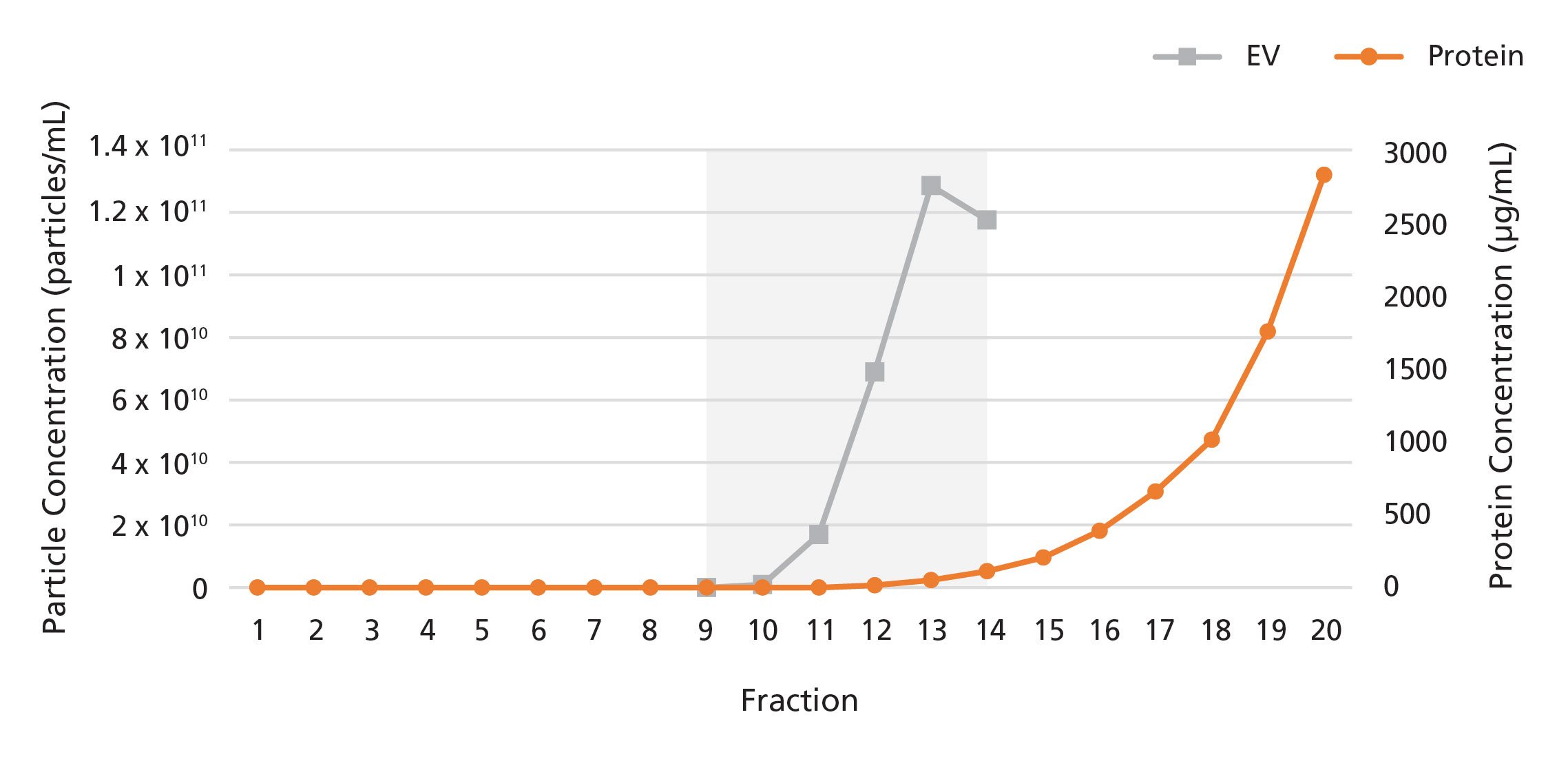
Figure 1. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles from Plasma Using a 0.5 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Column
The 0.5 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Column was loaded with 0.5 mL of human plasma. 100 μL fractions were collected and analyzed for particle and protein content by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assays, respectively. EVs were detected in fractions 9 - 14, while proteins were detected in fractions 15 onwards.
