EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit
15-Minute cell isolation kit using immunomagnetic negative selection
概要
The EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit is designed to isolate naïve CD4+ T cells from single-cell suspensions of splenocytes or other tissues by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with biotinylated antibodies directed against non-naïve CD4+ T cells (CD8, CD11b, CD11c, CD19, CD24, CD25, CD44, CD45R, CD49b, TCRγ/δ, TER119) and streptavidin-coated magnetic particles (RapidSpheres™ ). Labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns. Desired cells are poured off into a new tube.
Learn more about our next-generation EasySep™ mouse cell isolation kits, featuring RapidSphere™ technology.
Learn more about our next-generation EasySep™ mouse cell isolation kits, featuring RapidSphere™ technology.
Advantages
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Up to 95% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
• Up to 95% purity
• Untouched, viable cells
Components
- EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19765)
- EasySep™ Mouse CD4+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse Memory T Cell Depletion Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ Streptavidin RapidSpheres™ 50001, 1 mL
- Normal Rat Serum, 2 mL
- RoboSep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19765RF)
- EasySep™ Mouse CD4+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse Memory T Cell Depletion Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ Streptavidin RapidSpheres™ 50001, 1 mL
- Normal Rat Serum, 2 mL
- RoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)
- RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125)
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• EasyEights™ EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18103)
• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
T Cells, T Cells, CD4+
Species
Mouse
Sample Source
Other, Spleen
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep, RoboSep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | RoboSep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | RoboSep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | RoboSep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765RF | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | RoboSep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit | 19765RF | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
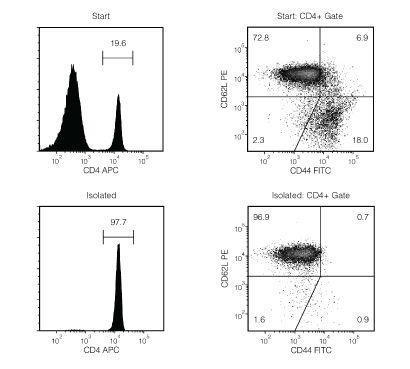
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Mouse Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Profile
Starting with mouse splenocytes from an uninfected mouse, the naïve CD4+ T cell (CD4+CD44lowCD62Lhigh) content of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 89.9 - 95.6%. In the example above, the final purities of the start and isolated fractions are 14.3% and 94.7%, respectively.
Publications (8)
Nature biomedical engineering 2020 oct
Prolonged residence of an albumin-IL-4 fusion protein in secondary lymphoid organs ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Abstract
Abstract
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) suppresses the development of multiple sclerosis in a murine model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Here, we show that, in mice with EAE, the accumulation and persistence in the lymph nodes and spleen of a systemically administered serum albumin (SA)-IL-4 fusion protein leads to higher efficacy in preventing disease development than the administration of wild-type IL-4 or of the clinically approved drug fingolimod. We also show that the SA-IL-4 fusion protein prevents immune-cell infiltration in the spinal cord, decreases integrin expression in antigen-specific CD4+ T cells, increases the number of granulocyte-like myeloid-derived suppressor cells (and their expression of programmed-death-ligand-1) in spinal cord-draining lymph nodes and decreases the number of T helper 17 cells, a pathogenic cell population in EAE. In mice with chronic EAE, SA-IL-4 inhibits immune-cell infiltration into the spinal cord and completely abrogates immune responses to myelin antigen in the spleen. The SA-IL-4 fusion protein may be prophylactically and therapeutically advantageous in the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Science advances 2020 jun
Synoviocyte-targeted therapy synergizes with TNF inhibition in arthritis reversal.
Abstract
Abstract
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) are joint-lining cells that promote rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathology. Current disease-modifying antirheumatic agents (DMARDs) operate through systemic immunosuppression. FLS-targeted approaches could potentially be combined with DMARDs to improve control of RA without increasing immunosuppression. Here, we assessed the potential of immunoglobulin-like domains 1 and 2 (Ig1{\&}2), a decoy protein that activates the receptor tyrosine phosphatase sigma (PTPRS) on FLS, for RA therapy. We report that PTPRS expression is enriched in synovial lining RA FLS and that Ig1{\&}2 reduces migration of RA but not osteoarthritis FLS. Administration of an Fc-fusion Ig1{\&}2 attenuated arthritis in mice without affecting innate or adaptive immunity. Furthermore, PTPRS was down-regulated in FLS by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated pathway, and TNF inhibition enhanced PTPRS expression in arthritic joints. Combination of ineffective doses of TNF inhibitor and Fc-Ig1{\&}2 reversed arthritis in mice, providing an example of synergy between FLS-targeted and immunosuppressive DMARD therapies.
Cell reports 2020 feb
Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation Regulates the Fate Decision between Pathogenic Th17 and Regulatory T Cells.
