EasySep™ Mouse ILC2 Enrichment Kit
Immunomagnetic negative selection kit
概要
This product is designed to enrich ILC2's (Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells) from single-cell suspensions of lung tissue or other tissues by negative selection. Unwanted cells are targeted for removal with biotinylated antibodies directed against non-ILC2 cells and streptavidin-coated magnetic particles (RapidSpheres™). Labeled cells are separated using an EasySep™ magnet without the use of columns.
Advantages
• Fast, easy-to-use and column-free
• Isolated cells are untouched
• Facilitates rapid flow sorting of ILC2s
• Isolated cells are untouched
• Facilitates rapid flow sorting of ILC2s
Components
- EasySep™ Mouse ILC2 Enrichment Kit (Catalog #19842)
- EasySep™ Mouse Enrichment Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ Streptavidin RapidSpheres™ 50001, 1.0 mL
Magnet Compatibility
EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
Innate Lymphoid Cells
Species
Mouse
Sample Source
Other
Selection Method
Negative
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | EasySep™ Mouse ILC2 Enrichment Kit | 19842 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | EasySep™ Mouse ILC2 Enrichment Kit | 19842 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | EasySep™ Mouse ILC2 Enrichment Kit | 19842 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | EasySep™ Mouse ILC2 Enrichment Kit | 19842 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
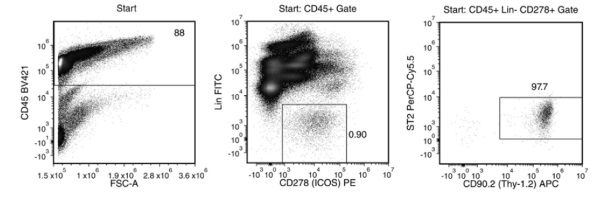

Starting with a naïve mouse lung single-cell suspension, the ILC2 content (CD45+Lin-CD278+CD90.2+ST2+) of the final enriched fraction typically ranges from 2.2 - 7.1%. In the above example, the percentage of ILC2s in the start and final enriched fractions are 0.8% and 6.5% (or 0.9% and 22.3% of CD45+ cells), respectively. NOTE: The ILC2 content of the start fraction typically ranges from 0.1 - 1%.
Publications (2)
Current protocols in immunology 2019 jun
Identification of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Mouse Lung, Liver, Small Intestine, Bone Marrow, and Mediastinal and Mesenteric Lymph Nodes.
Abstract
Abstract
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are a heterogeneous family of lymphocytes that populate barrier and non-barrier tissues. ILCs regulate immune responses to pathogens and commensals but also sustain metabolic homeostasis, tissue remodeling after injury and establish dialogue with the nervous system. ILCs rapidly become activated in the absence of adaptive antigen receptors by responding to signaling molecules provided by hematopoietic or non-hematopoietic cells. Here we provide protocols designed for processing the lung, liver, small intestine, bone marrow, mediastinal and mesenteric lymph nodes in order to obtain a purified leukocyte fraction of cells, in which ILC2 enrichment is optimized. In addition, we describe in detail the methodologies used to activate ILC2s and the assays necessary for the detection of their effector cytokines. We highlight the differences in ILC2 characterization within distinct tissues that we have recently identified. {\textcopyright} 2019 by John Wiley Sons, Inc.
Immunity 2016 JUL
Allergen-Experienced Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Acquire Memory-like Properties and Enhance Allergic Lung Inflammation.
Abstract
Abstract
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) in the lung are stimulated by inhaled allergens. ILC2s do not directly recognize allergens but they are stimulated by cytokines including interleukin (IL)-33 released by damaged epithelium. In response to allergens, lung ILC2s produce T helper 2 cell type cytokines inducing T cell-independent allergic lung inflammation. Here we examined the fate of lung ILC2s upon allergen challenges. ILC2s proliferated and secreted cytokines upon initial stimulation with allergen or IL-33, and this phase was followed by a contraction phase as cytokine production ceased. Some ILC2s persisted long after the resolution of the inflammation as allergen-experienced ILC2s and responded to unrelated allergens more potently than naive ILC2s, mediating severe allergic inflammation. The allergen-experienced ILC2s exhibited a gene expression profile similar to that of memory T cells. The memory-like properties of allergen-experienced ILC2s may explain why asthma patients are often sensitized to multiple allergens.


