EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit
Immunomagnetic negative selection from whole blood kit
概要
The EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit is designed to isolate CD8+ T cells from human whole blood by immunomagnetic negative selection. The EasySep™ Direct procedure involves labeling RBCs, platelets and unwanted cells present in human whole blood with antibody complexes and magnetic particles. The magnetically labeled RBCs, platelets and cells are separated from the untouched desired cells by using an EasySep™ magnet and simply pouring or pipetting the desired cells into a new tube.
Advantages
• > 99.9% red blood cell (RBC) depletion without the need for density gradient centrifugation, sedimentation, or lysis
• Up to 91% purity of isolated cells
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Isolated cells are untouched
• Up to 91% purity of isolated cells
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Isolated cells are untouched
Components
- EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19663)
- EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail, 2 x 2.5 mL
- EasySep™ Direct RapidSpheres™, 4 x 2.5 mL
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• Easy 50 EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18002)
• EasyEights™ EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18103)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
T Cells, T Cells, CD8+
Species
Human
Sample Source
Whole Blood
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19663 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19663 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19663 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
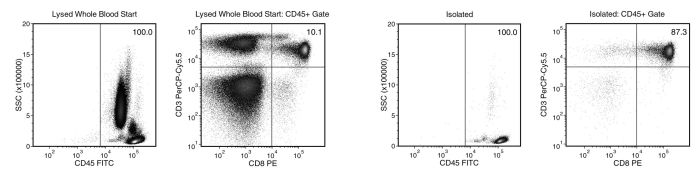
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Direct Human CD8+ T Cell Isolation Profile
Starting with human whole blood from normal healthy donors, the typical CD8+ T cell (CD3+CD8+) content of the non-lysed final isolated fraction is 82.4 ± 4.9% (gated on CD45) or 81.6 ± 4.9% (not gated on CD45). In the example above, the CD8+ T cell (CD3+CD8+) content of the lysed whole blood start sample and non-lysed final isolated fraction is 10.1% and 87.3% (gated on CD45), respectively, or 10.1% and 87.3% (not gated on CD45), respectively. The starting frequency of CD8+ T cells in the non-lysed whole blood start sample is 0.018% (data not shown).
Publications (1)
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2019 sep
Multispecific Targeting with Synthetic Ankyrin Repeat Motif Chimeric Antigen Receptors.
Abstract
Abstract
PURPOSE The outgrowth of antigen-negative variants is a significant challenge for adoptive therapy with T cells that target a single specificity. Chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) are typically designed with one or two scFvs that impart antigen specificity fused to activation and costimulation domains of T-cell signaling molecules. We designed and evaluated the function of CARs with up to three specificities for overcoming tumor escape using Designed Ankyrin Repeat Proteins (DARPins) rather than scFvs for tumor recognition. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN A monospecific CAR was designed with a DARPin binder (E01) specific for EGFR and compared with a CAR designed using an anti-EGFR scFv. CAR constructs in which DARPins specific for EGFR, EpCAM, and HER2 were linked together in a single CAR were then designed and optimized to achieve multispecific tumor recognition. The efficacy of CAR-T cells bearing a multispecific DARPin CAR for treating tumors with heterogeneous antigen expression was evaluated in vivo. RESULTS The monospecific anti-EGFR E01 DARPin conferred potent tumor regression against EGFR+ targets that was comparable with an anti-EGFR scFv CAR. Linking three separate DARPins in tandem was feasible and in an optimized format generated a single tumor recognition domain that targeted a mixture of heterogeneous tumor cells, each expressing a single antigen, and displayed synergistic activity when tumor cells expressed more than one target antigen. CONCLUSIONS DARPins can serve as high-affinity recognition motifs for CAR design, and their robust architecture enables linking of multiple binders against different antigens to achieve functional synergy and reduce antigen escape.