PancreaCult™ Organoid Media (Human)
PancreaCult™ (Human) culture medium system provides a complete and robust workflow to establish, expand, and maintain pancreatic duct organoids. Pancreatic organoids are established from fresh or cryopreserved islet-depleted exocrine fractions in PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (OIM), which is optimized to provide higher rates of organoid formation from tissue. These organoids are then transferred to PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (OGM) for long-term maintenance and passaging of pancreatic organoids, or for cryopreservation for future experiments. Organoids grown using the PancreaCult™ (Human) medium system can be adapted to various culture protocols, including two-dimensional Transwell® monolayer cultures, dilute Corning® Matrigel® suspension cultures, and highthroughput assay-compatible culture formats.
• Enables efficient organoid initiation and expansion across different pancreatic donor tissues
• Flexible growth medium allow expansion of normal and tumor-derived organoids
• Serum-free and conditioned medium-free
- PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (Human) (Catalog #100-0820)
- PancreaCult™ Organoid Basal Medium (Human) , 95 mL
- PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Supplement (Human), 5 mL
- Organoid Supplement, 50 mL
- PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human) (Catalog #100-0781)
- PancreaCult™ Organoid Basal Medium (Human) , 95 mL
- PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Supplement (Human), 5 mL
Scientific Resources
Product Documentation
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (Human) | 100-0820 | All | English |
| Product Information Sheet | PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human) | 100-0781 | All | English |
| Manual | PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human) | 100-0781 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (Human) | 100-0820 | 全部 | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (Human) | 100-0820 | 全部 | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (Human) | 100-0820 | 全部 | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human) | 100-0781 | 全部 | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | PancreaCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human) | 100-0781 | 全部 | English |
Product Applications
Data and Publications
数据
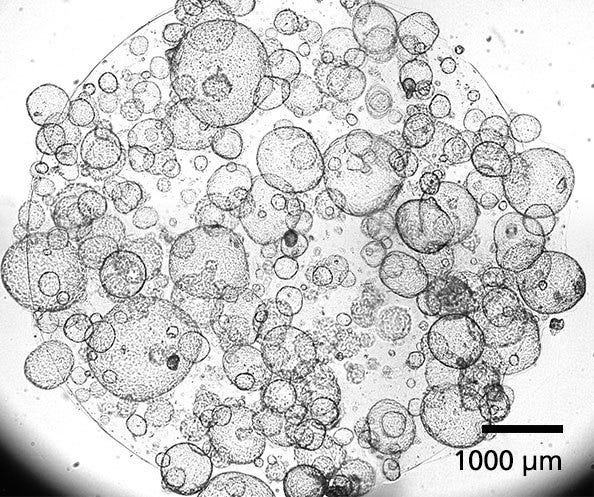
Figure 1. Human Pancreatic Duct Organoids
PancreaCult™ Organoid Initiation Medium (OIM; Human) and Organoid Growth Medium (OGM; Human) support the initiation and expansion of human pancreatic duct organoids from pancreatic tissue or previously established organoid cultures. Shown are organoids grown using PancreaCult™ OIM and OGM and imaged on day 7 of passage 3.
