MethoCult™ H4434 Classic
Methylcellulose-based medium with recombinant cytokines for human cells
概要
MethoCult™ H4434 Classic (MethoCult™ GF H4434) is a complete methylcellulose-based medium for the growth and enumeration of hematopoietic progenitor cells in colony-forming unit (CFU) assays of human bone marrow, mobilized peripheral blood, peripheral blood, and cord blood samples. MethoCult™ H4434 Classic is formulated to support the optimal growth of erythroid progenitor cells (BFU-E and CFU-E), granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells (CFU-GM, CFU-G and CFU-M), and multipotential granulocyte, erythroid, macrophage and megakaryocyte progenitor cells (CFU-GEMM).
Browse our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on performing the CFU assay and explore its utility as part of the cell therapy workflow.
Browse our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on performing the CFU assay and explore its utility as part of the cell therapy workflow.
Contains
• Methylcellulose in Iscove's MDM
• Fetal bovine serum
• Bovine serum albumin
• 2-Mercaptoethanol
• Recombinant human stem cell factor (SCF)
• Recombinant human interleukin 3 (IL-3)
• Recombinant human erythropoietin (EPO)
• Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
• Supplements
• Fetal bovine serum
• Bovine serum albumin
• 2-Mercaptoethanol
• Recombinant human stem cell factor (SCF)
• Recombinant human interleukin 3 (IL-3)
• Recombinant human erythropoietin (EPO)
• Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
• Supplements
Subtype
Semi-Solid Media, Specialized Media
Cell Type
Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Species
Human, Non-Human Primate
Application
Cell Culture, Colony Assay, Functional Assay
Brand
MethoCult
Area of Interest
Stem Cell Biology
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | MethoCult™ H4434 Classic | 04434, 04444 | All | English |
| Manual | MethoCult™ H4434 Classic | 04434 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | MethoCult™ H4434 Classic | 04434, 04444 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
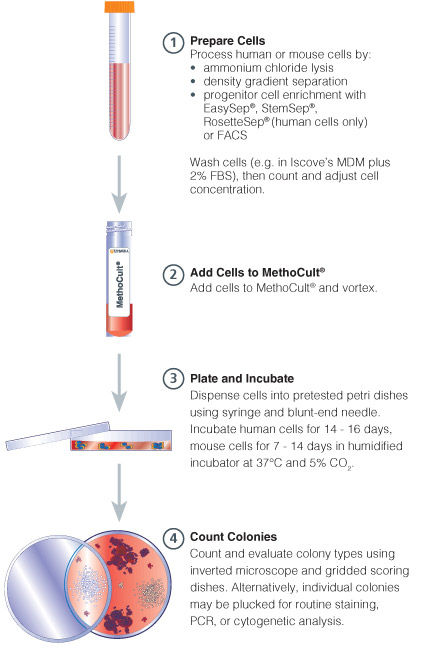
Figure 1. Procedure Summary for Hematopoietic CFU Assays
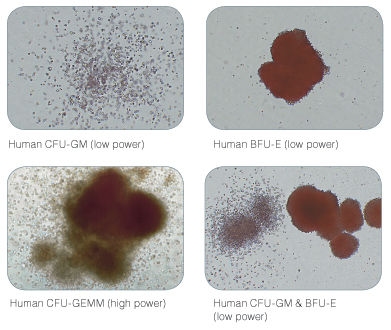
Figure 2. Examples of Colonies Derived from Human Hematopoietic Progenitors
Publications (63)
Leukemia 2020 jan
BCMA peptide-engineered nanoparticles enhance induction and function of antigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes against multiple myeloma: clinical applications.
Abstract
Abstract
The purpose of these studies was to develop and characterize B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-specific peptide-encapsulated nanoparticle formulations to efficiently evoke BCMA-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) with poly-functional immune activities against multiple myeloma (MM). Heteroclitic BCMA72-80 [YLMFLLRKI] peptide-encapsulated liposome or poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles displayed uniform size distribution and increased peptide delivery to human dendritic cells, which enhanced induction of BCMA-specific CTL. Distinct from liposome-based nanoparticles, PLGA-based nanoparticles demonstrated a gradual increase in peptide uptake by antigen-presenting cells, and induced BCMA-specific CTL with higher anti-tumor activities (CD107a degranulation, CTL proliferation, and IFN-$\gamma$/IL-2/TNF-$\alpha$ production) against primary CD138+ tumor cells and MM cell lines. The improved functional activities were associated with increased Tetramer+/CD45RO+ memory CTL, CD28 upregulation on Tetramer+ CTL, and longer maintenance of central memory (CCR7+ CD45RO+) CTL, with the highest anti-MM activity and less differentiation into effector memory (CCR7- CD45RO+) CTL. These results provide the framework for therapeutic application of PLGA-based BCMA immunogenic peptide delivery system, rather than free peptide, to enhance the induction of BCMA-specific CTL with poly-functional Th1-specific anti-MM activities. These results demonstrate the potential clinical utility of PLGA nanotechnology-based cancer vaccine to enhance BCMA-targeted immunotherapy against myeloma.
Nucleic acids research 2019 may
Highly efficient editing of the beta-globin gene in patient-derived hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells to treat sickle cell disease.
