EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit
Immunomagnetic negative selection cell isolation kit
概要
The EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit is designed to isolate B cells from fresh or previously frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing non-B cells and dextran-coated magnetic particles. The labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet and without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube and are ready for serology or flow cytometry crossmatch assays.
Advantages
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Up to 99% purity
• Isolated cells are untouched
• Compatible with downstream HLA assays
• Up to 99% purity
• Isolated cells are untouched
• Compatible with downstream HLA assays
Components
- EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19054HLA)
- EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ D Magnetic Particles, 2 x 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Human B Cell Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips (Catalog #19054RF)
- EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ D Magnetic Particles, 2 x 1 mL
- RoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)
- RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125)
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
B Cells
Species
Human
Sample Source
PBMC
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep, RoboSep
Area of Interest
Chimerism, HLA, Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit | 19054HLA | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19054HLARF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit | 19054HLA | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit | 19054HLA | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19054HLARF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit with Filter Tips | 19054HLARF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
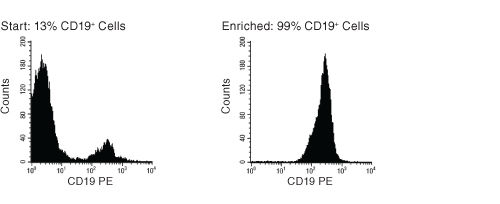
Figure 1. FACS Histogram Results with EasySep™ HLA B Cell Enrichment Kit
Starting with frozen mononuclear cells, the CD19+ cell content of the enriched fraction typically ranges from 95 - 99%.
Publications (1)
Transplantation proceedings 2013
Modified flow cytometry crossmatch detecting alloantibody-related cytotoxicity as a way to distinguish lytic antibodies from harmless in allosensitised kidney recipients.
Abstract
Abstract
The serological complement-dependent cytotoxicity crossmatch (CDC-XM) permits routine identification of anti-donor alloantibodies in the sera of allotransplant recipients. However, in a small group of recipients, antibodies below the threshold of detection may still be responsible for hyperacute rejection. For the same reason, approximately 20% of recipients develop acute rejection episodes. The flow cytometry crossmatch (FCXM) was designed to address these problems, but because of the presence of clinically insignificant antibodies (linked, non-lytic), the FCXM appears to be too sensitive yielding false-positive results. We compared FCXM with its modified version assessing cell viability (cytolytic flow cytometry crossmatch; cFCXM) using sera from previously sensitised kidney recipients. The presence of alloantibodies was detected using the Luminex platform. The cFCXM proved to be of greater sensitivity than CDC-XM, which was additionally confirmed with bead-based Luminex techniques. The cFCXM was also superior to FCXM because it distinguished lytic from non-lytic antibodies. The cFCXM was superior to assess donor specificity, sensitivity, and detection of clinically relevant lytic antibodies.



