RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail
Immunodensity negative selection cocktail
概要
The RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail is designed to isolate progenitor cells from cord blood and whole blood by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with Tetrameric Antibody Complexes recognizing CD2, CD3, CD14, CD16, CD19, CD24, CD56, CD61, CD66b and glycophorin A on red blood cells (RBCs). When centrifuged over a buoyant density medium such as Lymphoprep™ (Catalog #07801), the unwanted cells pellet along with the RBCs. The purified progenitor cells are present as a highly enriched population at the interface between the plasma and the buoyant density medium. If using large volumes of blood, we recommend the RosetteSep™ Cord Blood Progenitor Enrichment Kit with HetaSep™ (Catalog #15276).
Advantages
• Fast and easy-to-use
• Requires no special equipment or training
• Untouched, viable cells
• Can be combined with SepMate™ for consistent, high-throughput sample processing
• Requires no special equipment or training
• Untouched, viable cells
• Can be combined with SepMate™ for consistent, high-throughput sample processing
Components
- RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail (Catalog #15026)
- RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail, 2 mL
- RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail (Catalog #15066)
- RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail, 5 x 2 mL
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Species
Human
Sample Source
Cord Blood, Whole Blood
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
RosetteSep
Area of Interest
Immunology, Stem Cell Biology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail | 15026, 15066 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | RosetteSep™ Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Cocktail | 15026, 15066 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
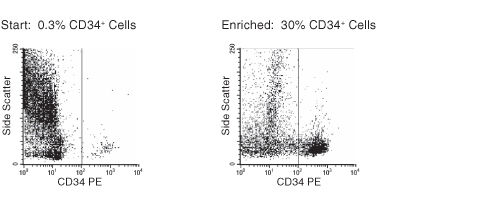
Figure 1. FACS Profile Results With RosetteSep™ Human Cord Blood Progenitor Cell Enrichment Kit
Starting with fresh cord blood, the enrichment of CD34+ cells is typically 29 ± 9%.
Publications (11)
Blood research 2016 MAR
Humanizing NOD/SCID/IL-2Rγnull (NSG) mice using busulfan and retro-orbital injection of umbilical cord blood-derived CD34(+) cells.
Abstract
Abstract
BACKGROUND Humanized mouse models are still under development, and various protocols exist to improve human cell engraftment and function. METHODS Fourteen NOD/SCID/IL-2Rγnull (NSG) mice (4‒5 wk old) were conditioned with busulfan and injected with human umbilical cord blood (hUCB)-derived CD34(+) hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) via retro-orbital sinuses. The bone marrow (BM), spleen, and peripheral blood (PB) were analyzed 8 and 12 weeks after HSC transplantation. RESULTS Most of the NSG mice tolerated the regimen well. The percentage of hCD45(+) and CD19(+) cells rose significantly in a time-dependent manner. The median percentage of hCD45(+)cells in the BM was 55.5% at week 8, and 67.2% at week 12. The median percentage of hCD45(+) cells in the spleen at weeks 8 and 12 was 42% and 51%, respectively. The median percentage of hCD19(+) cells in BM at weeks 8 and 12 was 21.5% and 39%, respectively (P=0.04). Similarly, the median percentage of hCD19(+) cells in the spleen at weeks 8 and 12 was 10% and 24%, respectively (P=0.04). The percentage of hCD19(+) B cells in PB was 23% at week 12. At week 8, hCD3(+) T cells were barely detectable, while hCD7(+) was detected in the BM and spleen. The percentage of hCD3(+) T cells was 2‒3% at week 12 in the BM, spleen, and PB of humanized NSG mice. CONCLUSION We adopted a simplified protocol for establishing humanized NSG mice. We observed a higher engraftment rate of human CD45(+) cells than earlier studies without any significant toxicity. And human CD45(+) cell engraftment at week 8 was comparable to that of week 12.
Immunity 2016 AUG
Cell-Extrinsic MHC Class I Molecule Engagement Augments Human NK Cell Education Programmed by Cell-Intrinsic MHC Class I.
Abstract
Abstract
The effector potential of NK cells is counterbalanced by their sensitivity to inhibition by self" MHC class I molecules in a process called "education." In humans�
Cell transplantation 2010 JAN
In vitro and in vivo analysis of endothelial progenitor cells from cryopreserved umbilical cord blood: are we ready for clinical application?
Abstract
Abstract
Umbilical cord blood (CB) represents a main source of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (cEPCs). In view of their clinical use, in either the autologous or allogeneic setting, cEPCs should likely be expanded from CB kept frozen in CB banks. In this study, we compared the expansion, functional features, senescence pattern over culture, and in vivo angiogenic potential of cEPCs isolated from fresh or cryopreserved CB (cryoCB). cEPCs could be isolated in only 59% of cryoCB compared to 94% for fresh CB, while CB units were matched in terms of initial volume, nucleated and CD34(+) cell number. Moreover, the number of endothelial colony-forming cells was significantly decreased when using cryoCB. Once cEPCs culture was established, the proliferation, migration, tube formation, and acetylated-LDL uptake potentials were similar in both groups. In addition, cEPCs derived from cryoCB displayed the same senescence status and telomeres length as that of cEPCs derived from fresh CB. Karyotypic aberrations were found in cells obtained from both fresh and cryoCB. In vivo, in a hind limb ischemia murine model, cEPCs from fresh and cryoCB were equally efficient to induce neovascularization. Thus, cEPCs isolated from cryoCB exhibited similar properties to those of fresh CB in vitro and in vivo. However, the low frequency of cEPCs colony formation after cryopreservation shed light on the need for specific freezing conditions adapted to cEPCs in view of their future clinical use.
