RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail
Immunodensity negative selection cocktail
概要
The RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail is designed to isolate monocytes from whole blood by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes (TAC) recognizing non-monocyte cells and red blood cells (RBCs). When centrifuged over a buoyant density medium such as Lymphoprep™ (Catalog #07801), the unwanted cells pellet along with the RBCs. The purified monocytes are present as a highly enriched population at the interface between the plasma and the buoyant density medium.
Advantages
• Fast and easy-to-use
• Requires no special equipment or training
• Isolated cells are untouched
• Can be combined with SepMate™ for consistent, high-throughput sample processing
• Requires no special equipment or training
• Isolated cells are untouched
• Can be combined with SepMate™ for consistent, high-throughput sample processing
Components
- RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail (Catalog #15028)
- RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail, 2 mL
- RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail (Catalog #15068)
- RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail, 5 x 2 mL
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
Monocytes
Species
Human
Sample Source
Buffy Coat, Whole Blood
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
RosetteSep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail | 15028, 15068 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail | 15028 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
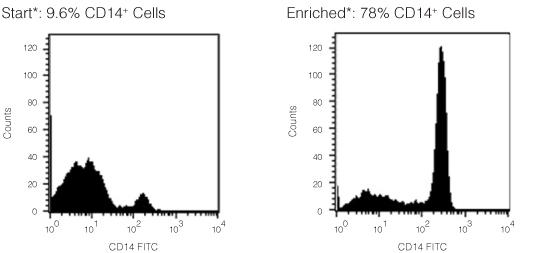
Figure 1. FACS Histogram Results Using RosetteSep™ Human Monocyte Enrichment Cocktail
Starting with fresh peripheral blood, the CD14+ cell content of the enriched fraction is typically 72% - 85%. *Note: Red blood cells were removed by lysis prior to flow cytometry.
Publications (43)
Journal of clinical medicine 2020 oct
Who Is Afraid of CRP? Elevated Preoperative CRP Levels Might Attenuate the Increase in Inflammatory Parameters in Response to Lung Cancer Surgery.
Abstract
Abstract
During surgery, ATP from damaged cells induces the release of interleukin-1$\beta$, a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine that contributes to the development of postoperative systemic inflammation, sepsis and multi-organ damage. We recently demonstrated that C-reactive protein (CRP) inhibits the ATP-induced release of monocytic interleukin-1$\beta$, although high CRP levels are deemed to be a poor prognostic marker. Here, we retrospectively investigated if preoperative CRP levels correlate with postoperative CRP, leukocyte counts and fever in the context of anatomical lung resection and systematic lymph node dissection as first line lung cancer therapy. No correlation was found in the overall results. In men, however, preoperative CRP and leukocyte counts positively correlated on postoperative days one to two, and a negative correlation of CRP and fever was seen in women. These correlations were more pronounced in men taking statins and in statin-na{\{i}}ve women. Accordingly the inhibitory effect of CRP on the ATP-induced interleukin-1$\beta$ release was blunted in monocytes from coronary heart disease patients treated with atorvastatin compared to monocytes obtained before medication. Hence the common notion that elevated CRP levels predict more severe postoperative inflammation should be questioned. We rather hypothesize that in women and statin-na{\"{i}}ve patients high CRP levels attenuate trauma-induced increases in inflammatory markers."""
Scientific reports 2020 mar
Novel elvitegravir nanoformulation for drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier to achieve HIV-1 suppression in the CNS macrophages.
Abstract
Abstract
The use of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has remarkably decreased the morbidity associated with HIV-1 infection, however, the prevalence of HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) is still increasing. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is the major impediment for penetration of antiretroviral drugs, causing therapeutics to reach only suboptimal level to the brain. Conventional antiretroviral drug regimens are not sufficient to improve the treatment outcomes of HAND. In our recent report, we have developed a poloxamer-PLGA nanoformulation loaded with elvitegravir (EVG), a commonly used antiretroviral drug. The nanoformulated EVG is capable of elevating intracellular drug uptake and simultaneously enhance viral suppression in HIV-1-infected macrophages. In this work, we identified the clinical parameters including stability, biocompatibility, protein corona, cellular internalization pathway of EVG nanoformulation for its potential clinical translation. We further assessed the ability of this EVG nanoformulation to cross the in vitro BBB model and suppress the HIV-1 in macrophage cells. Compared with EVG native drug, our EVG nanoformulation demonstrated an improved BBB model penetration cross the in vitro BBB model and an enhanced HIV-1 suppression in HIV-1-infected human monocyte-derived macrophages after crossing the BBB model without altering the BBB model integrity. Overall, this is an innovative and optimized treatment strategy that has a potential for therapeutic interventions in reducing HAND.
