EpiCult™-B Human Medium Kit
For culture and evaluation of human mammary epithelial cells in CFU assays
概要
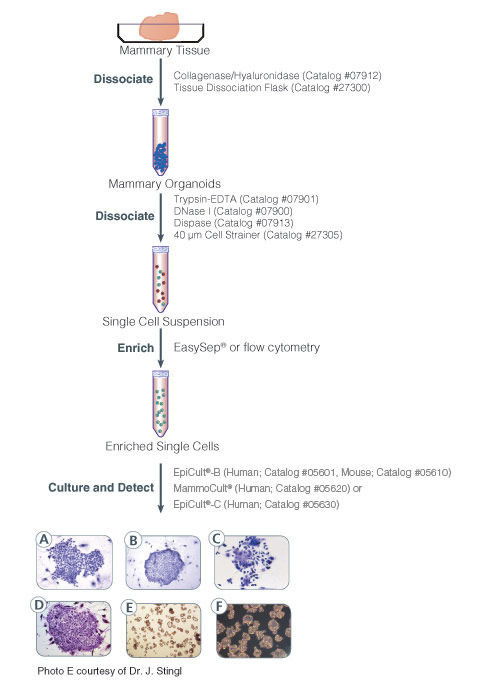
EpiCult™-B Human Medium Kit is a serum-free culture medium optimized for the culture of human mammary luminal and myoepithelial cells. It is ideal for the growth and evaluation of bipotent, luminal-restricted and myoepithelial-restricted mammary epithelial progenitor cells in the mammary colony-forming unit (CFU) assay when used in conjunction with an irradiated feeder layer such as NIH 3T3.
This kit contains EpiCult™-B Basal Medium (Human) and EpiCult™-B Proliferation Supplement (Human). Addition of Hydrocortisone Stock Solution (Catalog #07925) is required.
- EpiCult™-B Basal Medium (Human), 100 mL
- EpiCult™-B Proliferation Supplement (Human), 1 mL
Cell Culture, Colony Assay
数据及文献
Publications (9)
PloS one 2010 JAN
Molecular decoy to the Y-box binding protein-1 suppresses the growth of breast and prostate cancer cells whilst sparing normal cell viability.
Law JH et al.
Abstract
The Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) is an oncogenic transcription/translation factor that is activated by phosphorylation at S102 whereby it induces the expression of growth promoting genes such as EGFR and HER-2. We recently illustrated by an in vitro kinase assay that a novel peptide to YB-1 was highly phosphorylated by the serine/threonine p90 S6 kinases RSK-1 and RSK-2, and to a lesser degree PKCα and AKT. Herein, we sought to develop this decoy cell permeable peptide (CPP) as a cancer therapeutic. This 9-mer was designed as an interference peptide that would prevent endogenous YB-1(S102) phosphorylation based on molecular docking. In cancer cells, the CPP blocked P-YB-1(S102) and down-regulated both HER-2 and EGFR transcript level and protein expression. Further, the CPP prevented YB-1 from binding to the EGFR promoter in a gel shift assay. Notably, the growth of breast (SUM149, MDA-MB-453, AU565) and prostate (PC3, LNCap) cancer cells was inhibited by ∼90% with the CPP. Further, treatment with this peptide enhanced sensitivity and overcame resistance to trastuzumab in cells expressing amplified HER-2. By contrast, the CPP had no inhibitory effect on the growth of normal immortalized breast epithelial (184htert) cells, primary breast epithelial cells, nor did it inhibit differentiation of hematopoietic progenitors. These data collectively suggest that the CPP is a novel approach to suppressing the growth of cancer cells while sparing normal cells and thereby establishes a proof-of-concept that blocking YB-1 activation is a new course of cancer therapeutics.
Nature 2009 APR
Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stem cells.
Diehn M et al.
Abstract
The metabolism of oxygen, although central to life, produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) that have been implicated in processes as diverse as cancer, cardiovascular disease and ageing. It has recently been shown that central nervous system stem cells and haematopoietic stem cells and early progenitors contain lower levels of ROS than their more mature progeny, and that these differences are critical for maintaining stem cell function. We proposed that epithelial tissue stem cells and their cancer stem cell (CSC) counterparts may also share this property. Here we show that normal mammary epithelial stem cells contain lower concentrations of ROS than their more mature progeny cells. Notably, subsets of CSCs in some human and murine breast tumours contain lower ROS levels than corresponding non-tumorigenic cells (NTCs). Consistent with ROS being critical mediators of ionizing-radiation-induced cell killing, CSCs in these tumours develop less DNA damage and are preferentially spared after irradiation compared to NTCs. Lower ROS levels in CSCs are associated with increased expression of free radical scavenging systems. Pharmacological depletion of ROS scavengers in CSCs markedly decreases their clonogenicity and results in radiosensitization. These results indicate that, similar to normal tissue stem cells, subsets of CSCs in some tumours contain lower ROS levels and enhanced ROS defences compared to their non-tumorigenic progeny, which may contribute to tumour radioresistance.
