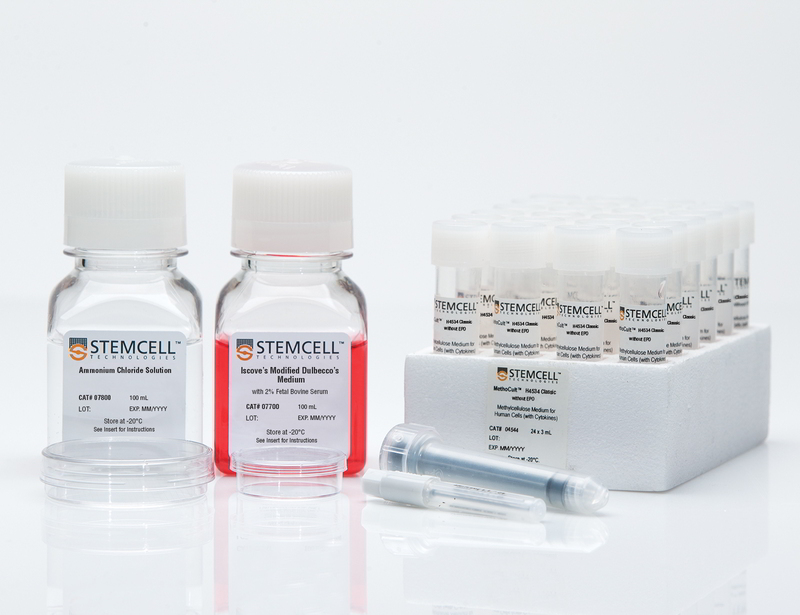
Starter Kit for MethoCult™ H4534 Classic Without EPO
Complete kit for hematopoietic CFU assays
概要
The Starter Kit for MethoCult™ H4534 Classic without EPO (MethoCult™ GF H4534) is recommended for laboratories in the initial stages of establishing procedures for assessing human hematopoietic progenitor cells using colony-forming unit (CFU) assays. These products support the growth of clonogenic hematopoietic progenitor cells from human bone marrow, peripheral blood, cord blood, leukapheresis products, and purified progenitor-enriched cells. H4534 without EPO is a complete methylcellulose-based medium that supports the growth of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (CFU-GM, CFU-G and CFU-M). Each kit contains instructional materials in addition to all reagents and materials necessary to perform 24 duplicate assays.
Browse our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on performing the CFU assay and explore its utility as part of the cell therapy workflow.
Browse our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on performing the CFU assay and explore its utility as part of the cell therapy workflow.
Components
- Starter Kit for MethoCult™ H4534 Classic without EPO (Catalog #4564)
- MethoCult™ H4534 Classic without EPO, 24 x 3 mL tubes (Catalog #04544)
- Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's Medium (IMDM) with 2% Fetal Bovine Serum, 100 mL (Catalog #07700)
- Ammonium Chloride Solution, 100 mL (Catalog #07800)
- 35 mm Culture Dishes, 10/pack (Catalog #27100)
- 60 mm Gridded Scoring Dishes, 20/pack (Catalog #100-0085)
- Blunt-End Needles, 30/bag (Catalog #28130)
- 3 cc Syringes, 30/bag (Catalog #28230)
- Colony Atlas (Catalog #28700)
Subtype
Semi-Solid Media, Specialized Media
Cell Type
Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Species
Human, Non-Human Primate
Application
Cell Culture, Colony Assay, Functional Assay
Brand
MethoCult
Area of Interest
Stem Cell Biology
技术资料
数据及文献
Data
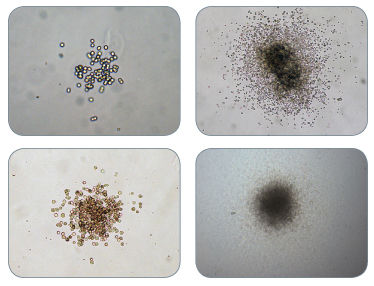
Figure 1. Examples of Colonies Derived From CFU-GM
Publications (13)
Circulation. Cardiovascular interventions 2011 FEB
Intraarterial administration of bone marrow mononuclear cells in patients with critical limb ischemia: a randomized-start, placebo-controlled pilot trial (PROVASA).