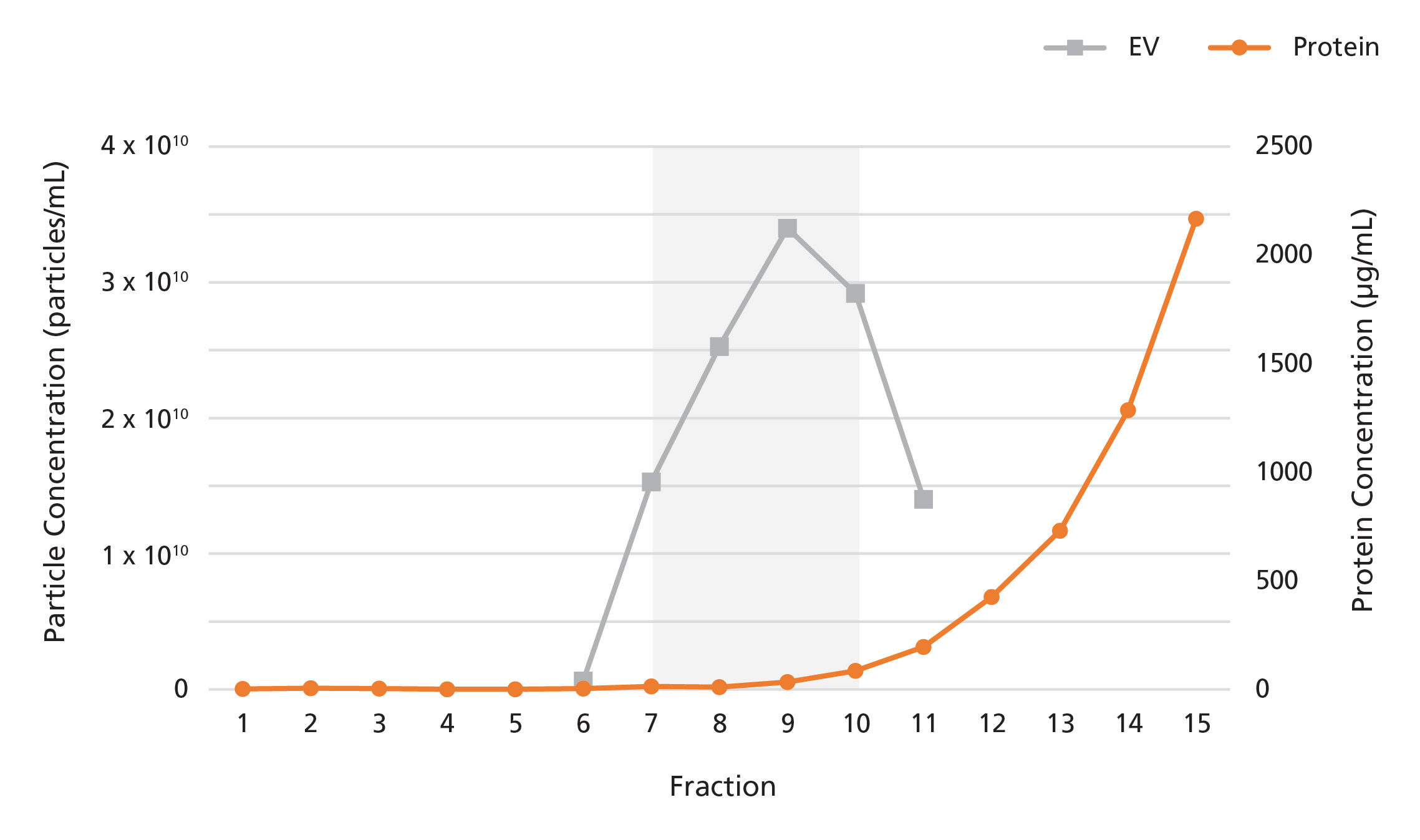
Figure 2. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles from Plasma Using a 2 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Column
The 2 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Column was loaded with 2 mL of human plasma. 500 μL fractions were collected and analyzed for particle and protein content by nanoparticle tracking analysis and bicinchoninic acid assays, respectively. EVs were detected in fractions 7 - 10, while proteins were detected in fractions 11 onwards.
