EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II
Immunomagnetic negative selection kit
概要
The EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II is designed to isolate hematopoietic progenitor cells from fresh cord blood and other cell preparations by negative selection. The EasySep™ procedure involves labeling unwanted cells with antibody complexes and magnetic particles. The magnetically labeled cells are separated from the desired cells by using an EasySep™ magnet and simply pouring or pipetting the desired cells into a new tube.
Advantages
⦁ Fast, easy-to-use, and column-free procedure
⦁ Up to 95% purity
⦁ Untouched, viable cells
⦁ Up to 95% purity
⦁ Untouched, viable cells
Components
- EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II (Catalog #17936)
- EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™, 2 x 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II (Catalog #17936RF)
- EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™, 2 x 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)
- RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125)
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Species
Human
Sample Source
Cord Blood
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep, RoboSep
Area of Interest
Stem Cell Biology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II | 17936 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II | 17936RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II | 17936 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II | 17936 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II | 17936RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II | 17936RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
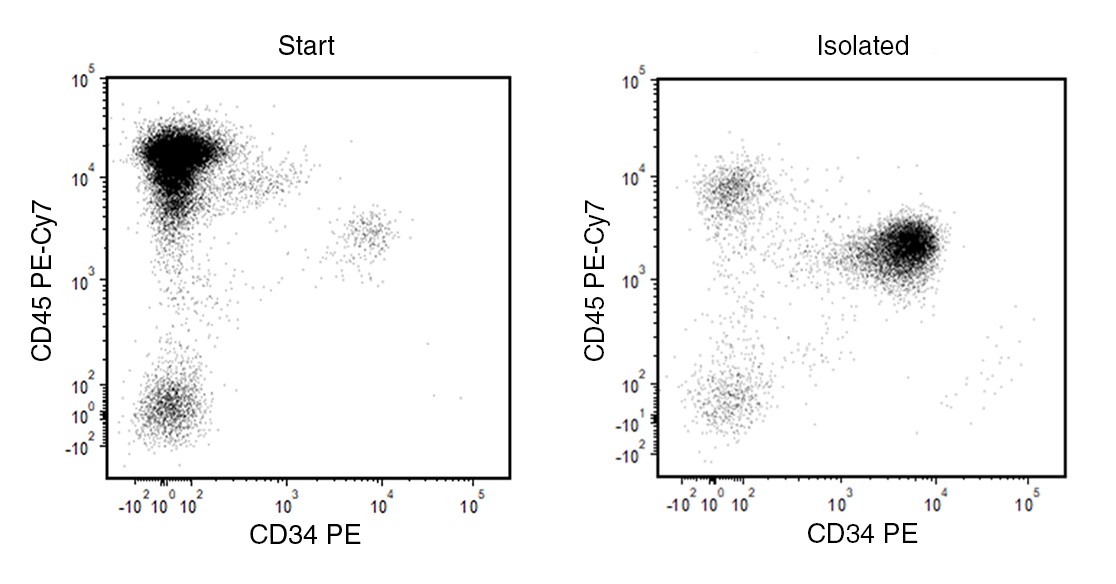
Figure 1. EasySep™ Human Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit II
Starting with 36- to 48-hour-old cord blood, the CD34+ cell content of the isolated fraction is typically 77.5 ± 16.0% (mean ± SD using the silver EasySep™ Magnet). In the above example, using fresh cord blood, the purities of the start and final isolated fractions are 0.7% and 82.4%, respectively.
Publications (2)
Blood 2020 jun
MYC-induced human acute myeloid leukemia requires a continuing IL3/GM-CSF co-stimulus.
Abstract
Abstract
Hematopoietic clones with leukemogenic mutations arise in healthy people as they age, but progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is rare. Recent evidence suggests that the microenvironment may play an important role in modulating human AML population dynamics. To investigate this concept further, we examined the combined and separate effects of an oncogene (c-MYC) and exposure to IL3, GM-CSF and SCF on the experimental genesis of a human AML in xenografted immunodeficient mice. Initial experiments showed that normal human CD34+ blood cells transduced with a lentiviral MYC vector and then transplanted into immunodeficient mice produced a hierarchically organized, rapidly fatal and serially transplantable blast population, phenotypically and transcriptionally similar to human AML cells, but only in mice producing IL3, GM-CSF and SCF transgenically, or in regular mice in which the cells were exposed to IL3 or GM-CSF delivered using a co-transduction strategy. In their absence, the MYC+ human cells produced a normal repertoire of lymphoid and myeloid progeny in transplanted mice for many months but, upon transfer to secondary mice producing the human cytokines, the MYC+ cells rapidly generated AML. Indistinguishable diseases were also obtained efficiently from both primitive (CD34+CD38-) and late (GMPs) cells. These findings underscore the critical role that these cytokines can play in activating a malignant state in normally differentiating human hematopoietic cells in which MYC expression has been deregulated. They also introduce a robust experimental model of human leukemogenesis to further elucidate key mechanisms involved and test strategies to suppress them.
Blood 2020 apr
The miR-185/PAK6 Axis Predicts Therapy Response and Regulates Survival of Drug-Resistant Leukemic Stem Cells in CML.
Abstract
Abstract
Overcoming drug resistance and targeting cancer stem cells remain challenges for curative cancer treatment. To investigate the role of miRNAs in regulating drug resistance and leukemic stem cell (LSCs) fate, we performed global transcriptome profiling in treatment-na{\{i}}ve chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) stem/progenitor cells and identified that miR-185 levels anticipate their response to ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). miR-185 functions as a tumor suppressor; its restored expression impaired survival of drug-resistant cells sensitized them to TKIs in vitro and markedly eliminated long-term repopulating LSCs and infiltrating blast cells conferring a survival advantage in pre-clinical xenotransplantation models. Integrative analysis with mRNA profiles uncovered PAK6 as a crucial target of miR-185 and pharmacological inhibition of PAK6 perturbed the RAS/MAPK pathway and mitochondrial activity sensitizing therapy-resistant cells to TKIs. Thus miR-185 presents as a potential predictive biomarker and dual targeting of miR-185-mediated PAK6 activity and BCR-ABL may provide a valuable strategy for overcoming drug resistance in patients."