MethoCult™ SF H4636
Serum-free methylcellulose-based medium with recombinant cytokines for human ES and iPS cell-derived cells
概要
MethoCult™ SF H4636 is recommended for the culture of human embryonic stem (ES) cell-derived and induced pluripotent stem (iPS)
cell-derived hematopoietic progenitor cells in defined serum-free conditions. MethoCult™ SF H4636 is formulated to support optimal growth of erythroid progenitor cells (CFU-E and BFU-E), granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells (CFU-GM, CFU-G, CFU-M), and multipotential progenitor cells (CFU-GEMM; granulocyte, erythrocyte, macrophage, megakaryocyte).
MethoCult™ SF H4636 is also recommended for CFU assays with mononuclear cells, CD34+ enriched cells, and cells isolated by other purification methods from human bone marrow (BM), mobilized peripheral blood (MPB), peripheral blood (PB), and cord blood (CB) samples.
Browse our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on performing the CFU assay and explore its utility as part of the cell therapy workflow.
cell-derived hematopoietic progenitor cells in defined serum-free conditions. MethoCult™ SF H4636 is formulated to support optimal growth of erythroid progenitor cells (CFU-E and BFU-E), granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells (CFU-GM, CFU-G, CFU-M), and multipotential progenitor cells (CFU-GEMM; granulocyte, erythrocyte, macrophage, megakaryocyte).
MethoCult™ SF H4636 is also recommended for CFU assays with mononuclear cells, CD34+ enriched cells, and cells isolated by other purification methods from human bone marrow (BM), mobilized peripheral blood (MPB), peripheral blood (PB), and cord blood (CB) samples.
Browse our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on performing the CFU assay and explore its utility as part of the cell therapy workflow.
Contains
• Methylcellulose in Iscove's IMDM
• Bovine serum albumin
• 2-Mercaptoethanol
• Recombinant human insulin
• Human transferrin (iron-saturated)
• Cytokines including recombinant human erythropoietin (EPO)
• Supplements
• Bovine serum albumin
• 2-Mercaptoethanol
• Recombinant human insulin
• Human transferrin (iron-saturated)
• Cytokines including recombinant human erythropoietin (EPO)
• Supplements
Subtype
Semi-Solid Media, Specialized Media
Cell Type
Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Species
Human
Application
Cell Culture, Colony Assay, Functional Assay
Brand
MethoCult
Area of Interest
Stem Cell Biology
Formulation
Serum-Free
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | MethoCult™ SF H4636 | 04636 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MethoCult™ SF H4636 | 04636 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
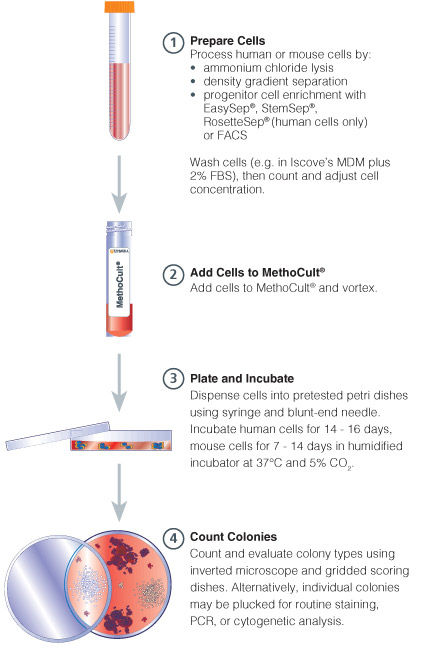
Figure 1. Procedure Summary for Hematopoietic CFU Assays
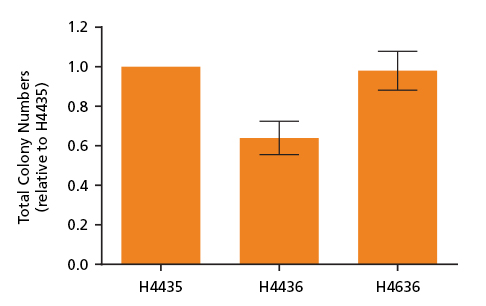
Figure 2. Total Colony Numbers of CD34+ Cells Grown in MethoCult™ SF H4436 and MethoCult™ SF H4636
CD34+ and mononuclear cells derived from CB, mPB and BM were isolated and plated in MethoCult™ media and counted after 14 days. Shown are the number of total colonies grown in serum-free MethoCult™ SF H4436 (Catalog #04436) and MethoCult™ SF H4636 (Catalog #04636) normalized relative to total colonies grown in serum-containing MethoCult™ H4435 (Catalog #04435). MethoCult™ SF H4636 provides improved conditions for colony growth in serum-free conditions as compared to MethoCult™ SF H4436. Shown are means with standard deviation (n = 6).
Publications (1)
Stem cell reports 2019 jun
Differentiation and Functional Comparison of Monocytes and Macrophages from hiPSCs with Peripheral Blood Derivatives.
Abstract
Abstract
A renewable source of human monocytes and macrophages would be a valuable alternative to primary cells from peripheral blood (PB) in biomedical research. We developed an efficient protocol to derive monocytes and macrophages from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and performed a functional comparison with PB-derived cells. hiPSC-derived monocytes were functional after cryopreservation and exhibited gene expression profiles comparable with PB-derived monocytes. Notably, hiPSC-derived monocytes were more activated with greater adhesion to endothelial cells under physiological flow. hiPSC-derived monocytes were successfully polarized to M1 and M2 macrophage subtypes, which showed similar pan- and subtype-specific gene and surface protein expression and cytokine secretion to PB-derived macrophages. hiPSC-derived macrophages exhibited higher endocytosis and efferocytosis and similar bacterial and tumor cell phagocytosis to PB-derived macrophages. In summary, we developed a robust protocol to generate hiPSC monocytes and macrophages from independent hiPSC lines that showed aspects of functional maturity comparable with those from PB.