EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit
Immunomagnetic negative selection cell isolation kit
概要
The EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit is designed to isolate monocytes from fresh or previously frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing non-monocyte cells and dextran-coated magnetic particles. The cocktail also contains an antibody to human Fc receptor to prevent nonspecific binding of monocytes. Labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube. For applications in which CD16+ cells are not removed, we recommend the EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit without CD16 Depletion (Catalog #19058).
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the new EasySep™ Human Monocyte Isolation Kit (19359) which isolates cells in as little as 12.5 minutes.
For even faster cell isolations, we recommend the new EasySep™ Human Monocyte Isolation Kit (19359) which isolates cells in as little as 12.5 minutes.
Advantages
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Up to 95% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
• Up to 95% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
Components
- EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19059)
- EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Magnetic Particles, 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips (Catalog #19059RF)
- EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Magnetic Particles, 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)
- RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125)
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• Easy 50 EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18002)
• EasyPlate™ EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog 18102)
• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
Monocytes
Species
Human
Sample Source
PBMC
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep, RoboSep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit | 19059 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19059RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit | 19059 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit | 19059 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19059RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19059RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
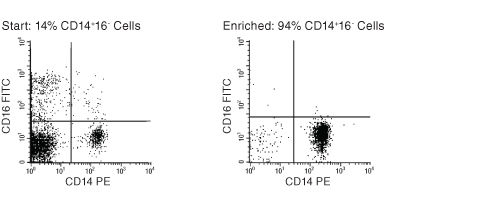
Figure 1. FACS Profile Results Using EasySep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Kit
Starting with previously frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells, the monocyte content of the enriched fraction typically ranges from 83% - 95%.
Publications (20)
Cell 2020 oct
Translocation of Viable Gut Microbiota to Mesenteric Adipose Drives Formation of Creeping Fat in Humans.
Abstract
Abstract
A mysterious feature of Crohn's disease (CD) is the extra-intestinal manifestation of creeping fat" (CrF) defined as expansion of mesenteric adipose tissue around the inflamed and fibrotic intestine. In the current study we explore whether microbial translocation in CD serves as a central cue for CrF development. We discovered a subset of mucosal-associated gut bacteria that consistently translocated and remained viable in CrF in CD ileal surgical resections and identified Clostridium innocuum as a signature of this consortium with strain variation between mucosal and adipose isolates suggesting preference for lipid-rich environments. Single-cell RNA sequencing characterized CrF as both pro-fibrotic and pro-adipogenic with a rich milieu of activated immune cells responding to microbial stimuli which we confirm in gnotobiotic mice colonized with C. innocuum. Ex vivo validation of expression patterns suggests C. innocuum stimulates tissue remodeling via M2 macrophages leading to an adipose tissue barrier that serves to prevent systemic dissemination of bacteria."
Immunity 2020 aug
The 10q26 Risk Haplotype of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Aggravates Subretinal Inflammation by Impairing Monocyte Elimination.
Abstract
Abstract
A minor haplotype of the 10q26 locus conveys the strongest genetic risk for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Here, we examined the mechanisms underlying this susceptibility. We found that monocytes from homozygous carriers of the 10q26 AMD-risk haplotype expressed high amounts of the serine peptidase HTRA1, and HTRA1 located to mononuclear phagocytes (MPs) in eyes of non-carriers with AMD. HTRA1 induced the persistence of monocytes in the subretinal space and exacerbated pathogenic inflammation by hydrolyzing thrombospondin 1 (TSP1), which separated the two CD47-binding sites within TSP1 that are necessary for efficient CD47 activation. This HTRA1-induced inhibition of CD47 signaling induced the expression of pro-inflammatory osteopontin (OPN). OPN expression increased in early monocyte-derived macrophages in 10q26 risk carriers. In models of subretinal inflammation and AMD, OPN deletion or pharmacological inhibition reversed HTRA1-induced pathogenic MP persistence. Our findings argue for the therapeutic potential of CD47 agonists and OPN inhibitors for the treatment of AMD.
Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland) 2019 nov
Distinct Effects of Immunosuppressive Drugs on the Anti-Aspergillus Activity of Human Natural Killer Cells.
Abstract
Abstract
As the prognosis of invasive aspergillosis remains unacceptably poor in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), there is a growing interest in the adoptive transfer of antifungal effector cells, such as Natural Killer (NK) cells. Because immunosuppressive agents are required in most HSCT recipients, knowledge of the impact of these compounds on the antifungal activity of NK cells is a prerequisite for clinical trials. We, therefore, assessed the effect of methylprednisolone (mPRED), cyclosporin A (CsA) and mycophenolic acid (MPA) at different concentrations on proliferation, apoptosis/necrosis, and the direct and indirect anti-Aspergillus activity of human NK cells. Methylprednisolone decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis of NK cells in a significant manner. After seven days, a reduction of viable NK cells was seen for all three immunosuppressants, which was significant for MPA only. Cyclosporin A significantly inhibited the direct hyphal damage by NK cells in a dose-dependent manner. None of the immunosuppressive compounds had a major impact on the measured levels of interferon-$\gamma$, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted; CCL5). Our data demonstrate that commonly used immunosuppressive compounds have distinct effects on proliferation, viability and antifungal activity of human NK cells, which should be considered in designing studies on the use of NK cells for adoptive antifungal immunotherapy.