Abstract
Abstract
Understanding metabolic pathways that regulate Th17 development is important to broaden therapeutic options for Th17-mediated autoimmunity. Here, we report a pivotal role of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) for lineage specification toward pathogenic Th17 differentiation. Th17 cells rapidly increase mitochondrial respiration during development, and this is necessary for metabolic reprogramming following T cell activation. Surprisingly, specific inhibition of mitochondrial ATP synthase ablates Th17 pathogenicity in a mouse model of autoimmunity by preventing Th17 pathogenic signature gene expression. Notably, cells activated under OXPHOS-inhibited Th17 conditions preferentially express Foxp3, rather than Th17 genes, and become suppressive Treg cells. Mechanistically, OXPHOS promotes the Th17 pioneer transcription factor, BATF, and facilitates T cell receptor (TCR) and mTOR signaling. Correspondingly, overexpression of BATF rescues Th17 development when ATP synthase activity is restricted. Together, our data reveal a regulatory role of mitochondrial OXPHOS in dictating the fate decision between Th17 and Treg cells by supporting early molecular events necessary for Th17 commitment.
Nature communications 2020
T cell-intrinsic role for Nod2 in protection against Th17-mediated uveitis.
Abstract
Abstract
Mutations in nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 (NOD2) cause Blau syndrome, an inflammatory disorder characterized by uveitis. The antimicrobial functions of Nod2 are well-established, yet the cellular mechanisms by which dysregulated Nod2 causes uveitis remain unknown. Here, we report a non-conventional, T cell-intrinsic function for Nod2 in suppression of Th17 immunity and experimental uveitis. Reconstitution of lymphopenic hosts with Nod2-/- CD4+ T cells or retina-specific autoreactive CD4+ T cells lacking Nod2 reveals a T cell-autonomous, Rip2-independent mechanism for Nod2 in uveitis. In naive animals, Nod2 operates downstream of TCR ligation to suppress activation of memory CD4+ T cells that associate with an autoreactive-like profile involving IL-17 and Ccr7. Interestingly, CD4+ T cells from two Blau syndrome patients show elevated IL-17 and increased CCR7. Our data define Nod2 as a T cell-intrinsic rheostat of Th17 immunity, and open new avenues for T cell-based therapies for Nod2-associated disorders such as Blau syndrome.
Scientific reports 2019 apr
Maf deficiency in T cells dysregulates Treg - TH17 balance leading to spontaneous colitis.
Abstract
Abstract
The maintenance of homeostasis in the gut is a major challenge for the immune system. Here we demonstrate that the transcription factor MAF plays a central role in T cells for the prevention of gastro-intestinal inflammation. Conditional knock out mice lacking Maf in all T cells developed spontaneous late-onset colitis, correlating with a decrease of FOXP3+RORgammat+ T cells proportion, dampened IL-10 production in the colon and an increase of inflammatory TH17 cells. Strikingly, FOXP3+ specific conditional knock out mice for MAF did not develop colitis and demonstrated normal levels of IL-10 in their colon, despite the incapacity of regulatory T cells lacking MAF to suppress colon inflammation in Rag1-/- mice transferred with na{\{i}}ve CD4+ T cells. We showed that one of the cellular sources of IL-10 in the colon of these mice are TH17 cells. Thus MAF is critically involved in the maintenance of the gut homeostasis by regulating the balance between Treg and TH17 cells either at the level of their differentiation or through the modulation of their functions."
Toxicology and applied pharmacology 2018 OCT
Astragaloside IV regulates differentiation and induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ T cells in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Abstract
Abstract
CD4+ T cells, especially T-helper (Th) cells (Th1, Th2 and Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg) play pivotal role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS), a demyelinating autoimmune disease occurring in central nervous system (CNS). Astragaloside IV (ASI, CAS: 84687-43-4) is one of the saponins isolated from Astragalus membranceus, a traditional Chinese medicine with immunomodulatory effect. So far, whether ASI has curative effect on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of MS, and how it affects the subsets of CD4+ T cells, as well as the underlying mechanism have not been clearly elucidated. In the present study, ASI was found to ameliorate the progression and hamper the recurrence of EAE effectively in the treatment regimens. It significantly reduced the demyelination and inflammatory infiltration of CNS in EAE mice by suppressing the percentage of Th1 and Th17 cells, which was closely associated with the inhibition of JAK/STAT and NF-$\kappa$B signaling pathways. ASI also increased the percentage of Treg cells in spleen and CNS, which was accompanied by elevated Foxp3. However, in vitro experiments disclosed that ASI could regulate the differentiation of Th17 and Treg cells but not Th1 cells. In addition, it induced the apoptosis of MOG-stimulated CD4+ T cells probably through modulating STAT3/Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways. Together, our findings suggested that ASI can modulate the differentiation of autoreactive CD4+ T cells and is a potential prodrug or drug for the treatment of MS and other similar autoimmune diseases.