SepMate™-50 (RUO)
Tube for density gradient centrifugation
概要
SepMate™ is a tube that facilitates the isolation of PBMCs or specific cell types by density gradient centrifugation. SepMate™ tubes contain an insert that provides a barrier between the density gradient medium and blood. SepMate™ eliminates the need for careful layering of blood (or bone marrow or cord blood) onto the density gradient medium, and allows for fast and easy harvesting of the isolated mononuclear cells with a simple pour. SepMate™ is also compatible with RosetteSep™ enrichment cocktails, allowing isolation of specific cell types in less than 30 minutes.
SepMate™-50 is designed for processing samples from 4 to 17 mL of sample.
SepMate™-50 (RUO) (Catalog #86450 and #86460) is manufactured under cGMP and is for Research Use Only. Users in Australia, Canada, Europe and USA, please refer to SepMate™-50 (IVD) (Catalog #85450 and #85460).
SepMate™-50 is designed for processing samples from 4 to 17 mL of sample.
SepMate™-50 (RUO) (Catalog #86450 and #86460) is manufactured under cGMP and is for Research Use Only. Users in Australia, Canada, Europe and USA, please refer to SepMate™-50 (IVD) (Catalog #85450 and #85460).
Advantages
• Eliminates the need for carefully layering blood over the density gradient medium (e.g. Ficoll-Paque™, Lymphoprep™ )
• Reduces total centrifuge time to 10 minutes with the brake on for fresh samples
• Allows fast and easy harvesting of the isolated mononuclear cells by simply pouring off the supernatant
• Can be combined with RosetteSep™ enrichment cocktails to isolate specific cell types in just 25 minutes
• Reduces total centrifuge time to 10 minutes with the brake on for fresh samples
• Allows fast and easy harvesting of the isolated mononuclear cells by simply pouring off the supernatant
• Can be combined with RosetteSep™ enrichment cocktails to isolate specific cell types in just 25 minutes
Components
- SepMate™-50 (RUO), 100 Tubes (Catalog #86450)
- Dispenser box containing 4 bags, 25 Tubes/Bag
- SepMate™-50 (RUO), 500 Tubes (Catalog #86460)
- Dispenser box containing 4 bags, 25 Tubes/Bag (Catalog #86450) x 5
Contains
Polypropylene tube containing an insert
Subtype
Centrifugation Tubes
Cell Type
B Cells, Dendritic Cells, Monocytes, Mononuclear Cells, NK Cells, T Cells, T Cells, CD4+, T Cells, CD8+, T Cells, Other Subsets, T Cells, Regulatory
Species
Human
Sample Source
Bone Marrow, Cord Blood, Whole Blood
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
SepMate
Area of Interest
Chimerism, HLA, Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | SepMate™-50 (RUO) | 86450, 86460 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
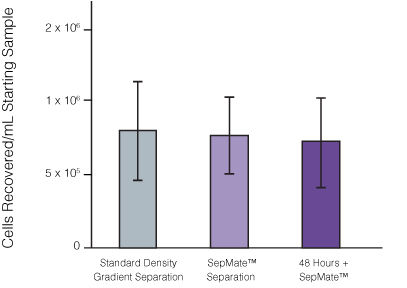
Figure 1. Recovery of mononuclear cells (MNCs) from peripheral blood using SepMate™-50 versus standard density gradient centrifiguation. Recovery of MNCs from fresh and 48-hour post blood draw enriched by density gradient centrifugation with SepMate™ (purple) or without (grey). There was no significant difference in the recovery of MNCS with and without SepMate™.
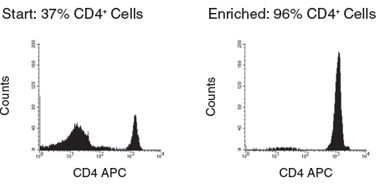
Figure 2. Human CD4+ T Cell Isolation using SepMate™-50 and RosetteSep™ Human CD4+ T Cell Enrichment Cocktail
Publications (27)
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2020 jan
Knee loading repairs osteoporotic osteoarthritis by relieving abnormal remodeling of subchondral bone via Wnt/$\beta$-catenin signaling.