Metabolites 2020 jun
Resolving Metabolic Heterogeneity in Experimental Models of the Tumor Microenvironment from a Stable Isotope Resolved Metabolomics Perspective.
Abstract
Abstract
The tumor microenvironment (TME) comprises complex interactions of multiple cell types that determines cell behavior and metabolism such as nutrient competition and immune suppression. We discuss the various types of heterogeneity that exist in solid tumors, and the complications this invokes for studies of TME. As human subjects and in vivo model systems are complex and difficult to manipulate, simpler 3D model systems that are compatible with flexible experimental control are necessary for studying metabolic regulation in TME. Stable Isotope Resolved Metabolomics (SIRM) is a valuable tool for tracing metabolic networks in complex systems, but at present does not directly address heterogeneous metabolism at the individual cell level. We compare the advantages and disadvantages of different model systems for SIRM experiments, with a focus on lung cancer cells, their interactions with macrophages and T cells, and their response to modulators in the immune microenvironment. We describe the experimental set up, illustrate results from 3D cultures and co-cultures of lung cancer cells with human macrophages, and outline strategies to address the heterogeneous TME.
Scientific reports 2020
Sarcoidosis exosomes stimulate monocytes to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and CCL2.
Abstract
Abstract
Pulmonary sarcoidosis has unknown etiology, a difficult diagnostic procedure and no curative treatment. Extracellular vesicles including exosomes are nano-sized entities released from all cell types. Previous studies of exosomes from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of sarcoidosis patients have revealed pro-inflammatory components and abilities, but cell sources and mechanisms have not been identified. In the current study, we found that BALF exosomes from sarcoidosis patients, but not from healthy individuals, induced a dose-dependent elevation of intracellular IL-1$\beta$ in monocytes. Analyses of supernatants showed that patient exosomes also induced release of IL-1$\beta$, IL-6 and TNF from both PBMCs and enriched monocytes, suggesting that the observed effect is direct on monocytes. The potently chemotactic chemokine CCL2 was induced by exosomes from a subgroup of patients, and in a blocking assay the exosome-induced CCL2 was reduced for 13 out of 19 patients by the asthma drug Montelukast, a cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist. Further, reactive oxygen species generation by PBMCs was induced to a higher degree by patient exosomes compared to healthy exosomes. These findings add to an emerging picture of exosomes as mediators and disseminators of inflammation, and open for further investigations of the link between CCL2 and exosomal leukotrienes in sarcoidosis.
Scientific Reports 2018 SEP
IL-27 amplifies cytokine responses to Gram-negative bacterial products and Salmonella typhimurium infection.
Abstract
Abstract
Cytokine responses from monocytes and macrophages exposed to bacteria are of particular importance in innate immunity. Focusing on the impact of the immunoregulatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-27 on control of innate immune system responses, we examined human immune responses to bacterial products and bacterial infection by E. coli and S. typhimurium. Since the effect of IL-27 treatment in human myeloid cells infected with bacteria is understudied, we treated human monocytes and macrophages with IL-27 and either LPS, flagellin, or bacteria, to investigate the effect on inflammatory signaling and cytokine responses. We determined that simultaneous stimulation with IL-27 and LPS derived from E. coli or S. typhimurium resulted in enhanced IL-12p40, TNF-$\alpha$, and IL-6 expression compared to that by LPS alone. To elucidate if IL-27 manipulated the cellular response to infection with bacteria, we infected IL-27 treated human macrophages with S. typhimurium. While IL-27 did not affect susceptibility to S. typhimurium infection or S. typhimurium-induced cell death, IL-27 significantly enhanced proinflammatory cytokine production in infected cells. Taken together, we highlight a role for IL-27 in modulating innate immune responses to bacterial infection.
Scientific reports 2018 OCT
Single-Stranded Nucleic Acids Regulate TLR3/4/7 Activation through Interference with Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis.
Abstract
Abstract
Recognition of nucleic acids by endosomal Toll-like receptors (TLR) is essential to combat pathogens, but requires strict control to limit inflammatory responses. The mechanisms governing this tight regulation are unclear. We found that single-stranded oligonucleotides (ssON) inhibit endocytic pathways used by cargo destined for TLR3/4/7 signaling endosomes. Both ssDNA and ssRNA conferred the endocytic inhibition, it was concentration dependent, and required a certain ssON length. The ssON-mediated inhibition modulated signaling downstream of TLRs that localized within the affected endosomal pathway. We further show that injection of ssON dampens dsRNA-mediated inflammatory responses in the skin of non-human primates. These studies reveal a regulatory role for extracellular ssON in the endocytic uptake of TLR ligands and provide a mechanistic explanation of their immunomodulation. The identified ssON-mediated interference of endocytosis (SOMIE) is a regulatory process that temporarily dampens TLR3/4/7 signaling, thereby averting excessive immune responses.