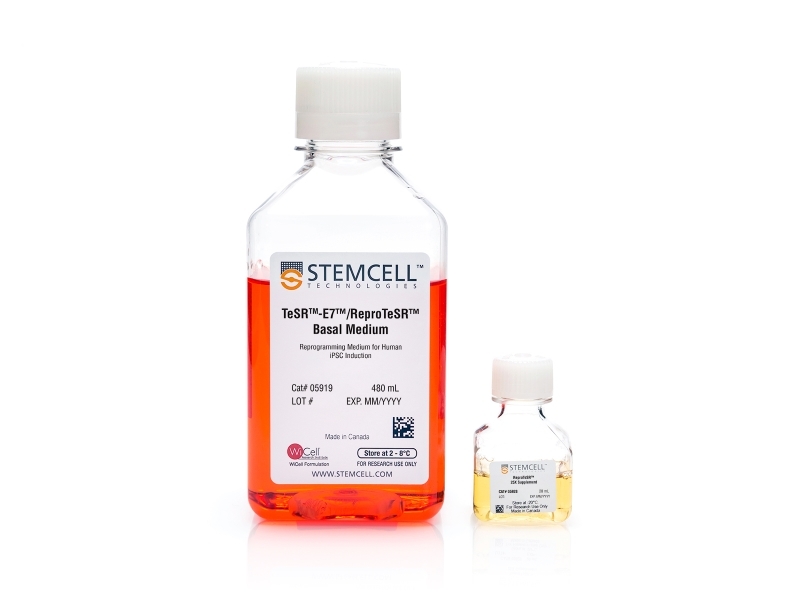
ReproTeSR™ Medium for Reprogramming (2-Component)
ReproTeSR™ (2-Component) is a complete and xeno-free reprogramming medium developed for generating human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells from fibroblasts, urine-derived cells, and blood-derived cells such as CD34+ or erythroid precursor cells under feeder-free conditions.
ReproTeSR™ is also available as part of an integrated set of tools that are optimized for reprogramming blood-derived cell types expanded in vitro from peripheral blood, such as CD34+ cells (CD34+ Progenitor Reprogramming Kit, Catalog #05925) or erythroid cells (Erythroid Progenitor Reprogramming Kit, Catalog #05924).
• Rapid emergence of large colonies with high-quality iPS cell-like morphology facilitates identification and subcloning for easily establishing iPS cell lines
• Seamlessly integrates with STEMCELL products prior to reprogramming and after iPS cell generation for maintenance and differentiation
Scientific Resources
Product Documentation
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | ReproTeSR™ Medium for Reprogramming (2-Component) | 05926 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | ReproTeSR™ Medium for Reprogramming (2-Component) | 05926 | 全部 | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | ReproTeSR™ Medium for Reprogramming (2-Component) | 05926 | 全部 | English |
相关产品
Educational Materials (8)
Product Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Data and Publications
数据
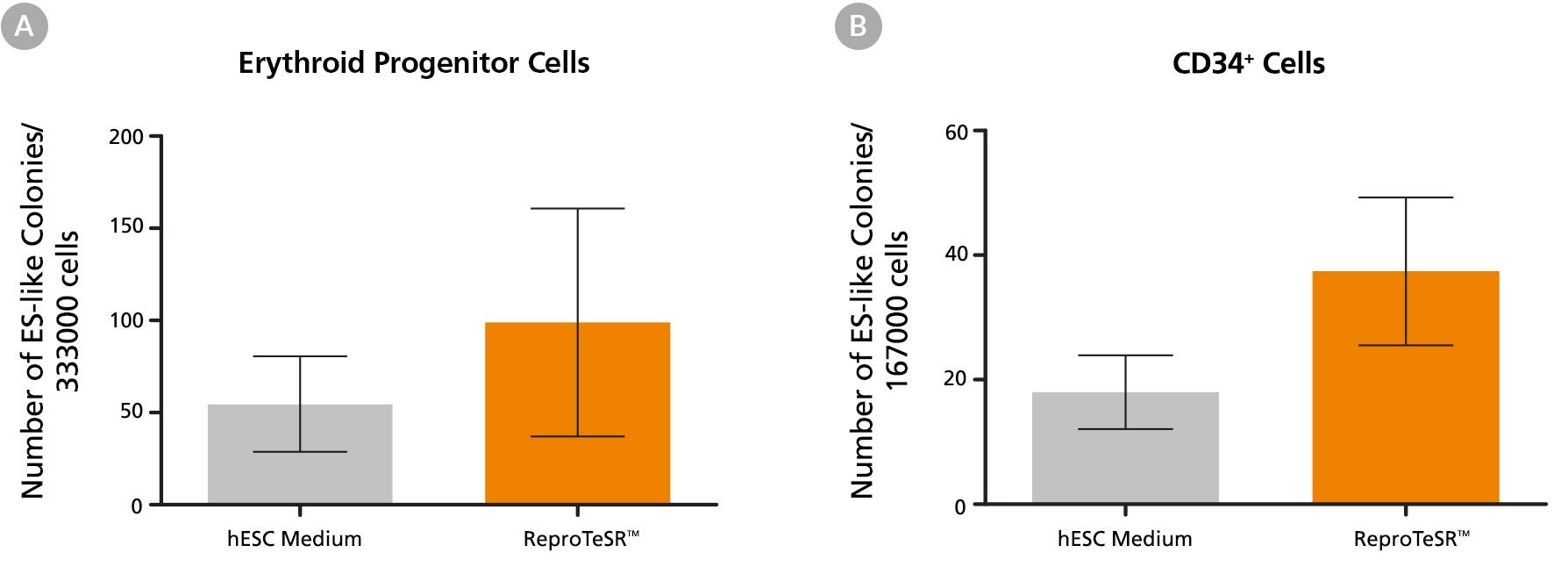
Figure 1. Blood Cell Reprogramming Efficiencies Are Higher in ReproTeSR™ Medium Compared to in hESC Medium
Efficiency of reprogramming (A) erythroid cells or (B) CD34+ cells using episomal reprogramming vectors is higher in ReproTeSR™ medium compared to in KOSR-containing hESC medium. Data shown are mean /- SEM; erythroid cells, n=4; CD34 cells, n=5.