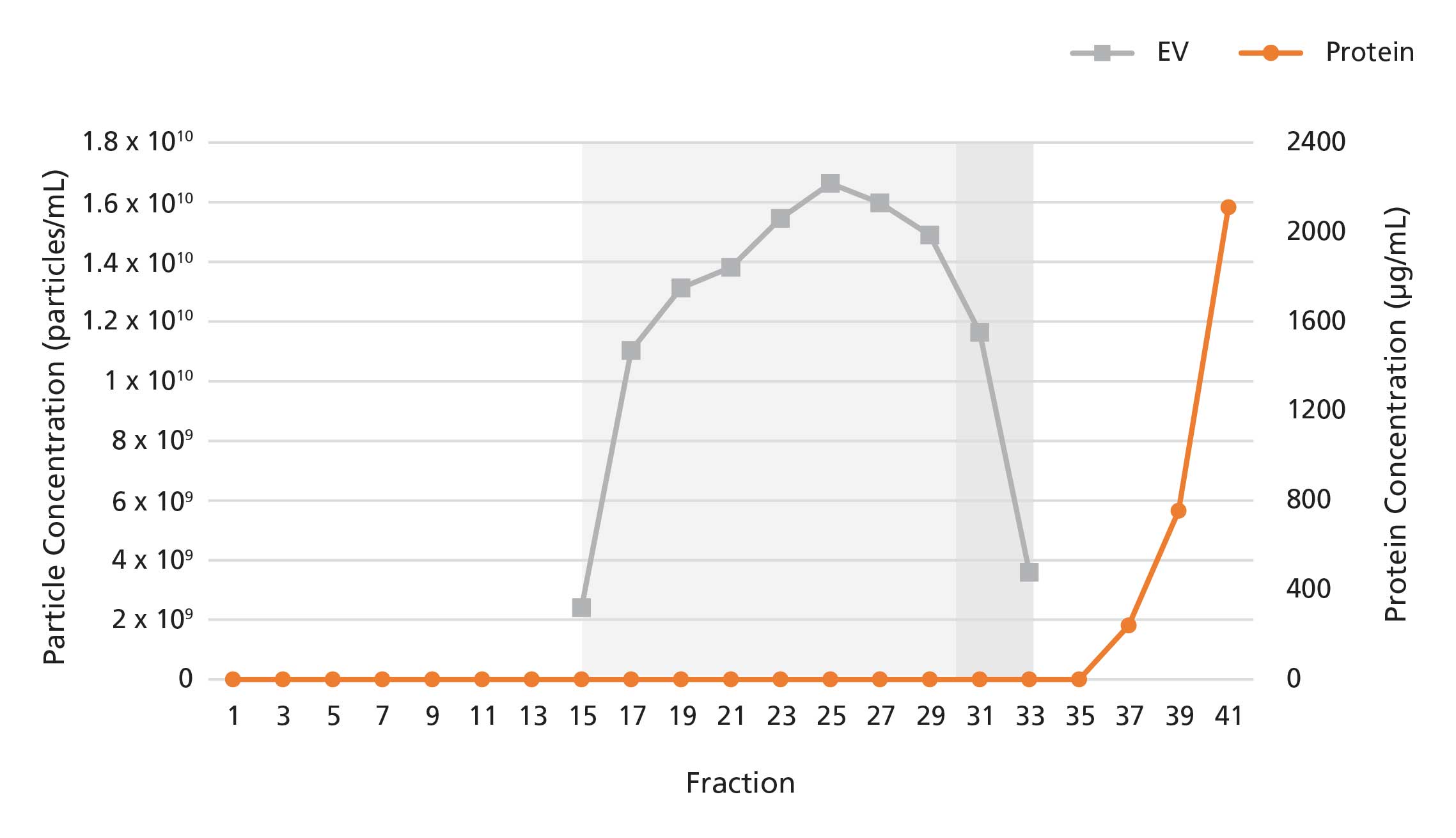
Figure 3. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles from Conditioned Medium Using a 20 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Column
The 20 mL Extracellular Vesicle SEC Column was loaded with 20 mL of 10-fold concentrated serum-free medium conditioned by mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) culture. 1 mL fractions were collected and analyzed for particle and protein content by nanoparticle tracking analysis and bicinchoninic acid assays, respectively. EVs were detected in fractions 15 - 30, while proteins were detected in fractions 35 onwards. Fractions 31-33, which are outside of the typical EV elution range, may still contain EVs with low protein contamination for serum-free media samples.