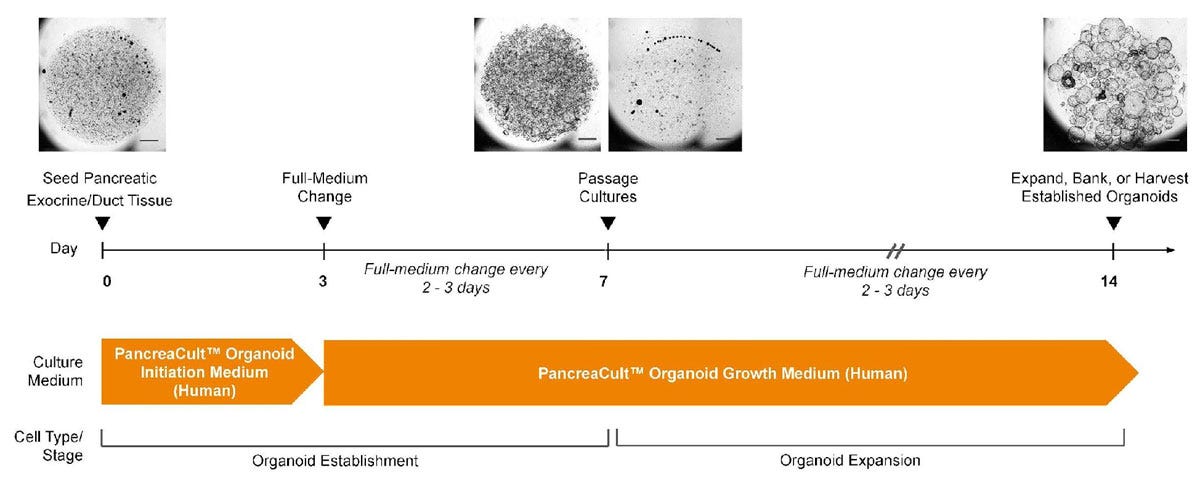
Figure 2. PancreaCult™ Human Enables Initiation and Expansion of Pancreatic Ductal Organoids
Human pancreatic ductal organoids are initiated in PancreaCult™ OIM for the first 3 days of culture, then switched to PancreaCult™ OGM for the remainder of culture. Alternatively, organoids can be grown in PancreaCult™ OGM for a completely serum-free protocol, however, proliferative pancreatic ductal cells are better supported in PancreaCult™ OIM during the first 3 days of culture. Cultures should be passaged after 7 days with further medium changes every 2-3 days. Pancreatic ductal organoids are suitable for experimentation or banking after one full passage in PancreaCult™ OGM. For full culture instructions please refer to the product manual (Document #10000011617)
