ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Kit
The ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Kit (Catalog #01739) contains an ErythroClear™ magnet and ErythroClear™ reagent. The ErythroClear™ magnet is not sold separately and is only available when purchased as a part of this kit.
The ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Reagent Kit (Catalog #01738) contains ErythroClear™ reagent only, and is suitable as a refill for labs that already have an ErythroClear™ magnet. The ErythroClear™ magnet is required for use of the ErythroClear™ reagent.
• Significantly more effective in depleting RBCs than gravity sedimentation methods
• Compatible with downstream assays (e.g. CFU assay, CD34, ALDEFLUOR™ [Catalog #01700], and ALDECOUNT™)
• Does not alter the frequency of CFUs, CD34+, or ALDHbr cells
- ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Kit (Catalog #01739)
- ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Reagent, 2 x 2 mL
- ErythroClear™ Magnet
- ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Reagent Kit (Catalog #01738)
- ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Reagent, 2 x 2 mL
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Kit | 01739 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Reagent Kit | 01738 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Kit | 01739 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | ErythroClear™ Red Blood Cell Depletion Reagent Kit | 01738 | All | English |
Data
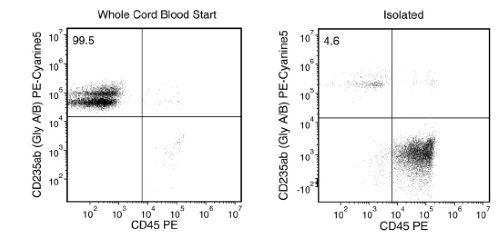
Figure 1. RBC Depletion of Whole Cord Blood Sample Using ErythroClear™
Representative Flow Cytometry Plots of Whole Cord Blood Samples Stained for GlyAB and CD45 Before and After RBC Depletion with ErythroClear™
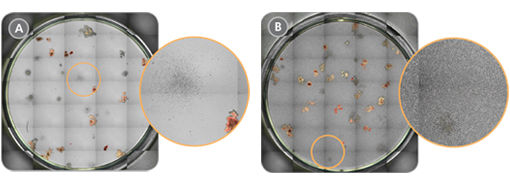
Figure 2. Improved Visualization of Cord Blood-Derived Colonies in CFU Assays After RBC Depletion with ErythroClear™
Representative STEMvision™ images of cord blood CFU assays (A) with and (B) without ErythroClear™ RBC depletion prior to plating. The expanded orange circles illustrate that it is easier to identify small or diffuse colonies in MethoCult™ medium that is free of RBC background (A vs. B).
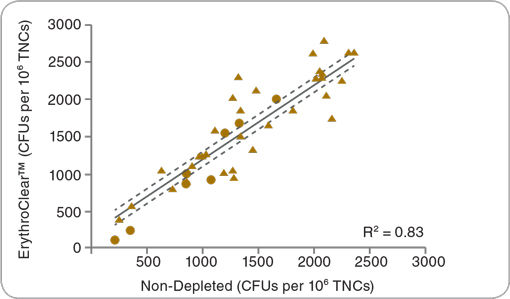
Figure 3. ErythroClear™ Does Not Change the Frequency of CFUs in Cord Blood Samples
The frequency of CFUs in Erythroclear™ depleted (y-axis) and non-depleted (x-axis) cord blood samples are shown. One half of each cord blood sample was processed with ErythroClear™ prior to plating in MethoCult™ H4434 Classic medium. The other half of each sample was plated without RBC depletion. The total number of CFUs in the RBC depleted and non-depleted samples were scored manually after 14 days of culture (n = 32 fresh (triangle) and 8 frozen (circle) cord blood samples, solid line = linear regression best-fit, dotted lines define 95% confidence intervals). The frequency of CFUs in each sample before and after removal of RBCs using ErythroClear™ is highly correlated (coefficient of determination R2 = 0.83). The average recovery of total nucleated cells (TNCs) after RBC depletion with ErythroClear™ was 75%.
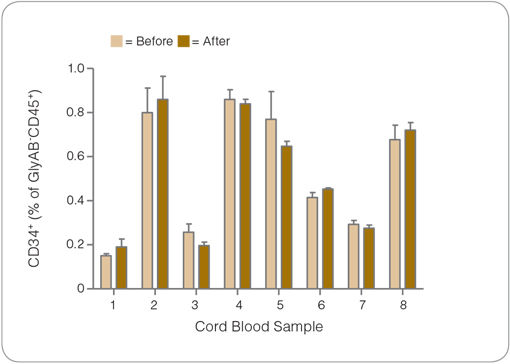
Figure 4. The Frequency of CD34+ Cells in Cord Blood is Not Changed After RBC Depletion with ErythroClear™
Shown are the percentages of GlyAB-CD45+ cells that are CD34+ in cord blood samples before (light gold) and after (gold) RBC depletion with ErythroClear™. There was no significant difference in the frequency of CD34+ cells in this population before and after RBC depletion for each sample (p>0.01). The recovery of CD34+ cells after RBC depletion with ErythroClear™ was 70%. Additionally the frequency of GlyAB-CD45+ that are ALDHbright (data not shown) was not significantly different after ErythroClear™ treatment (p>0.01), and the recovery of these cells was 66%. (n = 8 frozen whole cord blood samples, processed and analyzed separately in triplicate, columns with error bars represent mean ± S.D.).