EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit
Immunomagnetic negative selection kit
概要
The EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit is designed to isolate naïve CD8+ T cells from fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with antibody complexes recognizing CD4, CD14, CD16, CD19, CD20, CD36, CD45RO, CD56, CD57, CD94, CD123, CD244, TCRγ/δ, glycophorin A and dextran-coated magnetic particles. The labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube.
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit II (17968) which isolates cells in as little as 11 minutes.
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit II (17968) which isolates cells in as little as 11 minutes.
Advantages
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Up to 97% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
• Up to 97% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
Components
- EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19258)
- EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ D2 Magnetic Particles, 2 x 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Human Naive CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19258RF)
- EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ D2 Magnetic Particles, 5 x 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)
- RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125) x 2
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
T Cells, T Cells, CD8+
Species
Human
Sample Source
PBMC
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep, RoboSep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19258 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Naive CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19258RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | EasySep™ Human Naïve CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19258 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Naive CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19258RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
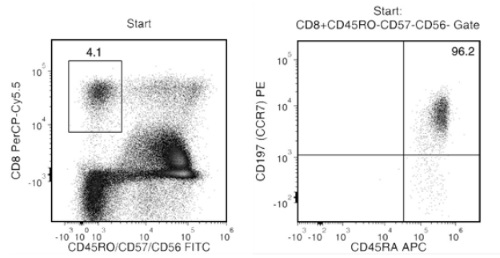
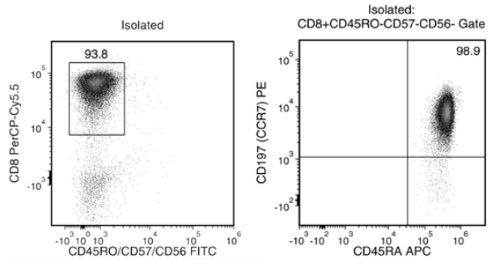
Starting with fresh PBMCs, the naïve CD8+ T cell content (CD8+CD45RA+CCR7+ and CD45RO-CD57-CD56-) of the isolated fraction is typically 92.3 ± 4.0% (mean ± SD using the purple EasySep™ Magnet). In the above example, the purities of the start and final isolated fractions are 3.9% and 92.8%, respectively.
Publications (1)
Nature communications 2020
Inherited salt-losing tubulopathies are associated with immunodeficiency due to impaired IL-17 responses.
Abstract
Abstract
Increased extracellular sodium activates Th17 cells, which provide protection from bacterial and fungal infections. Whilst high salt diets have been shown to worsen autoimmune disease, the immunological consequences of clinical salt depletion are unknown. Here, we investigate immunity in patients with inherited salt-losing tubulopathies (SLT). Forty-seven genotyped SLT patients (with Bartter, Gitelman or EAST Syndromes) are recruited. Clinical features of dysregulated immunity are recorded with a standardised questionnaire and immunological investigations of IL-17 responsiveness undertaken. The effects of altering extracellular ionic concentrations on immune responses are then assessed. Patients are hypokalaemic and hypomagnesaemic, with reduced interstitial sodium stores determined by 23Na-magnetic resonance imaging. SLT patients report increased mucosal infections and allergic disease compared to age-matched controls. Aligned with their clinical phenotype, SLT patients have an increased ratio of Th2:Th17 cells. SLT Th17 and Tc17 polarisation is reduced in vitro, yet STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation and calcium flux following T cell activation are unaffected. In control cells, the addition of extracellular sodium (+40 mM), potassium (+2 mM), or magnesium (+1 mM) reduces Th2:Th17 ratio and augments Th17 polarisation. Our results thus show that the ionic environment typical in SLT impairs IL-17 immunity, but the intracellular pathways that mediate salt-driven Th17 polarisation are intact and in vitro IL-17 responses can be reinvigorated by increasing extracellular sodium concentration. Whether better correction of extracellular ions can rescue the immunophenotype in vivo in SLT patients remains unknown.