EasySep™ Mouse CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cell Isolation Kit II
Immunomagnetic negative selection followed by positive selection kit
概要
The EasySep™ Mouse CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cell Isolation Kit II is designed to isolate CD4+CD25+ T cells from single-cell suspensions of splenocytes or other tissues by negative followed by positive selection. CD4+ T cells are first enriched by negative selection using the EasySep™ Mouse CD4+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail. CD25+ cells are then positively selected from the pre-enriched cells using EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Cocktail.
Advantages
• Fast and easy-to-use
• Up to 93% purity
• No columns required
• Up to 93% purity
• No columns required
Components
- EasySep™ Mouse CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cell Isolation Kit II (Catalog #18783)
- EasySep™ Mouse CD4+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ Streptavidin RapidSpheres™ 50001, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ PE Selection Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™ 50100, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse FcR Blocker, 0.5 mL
- Rat Serum, 2 mL
- RoboSep™ Mouse CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cell Isolation Kit II (Catalog #18783RF)
- EasySep™ Mouse CD4+ T Cell Isolation Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ Streptavidin RapidSpheres™ 50001, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse CD25 Regulatory T Cell Positive Selection Cocktail, 0.5 mL
- EasySep™ PE Selection Cocktail, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Dextran RapidSpheres™ 50100, 1 mL
- EasySep™ Mouse FcR Blocker, 0.5 mL
- Rat Serum, 2 mLRoboSep™ Buffer (Catalog #20104)RoboSep™ Filter Tips (Catalog #20125)
Magnet Compatibility• EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18000)• “The Big Easy” EasySep™ Magnet (Catalog #18001)• EasyEights™ Magnet (Catalog #18103)• RoboSep™-S (Catalog #21000)SubtypeCell Isolation KitsCell TypeT Cells, T Cells, RegulatorySpeciesMouseSample SourceSpleenBrandEasySep, RoboSepArea of InterestImmunology
技术资料
数据及文献
Data
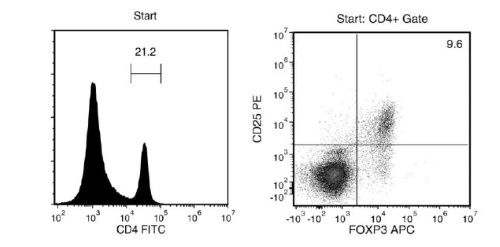
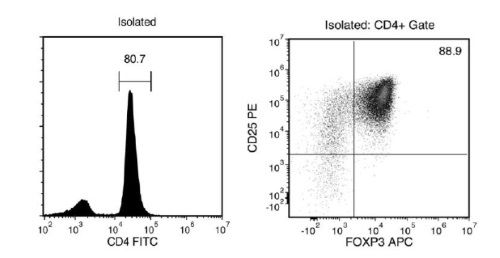
Figure 1. FACS Histogram Results with EasySep™ Mouse CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cell Isolation Kit II
Starting with mouse splenocytes, the regulatory T cell content (CD4+CD25+FOXP3+) of the isolated fraction typically ranges from 70 - 93%. In the above example, the purities of the start and final isolated fractions are 2% and 72%, respectively.
Publications (4)
Journal of immunology research 2020
miR-21 and Pellino-1 Expression Profiling in Autoimmune Premature Ovarian Insufficiency.
Abstract
Abstract
Background Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) represents the hypergonadotropic hypoestrogenic symptoms that result in the loss of ovarian follicles. 5-30{\%} POI cases are suggested to be involved in autoimmune etiology. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) plays a vital role in ovarian folliculogenesis via regulating and interacting with multiple target genes. Here, we conduct the target prediction of miR-21, identify the expression and correlation of miR-21 and its putative target Pellino-1 (Peli1), and confirm their relationship with clinical characteristics in autoimmune POI. Methods Bioinformatic analysis was conducted to screen the miR-21 putative target gene. Autoimmune POI mouse models were established by ZP3 immunization. Serum miR-21, Peli1 mRNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and regulatory T cells (Tregs), general status, spleen Tregs ratio, inflammatory factors, ovarian endocrine function, and ovarian structure were evaluated. For autoimmune POI patients, serum miR-21, PBMCs Peli1 mRNA levels, general data, immune parameters, hormone levels, and ultrasound examinations were obtained. The correlations of miR-21 with Peli1 and clinical characteristics in patients were analyzed. Results Peli1 was selected based on four microRNA prediction databases and literature retrieval. In mouse models, serum miR-21 level, PBMCs and Tregs Peli1 mRNA, and spleen Tregs ratio were 0.61 ± 0.09, 0.12 ± 0.12, 0.27±0.23 and 4.82 ± 0.58, respectively, lower than those in the control group. In patients, miR-21 level (0.60 ± 0.14) and Peli1 mRNA (0.30 ± 0.14) were lower than those in the control group (1.01 ± 0.07 and 1.63 ± 0.54); miR-21 was positively related with Peli1, AMH, E2, the size of the uterus, and ovarian volume and negatively related with FSH, LH, and the number of positive immune parameters (AOAb, EMAb, ACL, ANA, ds-DNA, ACA, IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, C3, and C4). Conclusions Low expressions of miR-21 and Peli1 were detected in autoimmune POI mice and patients. Positive correlation between miR-21 and Peli1 was observed in autoimmune POI patients, suggesting that miR-21 and Peli1 might be associated with the pathogenesis of autoimmune POI.