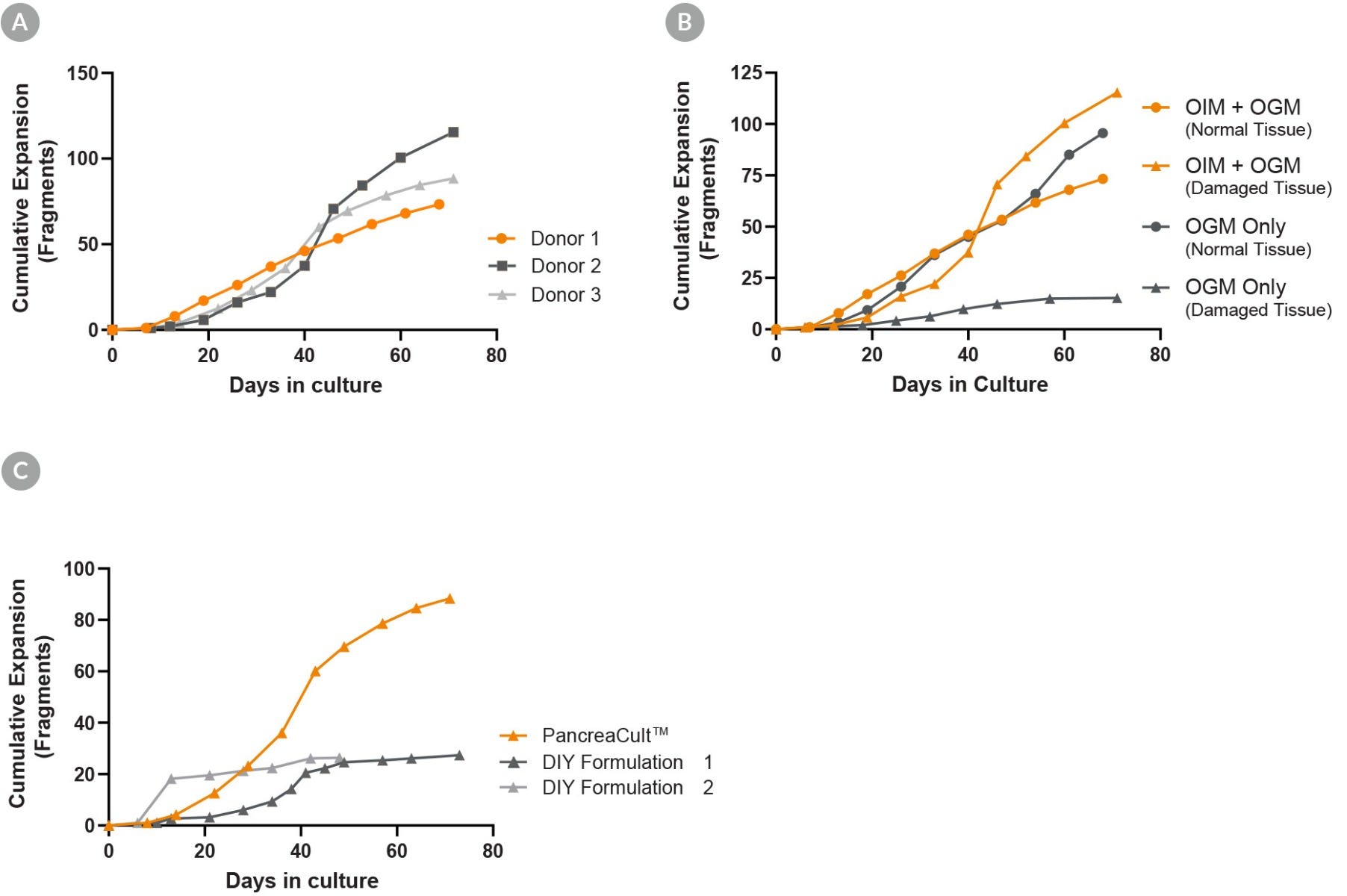
Figure 3. PancreaCult™ (Human) Provides Robust Expansion of Pancreatic Duct Organoids
(A) Organoid expansion in PancreaCult™ OGM provides robust expansion of organoids across different donors. (B) Organoids may be initiated in PancreaCult™ OGM for a completely serum-free workflow, however, initiation and maintenance of damaged tissue is better supported by initiating cultures in PancreaCult™ OIM. (C) Comparison of PancreaCult™ Human to two different DIY formulations showed more robust expansion of organoids in PancreaCult™ Human. Shown is the cumulative fold expansion of organoid fragments as counted at the end of each passage.