Blood 2009 MAR
The Axl/Gas6 pathway is required for optimal cytokine signaling during human natural killer cell development.
Abstract
Abstract
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is essential for natural killer (NK) cell differentiation. In this study, we assessed whether the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl and its ligand, Gas6, are involved in IL-15-mediated human NK differentiation from CD34(+) hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs). Blocking the Axl-Gas6 interaction with a soluble Axl fusion protein (Axl-Fc) or the vitamin K inhibitor warfarin significantly diminished the absolute number and percentage of CD3(-)CD56(+) NK cells derived from human CD34(+) HPCs cultured in the presence of IL-15, probably resulting in part from reduced phosphorylation of STAT5. In addition, CD3(-)CD56(+) NK cells derived from culture of CD34(+) HPCs with IL-15 and Axl-Fc had a significantly diminished capacity to express interferon-gamma or its master regulator, T-BET. Culture of CD34(+) HPCs in the presence of c-Kit ligand and Axl-Fc resulted in a significant decrease in the frequency of NK precursor cells responding to IL-15, probably the result of reduced c-Kit phosphorylation. Collectively, our data suggest that the Axl/Gas6 pathway contributes to normal human NK-cell development, at least in part via its regulatory effects on both the IL-15 and c-Kit signaling pathways in CD34(+) HPCs, and to functional NK-cell maturation via an effect on the master regulatory transcription factor T-BET.
Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.) 2009 MAR
Maitake beta-glucan enhances umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation in the NOD/SCID mouse.
Abstract
Abstract
Beta glucans are cell wall constituents of yeast, fungi and bacteria, as well as mushrooms and barley. Glucans are not expressed on mammalian cells and are recognized as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS) by pattern recognition receptors (PRR). Beta glucans have potential activity as biological response modifiers for hematopoiesis and enhancement of bone marrow recovery after injury. We have reported that Maitake beta glucan (MBG) enhanced mouse bone marrow (BMC) and human umbilical cord blood (CB) cell granulocyte-monocyte colony forming unit (GM-CFU) activity in vitro and protected GM-CFU forming stem cells from doxorubicin (DOX) toxicity. The objective of this study was to determine the effects of MBG on expansion of phenotypically distinct subpopulations of progenitor and stem cells in CB from full-term infants cultured ex vivo and on homing and engraftment in vivo in the nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse. MBG promoted a greater expansion of CD34+CD33+CD38- human committed hematopoietic progenitor (HPC) cells compared to the conventional stem cell culture medium (P = 0.002 by ANOVA). CD34+CXCR4+CD38- early, uncommitted human hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) numbers showed a trend towards increase in response to MBG. The fate of CD34+ enriched CB cells after injection into the sublethally irradiated NOS/SCID mouse was evaluated after retrieval of xenografted human CB from marrow and spleen by flow cytometric analysis. Oral administration of MBG to recipient NOS/SCID mice led to enhanced homing at 3 days and engraftment at 6 days in mouse bone marrow (P = 0.002 and P = 0.0005, respectively) compared to control mice. More CD34+ human CB cells were also retrieved from mouse spleen in MBG treated mice at 6 days after transplantation. The studies suggest that MBG promotes hematopoiesis through effects on CD34+ progenitor cell expansion ex vivo and when given to the transplant recipient could enhance CD34+ precursor cell homing and support engraftment.
Blood 2007 MAY
Mapping early conformational changes in alphaIIb and beta3 during biogenesis reveals a potential mechanism for alphaIIbbeta3 adopting its bent conformation.
Abstract
Abstract
Current evidence supports a model in which the low-affinity state of the platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3 results from alphaIIbbeta3 adopting a bent conformation. To assess alphaIIbbeta3 biogenesis and how alphaIIbbeta3 initially adopts the bent conformation, we mapped the conformational states occupied by alphaIIb and beta3 during biogenesis using conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). We found that alphaIIbbeta3 complex formation was not limited by the availability of either free pro-alphaIIb or free beta3, suggesting that other molecules, perhaps chaperones, control complex formation. Five beta3-specific, ligand-induced binding site (LIBS) mAbs reacted with much or all free beta3 but not with beta3 when in complex with mature alphaIIb, suggesting that beta3 adopts its mature conformation only after complex formation. Conversely, 2 alphaIIb-specific LIBS mAbs directed against the alphaIIb Calf-2 region adjacent to the membrane reacted with only minor fractions of free pro-alphaIIb, raising the possibility that pro-alphaIIb adopts a bent conformation early in biogenesis. Our data suggest a working model in which pro-alphaIIb adopts a bent conformation soon after synthesis, and then beta3 assumes its bent conformation by virtue of its interaction with the bent pro-alphaIIb.