Journal of autoimmunity 2019 may
IL233, an IL-2-IL-33 hybrid cytokine induces prolonged remission of mouse lupus nephritis by targeting Treg cells as a single therapeutic agent.
Abstract
Abstract
Lupus glomerulonephritis (GN) is an autoimmune disease characterized by immune complex-deposition, complement activation and glomerular inflammation. In lupus-prone NZM2328 mice, the occurrence of lupus GN was accompanied by a decrease in Treg cells and an increase in proinflammatory cytokine-producing T cells. Because IL-33 in addition to IL-2 has been shown to be important for Treg cell proliferation and ST2 (IL-33 receptor) positive Treg cells are more potent in suppressor activity, a hybrid cytokine with active domains of IL-2 and IL-33 was generated to target the ST2+ Treg cells as a therapeutic agent to treat lupus GN. Three mouse models were used: spontaneous and Ad-IFNalpha- accelerated lupus GN in NZM2328 and the lymphoproliferative autoimmune GN in MRL/lpr mice. Daily injections of IL233 for 5 days prevented Ad-IFNalpha-induced lupus GN and induced remission of spontaneous lupus GN. The remission was permanent in that no relapses were detected. The remission was accompanied by persistent elevation of Treg cells in the renal lymph nodes. IL233 is more potent than IL-2 and IL-33 either singly or in combination in the treatment of lupus GN. The results of this study support the thesis that IL233 should be considered as a novel agent for treating lupus GN.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2019 jul
Nanoparticles Containing an Insulin-ChgA Hybrid Peptide Protect from Transfer of Autoimmune Diabetes by Shifting the Balance between Effector T Cells and Regulatory T Cells.
Abstract
Abstract
CD4 T cells play a critical role in promoting the development of autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. The diabetogenic CD4 T cell clone BDC-2.5, originally isolated from a NOD mouse, has been widely used to study the contribution of autoreactive CD4 T cells and relevant Ags to autoimmune diabetes. Recent work from our laboratory has shown that the Ag for BDC-2.5 T cells is a hybrid insulin peptide (2.5HIP) consisting of an insulin C-peptide fragment fused to a peptide from chromogranin A (ChgA) and that endogenous 2.5HIP-reactive T cells are major contributors to autoimmune pathology in NOD mice. The objective of this study was to determine if poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLG) nanoparticles (NPs) loaded with the 2.5HIP Ag (2.5HIP-coupled PLG NPs) can tolerize BDC-2.5 T cells. Infusion of 2.5HIP-coupled PLG NPs was found to prevent diabetes in an adoptive transfer model by impairing the ability of BDC-2.5 T cells to produce proinflammatory cytokines through induction of anergy, leading to an increase in the ratio of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells to IFN-gamma+ effector T cells. To our knowledge, this work is the first to use a hybrid insulin peptide, or any neoepitope, to re-educate diabetogenic T cells and may have significant implications for the development of an Ag-specific therapy for type 1 diabetes patients.
Frontiers in oncology 2019
Development of a Bispecific Antibody Targeting CD30 and CD137 on Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells.
Abstract
Abstract
Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL) is a malignancy that frequently affects young adults. Although, there are effective treatments not every patient responds, necessitating the development of novel therapeutic approaches, especially for relapsed and refractory cases. The two TNF receptor family members CD30 and CD137 are expressed on Hodgkin and Reed Sternberg (HRS) cells, the malignant cells in HL. We found that this co-expression is specific for HRS cells. Based on this discovery we developed a bispecific antibody that binds preferentially to the CD30, CD137-double positive HRS cells. The CD30, CD137 bispecific antibody gets internalized into HRS cells opening up the possibility to use it as a carrier for a toxin. This antibody also induces antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity in CD30, CD137-double positive HRS cells. The enhances specificity of the CD30, CD137 bispecific antibody to HRS cells makes it a promising candidate for development as a novel HL treatment.