EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit
14-Minute cell isolation using immunomagnetic negative selection
概要
The EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit is designed to isolate neutrophils from a polymorphonuclear cell-rich fraction of peripheral blood by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing non-neutrophils and magnetic particles. Labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube. The isolation kit is compatible with cells prepared using HetaSep™ (Catalog #07906) sedimentation or red blood cell lysis.
This product replaces the EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19257), for even faster cell isolations.
This product replaces the EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19257), for even faster cell isolations.
Advantages
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Up to 99% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
• Up to 99% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
Components
- EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit (Catalog #17957)
- EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™, 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit with Filter Tips (Catalog #17957RF)
- EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™, 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)
- RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125)
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• EasyEights™ EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18103)
• EasyPlate™ EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18102)
• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
Granulocytes and Subsets
Species
Human
Sample Source
PMNC, Whole Blood
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep, RoboSep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | RoboSep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Kit | 17957RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
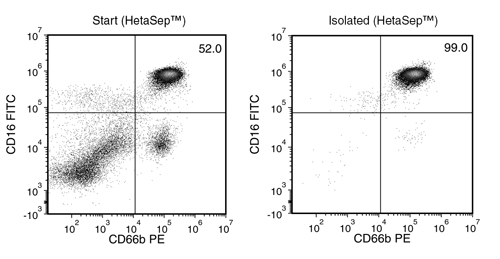
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Human Neutrophil Isolation Profile
Starting with whole blood prepared using HetaSep™ or Lymphoprep™ with RBC lysis, the neutrophil content (CD45+CD16+CD66b+) of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 98.7 ± 0.9% (mean ± SD). In the above example, the purities of the start and final isolated fractions are 52.0% and 99.0%, respectively.
Publications (1)
Journal of clinical immunology 2020 oct
Novel NCF2 Mutation Causing Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
Abstract
Abstract
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a rare primary immunodeficiency disorder caused by defects in the NADPH oxidase complex. Mutations in NCF2 encoding the cytosolic factor p67phox result in autosomal recessive CGD. We describe three patients with a novel c.855G{\textgreater}C NCF2 mutation presenting with diverse clinical phenotype. Two siblings were heterozygous for the novel mutation and for a previously described exon 8-9 duplication, while a third unrelated patient was homozygous for the novel mutation. Mutation pathogenicity was confirmed by abnormal DHR123 assay and absent p67phox production and by sequencing of cDNA which showed abnormal RNA splicing. Clinically, the homozygous patient presented with suspected early onset interstitial lung disease and NCF2 mutation was found on genetic testing performed in search for surfactant-related defects. The two siblings also had variable presentation with one having history of severe pneumonia, lymphadenitis, and recurrent skin abscesses and the other presenting in his 30s with discoid lupus erythematosus and without significant infectious history. We therefore identified a novel pathogenic NCF2 mutation causing diverse and unusual clinical phenotype.