Abstract
Abstract
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a monogenic disorder that affects millions worldwide. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the only available cure. Here, we demonstrate the use of CRISPR/Cas9 and a short single-stranded oligonucleotide template to correct the sickle mutation in the beta-globin gene in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) from peripheral blood or bone marrow of patients with SCD, with 24.5 ± 7.6{\%} efficiency without selection. Erythrocytes derived from gene-edited cells showed a marked reduction of sickle cells, with the level of normal hemoglobin (HbA) increased to 25.3 ± 13.9{\%}. Gene-corrected SCD HSPCs retained the ability to engraft when transplanted into non-obese diabetic (NOD)-SCID-gamma (NSG) mice with detectable levels of gene correction 16-19 weeks post-transplantation. We show that, by using a high-fidelity SpyCas9 that maintained the same level of on-target gene modification, the off-target effects including chromosomal rearrangements were significantly reduced. Taken together, our results demonstrate efficient gene correction of the sickle mutation in both peripheral blood and bone marrow-derived SCD HSPCs, a significant reduction in sickling of red blood cells, engraftment of gene-edited SCD HSPCs in vivo and the importance of reducing off-target effects; all are essential for moving genome editing based SCD treatment into clinical practice.
Cell stem cell 2019 aug
Interconversion between Tumorigenic and Differentiated States in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Abstract
Abstract
Tumors are composed of phenotypically heterogeneous cancer cells that often resemble various differentiation states of their lineage of origin. Within this hierarchy, it is thought that an immature subpopulation of tumor-propagating cancer stem cells (CSCs) differentiates into non-tumorigenic progeny, providing a rationale for therapeutic strategies that specifically eradicate CSCs or induce their differentiation. The clinical success of these approaches depends on CSC differentiation being unidirectional rather than reversible, yet this question remains unresolved even in prototypically hierarchical malignancies, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Here, we show in murine and human models of AML that, upon perturbation of endogenous expression of the lineage-determining transcription factor PU.1 or withdrawal of established differentiation therapies, some mature leukemia cells can de-differentiate and reacquire clonogenic and leukemogenic properties. Our results reveal plasticity of CSC maturation in AML, highlighting the need to therapeutically eradicate cancer cells across a range of differentiation states.
Cell stem cell 2019 apr
Precise Gene Editing Preserves Hematopoietic Stem Cell Function following Transient p53-Mediated DNA Damage Response.
Abstract
Abstract
Precise gene editing in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) holds promise for treating genetic diseases. However, responses triggered by programmable nucleases in HSPCs are poorly characterized and may negatively impact HSPC engraftment and long-term repopulation capacity. Here, we induced either one or several DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) with optimized zinc-finger and CRISPR/Cas9 nucleases and monitored DNA damage response (DDR) foci induction, cell-cycle progression, and transcriptional responses in HSPC subpopulations, with up to single-cell resolution. p53-mediated DDR pathway activation was the predominant response to even single-nuclease-induced DSBs across all HSPC subtypes analyzed. Excess DSB load and/or adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated delivery of DNA repair templates induced cumulative p53 pathway activation, constraining proliferation, yield, and engraftment of edited HSPCs. However, functional impairment was reversible when DDR burden was low and could be overcome by transient p53 inhibition. These findings provide molecular and functional evidence for feasible and seamless gene editing in HSPCs.
Cell 2018 JAN
Intrinsic Immunity Shapes Viral Resistance of Stem Cells.
Abstract
Abstract
Stem cells are highly resistant to viral infection compared to their differentiated progeny; however, the mechanism is mysterious. Here, we analyzed gene expression in mammalian stem cells and cells at various stages of differentiation. We find that, conserved across species, stem cells express a subset of genes previously classified as interferon (IFN) stimulated genes (ISGs) but that expression is intrinsic, as stem cells are refractory to interferon. This intrinsic ISG expression varies in a cell-type-specific manner, and many ISGs decrease upon differentiation, at which time cells become IFN responsive, allowing induction of a broad spectrum of ISGs by IFN signaling. Importantly, we show that intrinsically expressed ISGs protect stem cells against viral infection. We demonstrate the in vivo importance of intrinsic ISG expression for protecting stem cells and their differentiation potential during viral infection. These findings have intriguing implications for understanding stem cell biology and the evolution of pathogen resistance.
Nature 2017 MAY
Haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells.
Abstract
Abstract
A variety of tissue lineages can be differentiated from pluripotent stem cells by mimicking embryonic development through stepwise exposure to morphogens, or by conversion of one differentiated cell type into another by enforced expression of master transcription factors. Here, to yield functional human haematopoietic stem cells, we perform morphogen-directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into haemogenic endothelium followed by screening of 26 candidate haematopoietic stem-cell-specifying transcription factors for their capacity to promote multi-lineage haematopoietic engraftment in mouse hosts. We recover seven transcription factors (ERG, HOXA5, HOXA9, HOXA10, LCOR, RUNX1 and SPI1) that are sufficient to convert haemogenic endothelium into haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells that engraft myeloid, B and T cells in primary and secondary mouse recipients. Our combined approach of morphogen-driven differentiation and transcription-factor-mediated cell fate conversion produces haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from pluripotent stem cells and holds promise for modelling haematopoietic disease in humanized mice and for therapeutic strategies in genetic blood disorders.