EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Kit
Immunomagnetic positive selection cell isolation kit
概要
The EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Kit is designed to isolate highly purified CD25+ cells from single-cell suspensions of splenocytes or other tissues by positive selection. The kit targets CD25 regulatory T cells for positive selection with a PE-labeled antibody directed against the CD25 surface marker. Desired cells are labeled with antibodies and magnetic particles. The cells are separated without columns using an EasySep™ magnet. Unwanted cells are simply poured off, while desired cells remain in the tube.
Advantages
• Fast and easy-to-use
• Up to 93% purity
• No columns required
• Up to 93% purity
• No columns required
Components
- EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #18782)
- EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ PE Selection Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™ 50100, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse FcR Blocker, 0.5 mL
- RoboSep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T cell Positive Selection Kit (Catalog #18782RF)
- EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ PE Selection Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™ 50100, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse FcR Blocker, 0.5 mL
- RoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)
- RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125)
Magnet Compatibility
• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)
• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)
• EasyEights™ Magnet (Catalog #18103)
• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)
Subtype
Cell Isolation Kits
Cell Type
T Cells, T Cells, CD4+, T Cells, Regulatory
Species
Mouse
Sample Source
Other, Spleen
Selection Method
Positive
Application
Cell Isolation
Brand
EasySep, RoboSep
Area of Interest
Immunology
技术资料
数据及文献
Data
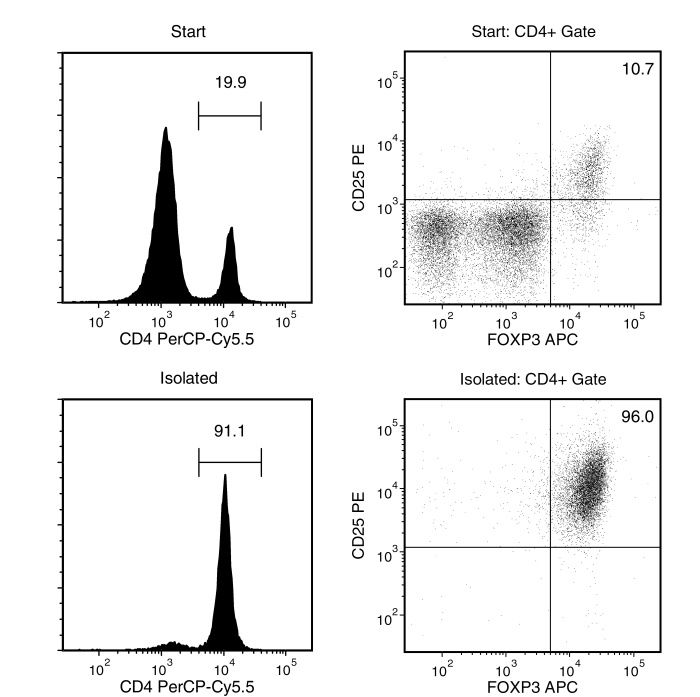
Figure 1. Typical EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Profile
Starting with mouse splenocytes, the CD25 regulatory T cell content (CD4+CD25+FOXP3+) of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 80 - 93%. In the example above, the final purities of the start and isolated fractions are 2.1% and 87.5%, respectively.
Publications (2)
Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2019 sep
Selective Cannabinoid 2 Receptor Agonists as Potential Therapeutic Drugs for the Treatment of Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis.
Abstract
Abstract
(1) Background: The cannabinoid 2 receptor (CB2R) is a promising anti-inflammatory drug target and development of selective CB2R ligands may be useful for treating sight-threatening ocular inflammation. (2) Methods: This study examined the pharmacology of three novel chemically-diverse selective CB2R ligands: CB2R agonists, RO6871304, and RO6871085, as well as a CB2R inverse agonist, RO6851228. In silico molecular modelling and in vitro cell-based receptor assays were used to verify CB2R interactions, binding, cell signaling ({\ss}-arrestin and cAMP) and early absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicology (ADMET) profiling of these receptor ligands. All ligands were evaluated for their efficacy to modulate leukocyte-neutrophil activity, in comparison to the reported CB2R ligand, HU910, using an in vivo mouse model of endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) in wild-type (WT) and CB2R-/- mice. The actions of RO6871304 on neutrophil migration and adhesion were examined in vitro using isolated neutrophils from WT and CB2R-/- mice, and in vivo in WT mice with EIU using adoptive transfer of WT and CB2R-/- neutrophils, respectively. (3) Results: Molecular docking studies indicated that RO6871304 and RO6871085 bind to the orthosteric site of CB2R. Binding studies and cell signaling assays for RO6871304 and RO6871085 confirmed high-affinity binding to CB2R and selectivity for CB2R {\textgreater} CB1R, with both ligands acting as full agonists in cAMP and {\ss}-arrestin assays (EC50s in low nM range). When tested in EIU, topical application of RO6871304 and RO6871085 decreased leukocyte-endothelial adhesion and this effect was antagonized by the inverse agonist, RO6851228. The CB2R agonist, RO6871304, decreased in vitro neutrophil migration of WT neutrophils but not neutrophils from CB2R-/-, and attenuated adhesion of adoptively-transferred leukocytes in EIU. (4) Conclusions: These unique ligands are potent and selective for CB2R and have good immunomodulating actions in the eye. RO6871304 and RO6871085, as well as HU910, decreased leukocyte adhesion in EIU through inhibition of resident ocular immune cells. The data generated with these three structurally-diverse and highly-selective CB2R agonists support selective targeting of CB2R for treating ocular inflammatory diseases.
Immunity 2016 MAY
Thymus-Derived Regulatory T Cells Are Positively Selected on Natural Self-Antigen through Cognate Interactions of High Functional Avidity.
Abstract
Abstract
Regulatory T (Treg) cells expressing Foxp3 transcripton factor are essential for immune homeostasis. They arise in the thymus as a separate lineage from conventional CD4(+)Foxp3(-) T (Tconv) cells. Here, we show that the thymic development of Treg cells depends on the expression of their endogenous cognate self-antigen. The formation of these cells was impaired in mice lacking this self-antigen, while Tconv cell development was not negatively affected. Thymus-derived Treg cells were selected by self-antigens in a specific manner, while autoreactive Tconv cells were produced through degenerate recognition of distinct antigens. These distinct modes of development were associated with the expression of T cell receptor of higher functional avidity for self-antigen by Treg cells than Tconv cells, a difference subsequently essential for the control of autoimmunity. Our study documents how self-antigens define the repertoire of thymus-derived Treg cells to subsequently endow this cell type with the capacity to undermine autoimmune attack.