Abstract
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Critical limb ischemia due to peripheral arterial occlusive disease is associated with a severely increased morbidity and mortality. There is no effective pharmacological therapy available. Injection of autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells (BM-MNC) is a promising therapeutic option in patients with critical limb ischemia, but double-blind, randomized trials are lacking. METHODS AND RESULTS: Forty patients with critical limb ischemia were included in a multicenter, phase II, double-blind, randomized-start trial to receive either intraarterial administration of BM-MNC or placebo followed by active treatment with BM-MNC (open label) after 3 months. Intraarterial administration of BM-MNC did not significantly increase ankle-brachial index and, thus, the trial missed its primary end point. However, cell therapy was associated with significantly improved ulcer healing (ulcer area, 3.2±4.7 cm(2) to 1.89±3.5 cm(2) [P=0.014] versus placebo, 2.92±3.5 cm(2) to 2.89±4.1 cm(2) [P=0.5]) and reduced rest pain (5.2±1.8 to 2.2±1.3 [P=0.009] versus placebo, 4.5±2.4 to 3.9±2.6 [P=0.3]) within 3 months. Limb salvage and amputation-free survival rates did not differ between the groups. Repeated BM-MNC administration and higher BM-MNC numbers and functionality were the only independent predictors of improved ulcer healing. Ulcer healing induced by repeated BM-MNC administration significantly correlated with limb salvage (r=0.8; Ptextless0.001). CONCLUSIONS: Intraarterial administration of BM-MNC is safe and feasible and accelerates wound healing in patients without extensive gangrene and impending amputation. These exploratory findings of this pilot trial need to be confirmed in a larger randomized trial in patients with critical limb ischemia and stable ulcers.
Blood 2007 SEP
AZD1152, a novel and selective aurora B kinase inhibitor, induces growth arrest, apoptosis, and sensitization for tubulin depolymerizing agent or topoisomerase II inhibitor in human acute leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo.
Abstract
Abstract
Aurora kinases play an important role in chromosome alignment, segregation, and cytokinesis during mitosis. We have recently shown that hematopoietic malignant cells including those from acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) aberrantly expressed Aurora A and B kinases, and ZM447439, a potent inhibitor of Aurora kinases, effectively induced growth arrest and apoptosis of a variety of leukemia cells. The present study explored the effect of AZD1152, a highly selective inhibitor of Aurora B kinase, on various types of human leukemia cells. AZD1152 inhibited the proliferation of AML lines (HL-60, NB4, MOLM13), ALL line (PALL-2), biphenotypic leukemia (MV4-11), acute eosinophilic leukemia (EOL-1), and the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells with an IC50 ranging from 3 nM to 40 nM, as measured by thymidine uptake on day 2 of culture. These cells had 4N/8N DNA content followed by apoptosis, as measured by cell-cycle analysis and annexin V staining, respectively. Of note, AZD1152 synergistically enhanced the antiproliferative activity of vincristine, a tubulin depolymerizing agent, and daunorubicin, a topoisomerase II inhibitor, against the MOLM13 and PALL-2 cells in vitro. Furthermore, AZD1152 potentiated the action of vincristine and daunorubicin in a MOLM13 murine xenograft model. Taken together, AZD1152 is a promising new agent for treatment of individuals with leukemia. The combined administration of AZD1152 and conventional chemotherapeutic agent to patients with leukemia warrants further investigation.
European heart journal 2007 MAR
Cell isolation procedures matter: a comparison of different isolation protocols of bone marrow mononuclear cells used for cell therapy in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Abstract
Abstract
AIM: The recently published REPAIR-AMI and ASTAMI trial showed differences in contractile recovery of left ventricular function after infusion of bone marrow-derived cells in acute myocardial infarction. Since the trials used different protocols for cell isolation and storage (REPAIR-AMI: Ficoll, storage in X-vivo 10 medium plus serum; ASTAMI: Lymphoprep, storage in NaCl plus plasma), we compared the functional activity of BMC isolated by the two different protocols. METHODS AND RESULTS: The recovery of total cell number, colony-forming units (CFU), and the number of mesenchymal stem cells were significantly reduced to 77 +/- 4%, 83 +/- 16%, and 65 +/- 15%, respectively, when using the ASTAMI protocol compared with the REPAIR protocol. The capacity of the isolated BMC to migrate in response to stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) was profoundly reduced when using the ASTAMI cell isolation procedure (42 +/- 8% and 78 +/- 3% reduction in healthy and CAD-patient cells, respectively). Finally, infusion of BMC into a hindlimb ischaemia model demonstrated a significantly blunted blood-flow-recovery by BMC isolated with the ASTAMI protocol (54 +/- 6% of the effect obtained by REPAIR cells). Comparison of the individual steps identified the use of NaCl and plasma for cell storage as major factors for functional impairment of the BMC. CONCLUSION: Cell isolation protocols have a major impact on the functional activity of bone marrow-derived progenitor cells. The assessment of cell number and viability may not entirely reflect the functional capacity of cells in vivo. Additional functional testing appears to be mandatory to assure proper cell function before embarking on clinical cell therapy trials.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2006 APR
Cytoprotective doses of erythropoietin or carbamylated erythropoietin have markedly different procoagulant and vasoactive activities.
