ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement
This product is recommended for:
• Research into the regulation of human naïve T cell differentiation and Th1 function
• Development of procedures to expand and polarize naïve T cells toward a Th1 subset
• Optimized for use with ImmunoCult™-XF T Cell Expansion Medium
• Supports significantly higher levels of memory T cells in comparison to competitor Th1 differentiation kit
• Supports up to 1.6X higher expansion of IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T cells in comparison to competitor Th1 differentiation kit
• Supplied as a 50X concentrate; after thawing and mixing, the tube contents can be added directly to medium
• Recombinant human interleukin 18 (IL-18)
• Mouse anti-human interleukin 4 (anti-IL-4)
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement | 10973 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet | ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement | 10973 | All | English |
Data
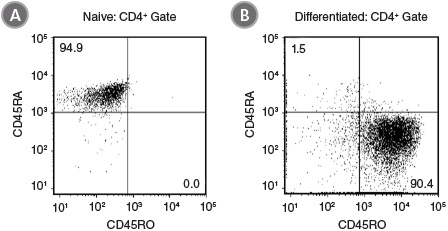
Figure 1. ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement Produces Differentiated CD4+CD45RA-CD45RO+ Cells Under Th1 Polarizing Conditions
Naïve CD4+ T cells were isolated from human peripheral blood samples using the EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19555). Cells were stimulated with ImmunoCult™ Human CD3/CD28 T Cell Activator (Catalog #10971) and ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement (Catalog #10973), cultured in ImmunoCult™-XF T Cell Expansion Medium (Catalog #10981) for 7 days. Shown are flow cytometry results of cell samples stained and analyzed for expression of CD45RA and CD45RO (A) before and (B) after 7 days of culture. After 7 days the majority of cells in culture display a memory T cell phenotype (CD45RA-CD45RO+).
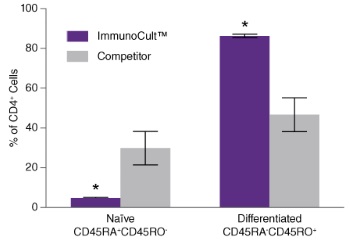
Figure 2. ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement Produces More Differentiated CD4+CD45RA-CD45RO+ Cells Under Th1 Polarizing Conditions Than Competitor
Naïve CD4+ T cells were isolated from human peripheral blood samples using the EasySep™ Human Naïve CD4+ T Cell Isolation Kit (Catalog #19555) and cultured with ImmunoCult™ Human CD3/CD28 T Cell Activator (Catalog #10971) and ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement (Catalog #10973) in ImmunoCult™ and differentiated (CD45RA-CD45RO+) cells after culture was compared after staining cells for CD45RA and CD45RO and analysis by flow cytometry. The percentage of cells expressing a naïve phenotype was significantly lower and the percentage of cells expressing a differentiated phenotype was significantly higher with ImmunoCult™ than with competitor medium and activator. Shown are the differences in the percentage of naïve and differentiated T cells in either ImmunoCult™ (purple) and competitor (grey) culture conditions (mean ± S.E.M.; *p < 0.05; paired t-test on logit transformed data; n = 4).
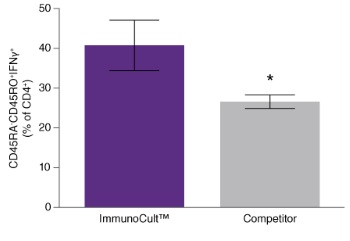
Figure 3. Culture with ImmunoCult™ Human Th1 Differentiation Supplement Produces More IFNγ-Expressing Cells Than Culture Under Competitor Conditions
Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured for 5 days in ImmunoCult™ activator, supplement and medium, or competitor medium and activator using the protocol described in Figure 2. After culture, differentiated CD4+ T cells (CD45RA-CD45RO+) were analyzed for IFNγ and IL-4 (not shown) expression, following stimulation with PMA and Ionomycin for 4 hours. A greater percentage of cells generated with ImmunoCult™ expressed intracellular IFNγ compared to those generated under competitor conditions, while no significant difference was found in the percentage of cells which expressed intracellular IL-4, with very low numbers of cells expressing IL-4 for both ImmunoCult™ and competitor. Shown are the differences in the percentage of naïve and differentiated T cells in either ImmunoCult™ (purple) and competitor (grey) culture conditions (mean ± S.E.M.; *p< 0.05; paired t-test on logit transformed data; n = 4).