Abstract
Abstract
Osteoporotic osteoarthritis (OPOA) is a common bone disease mostly in the elderly, but the relationship between Osteoporotic (OP) and osteoarthritis (OA) is complex. It has been shown that knee loading can mitigate OA symptoms. However, its effects on OPOA remain unclear. In this study, we characterized pathological linkage of OP to OA, and evaluated the effect of knee loading on OPOA. We employed two mouse models (OA and OPOA), and conducted histology, cytology, and molecular analyses. In the OA and OPOA groups, articular cartilage was degenerated and Osteoarthritis Research Society International score was increased. Subchondral bone underwent abnormal remodeling, the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) to osteoblasts and chondrocytes was reduced, and migration and adhesion of pre-osteoclasts were enhanced. Compared to the OA group, the pathological changes of OA in the OPOA group were considerably aggravated. After knee loading, however, cartilage degradation was effectively prevented, and the abnormal remodeling of subchondral bone was significantly inhibited. The differentiation of BMSCs was also improved, and the expression of Wnt/$\beta$-catenin was elevated. Collectively, this study demonstrates that osteoporosis aggravates OA symptoms. Knee loading restores OPOA by regulating subchondral bone remodeling, and may provide an effective method for repairing OPOA.
Frontiers in oncology 2020
High Dimensional Mass Cytometry Analysis Reveals Characteristics of the Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Diffuse Astrocytomas.
Abstract
Abstract
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) plays a pivotal role in tumor development, progression, and prognosis. However, the characteristics of the TIME in diffuse astrocytoma (DA) are still unclear. Leveraging mass cytometry with a panel of 33 markers, we analyzed the infiltrating immune cells from 10 DA and 4 oligodendroglioma (OG) tissues and provided a single cell-resolution landscape of the intricate immune microenvironment. Our study profiled the composition of the TIME in DA and confirmed the presence of immune cells, such as glioma-associated microglia/macrophages (GAMs), CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and natural killer cells. Increased percentages of PD-1+ CD8+ T cells, TIM-3+ CD4+ T cell subpopulations, Tregs and pro-tumor phenotype GAMs substantially contribute to the local immunosuppressive microenvironment in DA. DAs and OGs share similar compositions in terms of immune cells, while GAMs in DA exhibit more inhibitory characteristics than those in OG.
Cancer biology {\&} therapy 2019 sep
Identification of anti-CD16a single domain antibodies and their application in bispecific antibodies.
Abstract
Abstract
CD16a (Fc$\gamma$RIIIa) mediates the antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and is important for anti-tumor activities of many therapeutic antibodies. Bispecific antibody targeting natural killer (NK) cells has been studied for cancer therapy. In this work, anti-CD16a single-domain antibodies were identified from hCD16a immunized camel. Bispecific antibodies are then constructed by fusing these single domain antibodies with an anti-CEA single domain antibody. These bispecific antibodies can recruite NK cells to kill CEA-positive tumor cells, and inhibit tumor growth in vivo, suggesting that these anti-CD16a single domain antibodies are powerful tools to engaging NK cells for cancer therapy.
Cell death {\&} disease 2019 sep
LncRNA SNHG14/miR-5590-3p/ZEB1 positive feedback loop promoted diffuse large B cell lymphoma progression and immune evasion through regulating PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint.