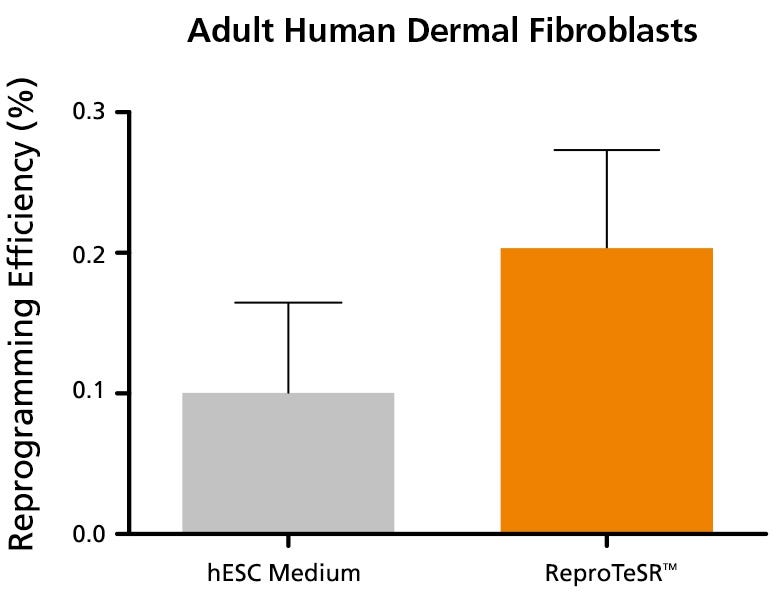
Figure 2. ReproTeSR™ Efficiently Reprograms Fibroblasts
Dermal fibroblasts were transfected with the ReproRNA™-OKSGM vector and reprogrammed under feeder-dependent (standard KOSR-containing hES cell medium on inactivated mouse embryonic fibroblasts (iMEFs)) or feeder-independent conditions (ReproTeSR™ on Corning® Matrigel®). Fibroblasts (passage 4) were reprogrammed with average efficiencies of 0.10 ± 0.06% (hES cell medium) and 0.20 ± 0.07% (ReproTeSR™). Reprogramming efficiency of fibroblasts with ReproRNA™ and ReproTeSR™ is comparable to that reported with Sendai virus. (Schlaeger TM, et al. (2015) Nat Biotechnol 33(1): 58-63.) (n ≥ 6; Data shown are mean ± SD).
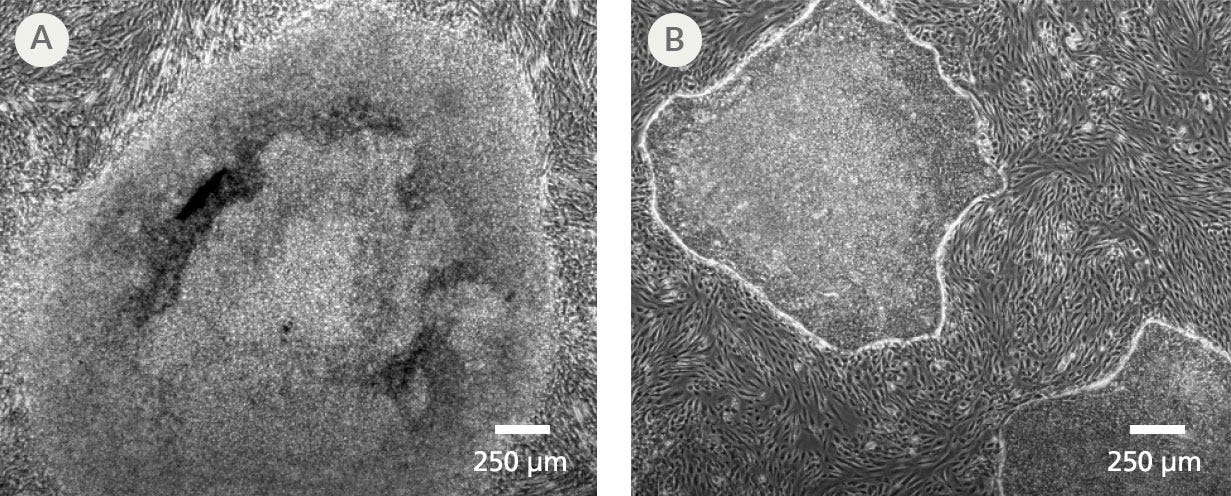
Figure 3. Feeder-Free Reprogramming with ReproRNA™-OKSGM Vector and ReproTeSR™ Generates iPS Cell Colonies with Superior Colony Morphology
Representative images of iPS cell colonies were generated using ReproRNA™‑OKSGM and cultured in (A) standard hES cell medium on irradiated mouse embryonic fibroblasts (iMEFs) or (B) ReproTeSR™ on Corning® Matrigel®. iPS cell colonies derived using ReproTeSR™ exhibit more defined borders, compact morphology, and reduced differentiation as compared to the ES cell medium.