Science signaling 2019
GPR35 promotes glycolysis, proliferation, and oncogenic signaling by engaging with the sodium potassium pump.
Abstract
Abstract
The sodium potassium pump (Na/K-ATPase) ensures the electrochemical gradient of a cell through an energy-dependent process that consumes about one-third of regenerated ATP. We report that the G protein-coupled receptor GPR35 interacted with the $\alpha$ chain of Na/K-ATPase and promotes its ion transport and Src signaling activity in a ligand-independent manner. Deletion of Gpr35 increased baseline Ca2+ to maximal levels and reduced Src activation and overall metabolic activity in macrophages and intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). In contrast, a common T108M polymorphism in GPR35 was hypermorphic and had the opposite effects to Gpr35 deletion on Src activation and metabolic activity. The T108M polymorphism is associated with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis, inflammatory diseases with a high cancer risk. GPR35 promoted homeostatic IEC turnover, whereas Gpr35 deletion or inhibition by a selective pepducin prevented inflammation-associated and spontaneous intestinal tumorigenesis in mice. Thus, GPR35 acts as a central signaling and metabolic pacesetter, which reveals an unexpected role of Na/K-ATPase in macrophage and IEC biology.
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2018 OCT
Targeting cancer cells and tumor microenvironment in preclinical and clinical models of Hodgkin lymphoma using the dual PI3K$\delta$/$\gamma$ inhibitor RP6530.
Abstract
Abstract
PURPOSE Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and the hyperactivation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase(PI3K)/AKT pathway are involved in the pathogenesis of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and affect disease outcome. Since the $\delta$ and $\gamma$ isoforms of PI3K are overexpressed in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells and the tumor microenvironment (TME), we propose that the PI3K$\delta$/$\gamma$ inhibitor RP6530 might affect both HRS cells and TME, ultimately leading to an enhanced antitumor response. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN HL cell lines (L-540, KM-H2 and L-428) and primary human macrophages were used to investigate the activity of RP6530 in vitro and in vivo in HL cell line xenografts. RESULTS In vitro, RP6530 besides killing and inhibiting the proliferation of HL cells, downregulated lactic acid metabolism, switching the activation of macrophages from an immunosuppressive M2-like phenotype to a more inflammatory M1-like state. By RNA sequencing, we define tumor glycolysis as a specific PI3K$\delta$/$\gamma$-dependent pathway implicated in the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells. We identify the metabolic regulator Pyruvate Kinase M2 (PKM2) as the main mediator of tumor-induced immunosuppressive phenotype of macrophages. Furthermore, we show in human tumor xenografts that RP6530 repolarizes TAMs into pro-inflammatory macrophages and inhibits tumor vasculature, leading to tumor regression. Interestingly, HL patients experiencing objective responses (CR and PR) in a phase 1 trial using RP6530 showed a significant inhibition of circulating MDSCs and an average mean reduction in serum TARC levels of 40{\%} (range, 4-76{\%}). CONCLUSIONS Our results support PI3K$\delta$/$\gamma$ inhibition as a novel therapeutic strategy that targets both malignant cells and the TME to treat HL patients.
Cell reports 2018 NOV
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Promotes the Recruitment and Polarization of Macrophages in Cancer.
Abstract
Abstract
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) has a pro-tumorigenic function via its pro-angiogenic and anti-apoptotic activities. Here, we demonstrate that PAI-1 promotes the recruitment and M2 polarization of monocytes/macrophages through different structural domains. Its LRP1 interacting domain regulated macrophage migration, while its C-terminal uPA interacting domain promoted M2 macrophage polarization through activation of p38MAPK and nuclear factor $\kappa$B (NF-$\kappa$B) and induction of an autocrine interleukin (IL)-6/STAT3 activation pathway. We then show in several experiments in mice that expression of PAI-1 is associated with increased tumorigenicity, increased presence of M2 macrophages, higher levels of IL-6, and increased STAT3 phosphorylation in macrophages. Strong positive correlations between PAI-1, IL-6, and CD163 (M2 marker) expression were also found by meta-analysis of transcriptome data in many human cancers. Altogether, these data provide evidence for a mechanism explaining the paradoxical pro-tumorigenic function of PAI-1 in cancer.