Abstract
Abstract
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the commonest disorder derived from the B-lymphocytes. Inhibiting the immune checkpoint through naturalizing programmed death-1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is proved to be a successful therapeutic regime for lymphoma. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are unceasingly reported to be promising biological targets for the cancer therapies. This study planned to explore the regulation of small nucleolar RNA host gene 14 (SNHG14) on DLBCL. SNHG14 level in DLBCL samples and cell lines was analyzed by GEPIA bioinformatics tool and RT-qPCR. Biological functions of SNHG14 in DLBCL were detected by CCK-8, colony formation, and transwell invasion assays. Molecular interaction was determined by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and luciferase reporter assays. MiR-5590-3p-related pathway was identified through KEGG pathway analysis applying DAVID6.8 online bioinformatics tool. Effect of SNHG14 on CD8+ T cells was detected by flow cytometry. Results depicted that SNHG14 was upregulated in DLBCL and its depletion retarded proliferation, migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Mechanistically, SNHG14 sponged miR-5590-3p to upregulate Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1), and ZEB1 transcriptionally activated SNHG14 and PD-L1 to promote the immune evasion of DLBCL cells. In conclusion, we firstly showed that SNHG14/miR-5590-3p/ZEB1 positive feedback loop promoted diffuse large B cell lymphoma progression and immune evasion through regulating PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint, indicating that targeting SNHG14 was a potential approach to improve the efficacy of immunotherapy in DLBCL.
Immunologic research 2019
Characterization of IL-17-producing Treg cells in type 2 diabetes patients.
Abstract
Abstract
The association between type 2 diabetes (T2D) pathogenesis and immune-mediated tissue damage and insulin resistance suggests that T2D patients might benefit from the suppression of pathogenic inflammation. Foxp3+ Treg cells are crucial suppressors of inflammation, but the differentiation of Foxp3+ Treg cells is not static and is subject to conversion into IL-17-producing Th17-like cells upon receiving external signals. In this study, we examined the production of IL-17 by Treg cells. Compared to non-T2D controls, T2D patients presented significantly higher levels of IL-17-expressing cells in both Foxp3- CD4 T cells and Foxp3+ Treg cells. The frequencies of IL-17-nonexpressing Foxp3+ Treg cells, on the other hand, were not changed. Interestingly, IL-17-expressing Foxp3+ Treg cells were mutually exclusive from IL-10-expressing and TGF-$\beta$-expressing Foxp3+ Treg cells, suggesting that multiple subpopulations exist within the Foxp3+ Treg cells from T2D patients. In T2D patients, the frequencies of IL-17-expressing Foxp3+ Treg cells were positively correlated with the body mass index (BMI) and the HbA1c levels of T2D patients. The frequencies of IL-10-expressing Treg cells, on the other hand, were inversely associated with the BMI of both non-T2D controls and T2D patients. In addition, the suppressive activity of Treg cells was significantly lower in T2D patients than in non-T2D controls. Together, our study uncovered a dysregulation in Foxp3+ Treg cells from T2D patients, characterized by high IL-17 expression and low suppression activity.
Scientific Reports 2018 SEP
IL-27 amplifies cytokine responses to Gram-negative bacterial products and Salmonella typhimurium infection.
Abstract
Abstract
Cytokine responses from monocytes and macrophages exposed to bacteria are of particular importance in innate immunity. Focusing on the impact of the immunoregulatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-27 on control of innate immune system responses, we examined human immune responses to bacterial products and bacterial infection by E. coli and S. typhimurium. Since the effect of IL-27 treatment in human myeloid cells infected with bacteria is understudied, we treated human monocytes and macrophages with IL-27 and either LPS, flagellin, or bacteria, to investigate the effect on inflammatory signaling and cytokine responses. We determined that simultaneous stimulation with IL-27 and LPS derived from E. coli or S. typhimurium resulted in enhanced IL-12p40, TNF-$\alpha$, and IL-6 expression compared to that by LPS alone. To elucidate if IL-27 manipulated the cellular response to infection with bacteria, we infected IL-27 treated human macrophages with S. typhimurium. While IL-27 did not affect susceptibility to S. typhimurium infection or S. typhimurium-induced cell death, IL-27 significantly enhanced proinflammatory cytokine production in infected cells. Taken together, we highlight a role for IL-27 in modulating innate immune responses to bacterial infection.