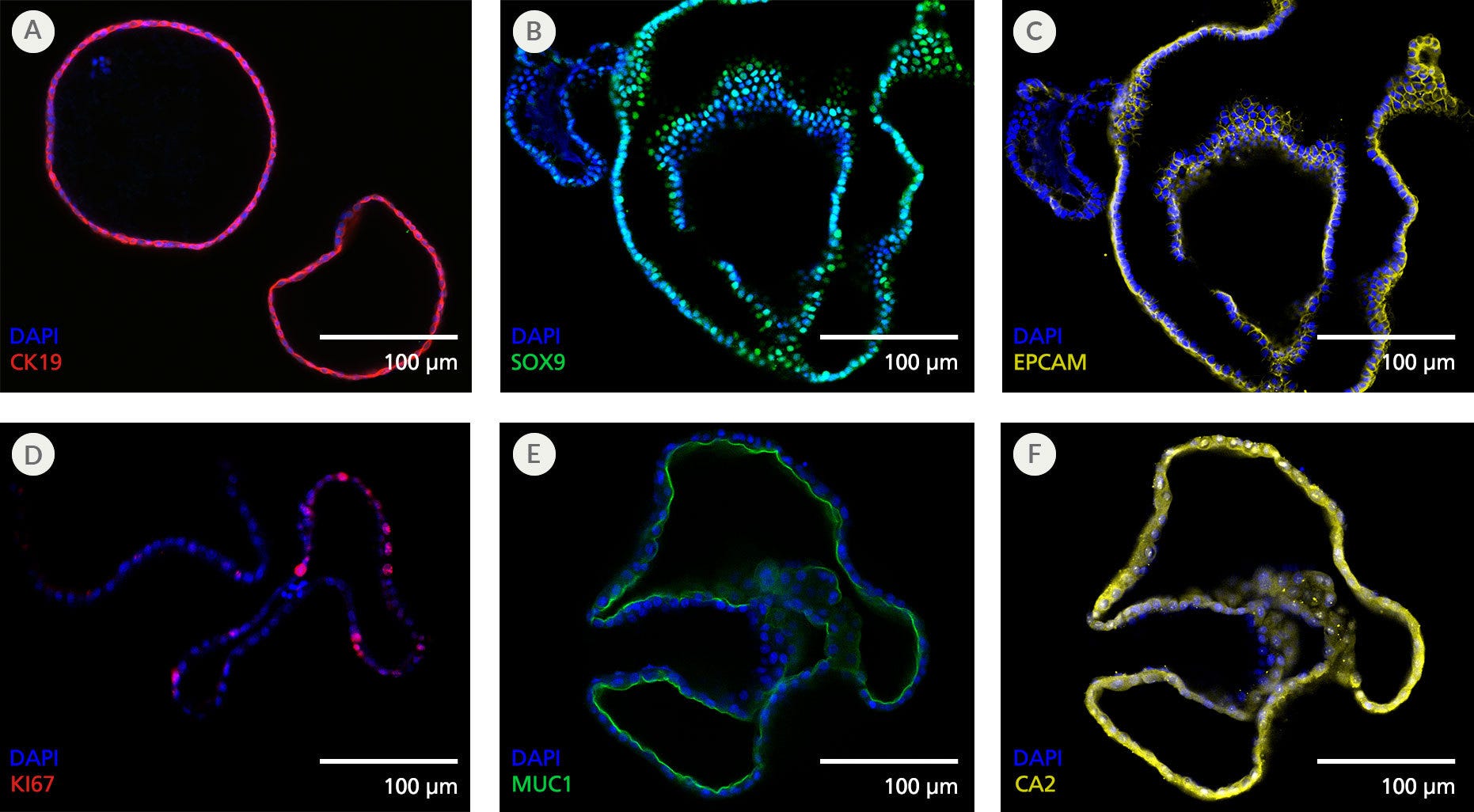
Figure 4. Pancreatic Duct Organoids Display Features of the Pancreatic Ductal Epithelium
Organoids grown using the PancreaCult™ (Human) display marker expression consistent with the pancreatic ductal epithelium when imaged using immunocytochemistry. Shown are organoids grown in PancreaCult™ OGM and stained for (A) pancreatic ductal marker CK19, (B) pancreatic ductal marker SOX9, (C) epithelial marker EPCAM, (D) proliferation marker KI67, (E) apical pancreatic duct marker MUC1, and (F) pancreatic ductal marker CA2. Organoids were imaged on passage 2 (A), passage 3 (B, C) or passage 10 (D-F).