Cell stem cell 2008 JUL
Transcriptome analysis of the normal human mammary cell commitment and differentiation process.
Raouf A et al.
Abstract
Mature mammary epithelial cells are generated from undifferentiated precursors through a hierarchical process, but the molecular mechanisms involved, particularly in the human mammary gland, are poorly understood. To address this issue, we isolated highly purified subpopulations of primitive bipotent and committed luminal progenitor cells as well as mature luminal and myoepithelial cells from normal human mammary tissue and compared their transcriptomes obtained using three different methods. Elements unique to each subset of mammary cells were identified, and changes that accompany their differentiation in vivo were shown to be recapitulated in vitro. These include a stage-specific change in NOTCH pathway gene expression during the commitment of bipotent progenitors to the luminal lineage. Functional studies further showed NOTCH3 signaling to be critical for this differentiation event to occur in vitro. Taken together, these findings provide an initial foundation for future delineation of mechanisms that perturb primitive human mammary cell growth and differentiation.
Nature medicine 2008 DEC
A method for quantifying normal human mammary epithelial stem cells with in vivo regenerative ability.
Eirew P et al.
Abstract
Previous studies have demonstrated that normal mouse mammary tissue contains a rare subset of mammary stem cells. We now describe a method for detecting an analogous subpopulation in normal human mammary tissue. Dissociated cells are suspended with fibroblasts in collagen gels, which are then implanted under the kidney capsule of hormone-treated immunodeficient mice. After 2-8 weeks, the gels contain bilayered mammary epithelial structures, including luminal and myoepithelial cells, their in vitro clonogenic progenitors and cells that produce similar structures in secondary transplants. The regenerated clonogenic progenitors provide an objective indicator of input mammary stem cell activity and allow the frequency and phenotype of these human mammary stem cells to be determined by limiting-dilution analysis. This new assay procedure sets the stage for investigations of mechanisms regulating normal human mammary stem cells (and possibly stem cells in other tissues) and their relationship to human cancer stem cell populations.
The Journal of biological chemistry 2006 NOV
The Wnt signaling receptor Lrp5 is required for mammary ductal stem cell activity and Wnt1-induced tumorigenesis.
Lindvall C et al.
Abstract
Canonical Wnt signaling has emerged as a critical regulatory pathway for stem cells. The association between ectopic activation of Wnt signaling and many different types of human cancer suggests that Wnt ligands can initiate tumor formation through altered regulation of stem cell populations. Here we have shown that mice deficient for the Wnt co-receptor Lrp5 are resistant to Wnt1-induced mammary tumors, which have been shown to be derived from the mammary stem/progenitor cell population. These mice exhibit a profound delay in tumorigenesis that is associated with reduced Wnt1-induced accumulation of mammary progenitor cells. In addition to the tumor resistance phenotype, loss of Lrp5 delays normal mammary development. The ductal trees of 5-week-old Lrp5-/- females have fewer terminal end buds, which are structures critical for juvenile ductal extension presumed to be rich in stem/progenitor cells. Consequently, the mature ductal tree is hypomorphic and does not completely fill the fat pad. Furthermore, Lrp5-/- ductal cells from mature females exhibit little to no stem cell activity in limiting dilution transplants. Finally, we have shown that Lrp5-/- embryos exhibit substantially impaired canonical Wnt signaling in the primitive stem cell compartment of the mammary placodes. These findings suggest that Lrp5-mediated canonical signaling is required for mammary ductal stem cell activity and for tumor development in response to oncogenic Wnt effectors.
Nature 2006 JAN
Generation of a functional mammary gland from a single stem cell.
Shackleton M et al.
Abstract
The existence of mammary stem cells (MaSCs) has been postulated from evidence that the mammary gland can be regenerated by transplantation of epithelial fragments in mice. Interest in MaSCs has been further stimulated by their potential role in breast tumorigenesis. However, the identity and purification of MaSCs has proved elusive owing to the lack of defined markers. We isolated discrete populations of mouse mammary cells on the basis of cell-surface markers and identified a subpopulation (Lin-CD29hiCD24+) that is highly enriched for MaSCs by transplantation. Here we show that a single cell, marked with a LacZ transgene, can reconstitute a complete mammary gland in vivo. The transplanted cell contributed to both the luminal and myoepithelial lineages and generated functional lobuloalveolar units during pregnancy. The self-renewing capacity of these cells was demonstrated by serial transplantation of clonal outgrowths. In support of a potential role for MaSCs in breast cancer, the stem-cell-enriched subpopulation was expanded in premalignant mammary tissue from MMTV-wnt-1 mice and contained a higher number of MaSCs. Our data establish that single cells within the Lin-CD29hiCD24+ population are multipotent and self-renewing, properties that define them as MaSCs.
View All Publications