Abstract
Abstract
Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) is receiving increasing attention as a potential therapy for prevention of injury and restoration of function in nonhematopoietic tissues. However, the minimum effective dose required to mimic and augment these normal paracrine functions of erythropoietin (EPO) in some organs (e.g., the brain) is higher than for treatment of anemia. Notably, a dose-dependent risk of adverse effects has been associated with rhEPO administration, especially in high-risk groups, including polycythemia-hyperviscosity syndrome, hypertension, and vascular thrombosis. Of note, several clinical trials employing relatively high dosages of rhEPO in oncology patients were recently halted after an increase in mortality and morbidity, primarily because of thrombotic events. We recently identified a heteromeric EPO receptor complex that mediates tissue protection and is distinct from the homodimeric receptor responsible for the support of erythropoiesis. Moreover, we developed receptor-selective ligands that provide tools to assess which receptor isoform mediates which biological consequence of rhEPO therapy. Here, we demonstrate that rhEPO administration in the rat increases systemic blood pressure, reduces regional renal blood flow, and increases platelet counts and procoagulant activities. In contrast, carbamylated rhEPO, a heteromeric receptor-specific ligand that is fully tissue protective, increases renal blood flow, promotes sodium excretion, reduces injury-induced elevation in procoagulant activity, and does not effect platelet production. These preclinical findings suggest that nonerythropoietic tissue-protective ligands, which appear to elicit fewer adverse effects, may be especially useful in clinical settings for tissue protection.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2003 JAN
Engraftment capacity of umbilical cord blood cells processed by either whole blood preparation or filtration.
Abstract
Abstract
Umbilical cord blood (UCB) preparation needs to be optimized in order to develop more simplified procedures for volume reduction, as well as to reduce the amount of contaminating cells within the final stem cell transplant. We evaluated a novel filter device (StemQuick((TM))E) and compared it with our routine buffy coat (BC) preparation procedure for the enrichment of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs). Two groups of single or pooled UCB units were filtered (each n = 6), or equally divided in two halves and processed by filtration and BC preparation in parallel (n = 10). The engraftment capacity of UCB samples processed by whole blood (WB) preparation was compared with paired samples processed by filtration in the nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse animal model. Filtration of UCB units in the two groups with a mean volume of 87.8 and 120.7 ml, respectively, and nucleated cell (NC) content of 9.7 and 23.8 x 10(8) resulted in a sufficient mean cell recovery for mononucleated cells ([MNCs] 74.2%-77.5%), CD34(+) cells (76.3%-79.0%), and colony-forming cells (64.1%-86.3%). Moreover, we detected a relevant depletion of the transplants for RBCs (89.2%-90.0%) and platelets ([PLTs] 77.5%-86.1%). In contrast, the mean depletion rate using BC processing proved to be significantly different for PLTs (10%, p = 0.03) and RBCs (39.6%, p textless 0.01). The NC composition showed a highly significant increase in MNCs and a decrease in granulocytes after filtration (p textless 0.01), compared with a less significant MNC increase in the BC group (p textless 0.05). For mice transplanted with WB-derived progenitors, we observed a mean of 15.3% +/- 15.5% of human CD45(+) cells within the BM compared with 19.9% +/- 16.8% for mice transplanted with filter samples (p = 0.03). The mean percentage of human CD34(+) cells was 4.2% +/- 3.1% for WB samples and 4.5% +/- 3.2% for filter samples (p = 0.68). As the data of NOD/SCID mice transplantation demonstrated a significant engraftment capacity of HPCs processed by filtration, no negative effect on the engraftment potential of filtered UCB cells versus non-volume-reduced cells from WB transplants was found. The StemQuick((TM))E filter devices proved to be a useful tool for Good Manufacturing Practices conform enrichment of HPCs and MNCs out of UCB. Filtration enables a quick and standardized preparation of a volume-reduced UCB transplant, including a partial depletion of granulocytes, RBCs, and PLTs without the need for centrifugation. Therefore, it seems very probable that filter-processed UCB transplants will also result in sufficient hematopoietic reconstitution in humans.
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2002 OCT
In vitro myelotoxicity of propanil and 3,4-dichloroaniline on murine and human CFU-E/BFU-E progenitors.
Abstract
Abstract
Because of the wide use of pesticides for domestic and industrial purposes, the evaluation of their potential effects is of major concern for public health. The myelotoxicity of the herbicide propanil (3,4-dichloroproprioanilide) and its metabolite 3,4-dichloroaniline (DCA) is well documented in mice, but evidence that pesticides may severely compromise hematopoiesis in humans is lacking. In this study, an interspecies comparison of in vitro toxicity of these two compounds on murine and human burst- and colony-forming unit-erythrocyte (BFU-E, CFU-E) and colony-forming unit-granulocyte/macrophage (CFU-GM) progenitors, has been carried out. Murine bone marrow progenitors and human cord blood cells were exposed to propanil or DCA in doses ranging from 10 micro M to 1000 micro M, and the toxic effect was detected by a clonogenic assay with continuous exposure to the compounds. The results on murine cells indicate that the erythrocytic lineage is the most sensitive target for propanil and DCA. On the other hand, human progenitors seem to be less sensitive to the toxic effects of both compounds than murine progenitors at the same concentrations (IC(50) values are 305.2 +/- 22.6 micro M [total erythroid colonies] and textgreater500 micro M [CFU-GM] for propanil). Propanil was significantly more toxic to human erythroid progenitors than to human CFU-GM progenitors, as was found for the murine cells, emphasizing the role of the heme pathway as the target for propanil. These data confirm the evidence that the compounds investigated interfere with erythroid colony formation at different stages of the differentiation pathway and have different effects according to the dose.