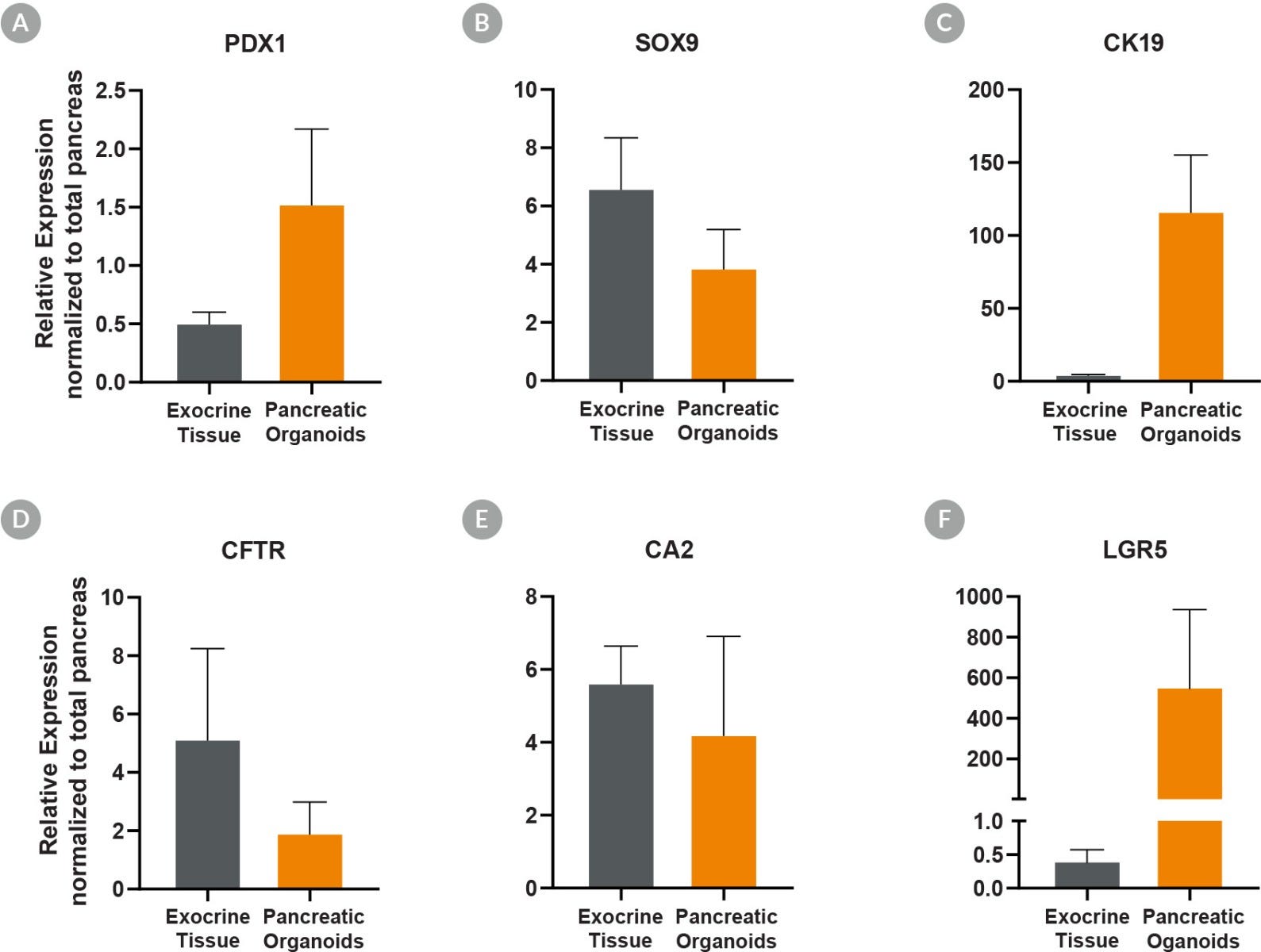
Figure 5. Pancreatic Duct Organoids Cultured With PancreaCult™ Human Show Pancreatic Marker Expression Levels Similar to Exocrine Tissue
Pancreatic duct organoids grown using the PancreaCult™ Human show marker expression levels similar to those observed in exocrine tissue. Analysis by qPCR showed pancreatic duct organoids were enriched for (A) PDX1 (C) CK19 and (F) LGR5 as compared to total pancreatic tissue, demonstrating enrichment of proliferative duct organoids. Comparable expression of (B) SOX9, (D) cystic fibrosis transmembrane receptor (CFTR), and (E) CA2 was observed in pancreatic duct organoids. Expression levels are normalized to TBP and UBC housekeeping genes (ΔCT) and total pancreas for relative expression levels (ΔΔCT).
Legal Statement:
This product was developed under a license to intellectual property owned by HUB Organoids (HUB). This product is sold for research use only. Purchase of this product does not include the right to use this product for growing organoids for drug screening aiming for commercial gain or for other commercial purposes. Purchasers wishing to use the product for purposes other than research use should contact HUB to obtain a further license (an “Organoid-Growth License”). Purchasers may apply for an Organoid-Growth License from HUB and such license will not be unreasonably withheld by HUB.
Quality Statement:
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL