STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit
STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic - EB reagents are animal-component free and optimized for lymphoid differentiation potential. Using these reagents, CD34⁺ hematopoietic progenitor cells are first generated from PSCs; these can then be differentiated to NK cells using the StemSpan™ components.
⦁ Uniform generation of embryoid bodies
⦁ Robust generation of CD56+ NK cells across multiple ES and iPS cell lines
- STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic - EB Basal Medium, 120 mL
- STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic - EB Supplement A, 265 μL
- STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic - EB Supplement B, 7 mL
- StemSpan™ SFEM II, 100 mL (Catalog #09605)
- StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Supplement (10X), 5 mL (Catalog #09915)
- StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material (100X), 0.25 mL (Catalog #09925)
- StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Supplement (100X), 0.5 mL (Catalog #09950)
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Manual | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 4 | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 5 | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 6 | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 7 | STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit | 100-0170 | All | English |
Data
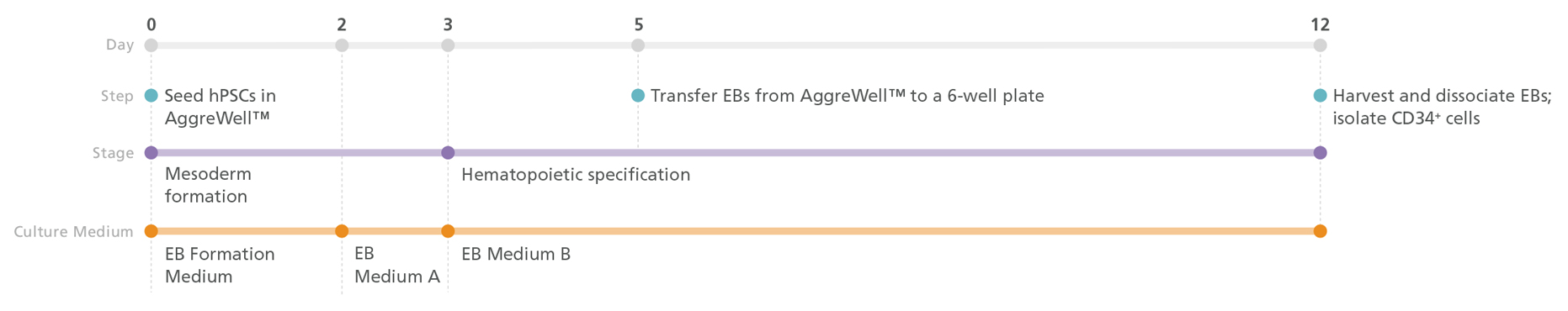
Figure 1. STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic-EB Progenitor Differentiation Protocol
PSCs are harvested and dissociated into a single-cell suspension prior to seeding into AggreWell™ plates in EB Formation Medium (EB Medium A +10 μM Y-27632) to form 500 cell aggregates. After 3 days of mesoderm formation, the medium is changed to EB Medium B to induce hematopoietic lineage differentiation. On day 5, embryoid bodies (EBs) are transferred onto non-tissue culture-treated plates. After a total of 12 days, the EBs are harvested and dissociated, then CD34+ cells are enriched by EasySep™ positive selection.
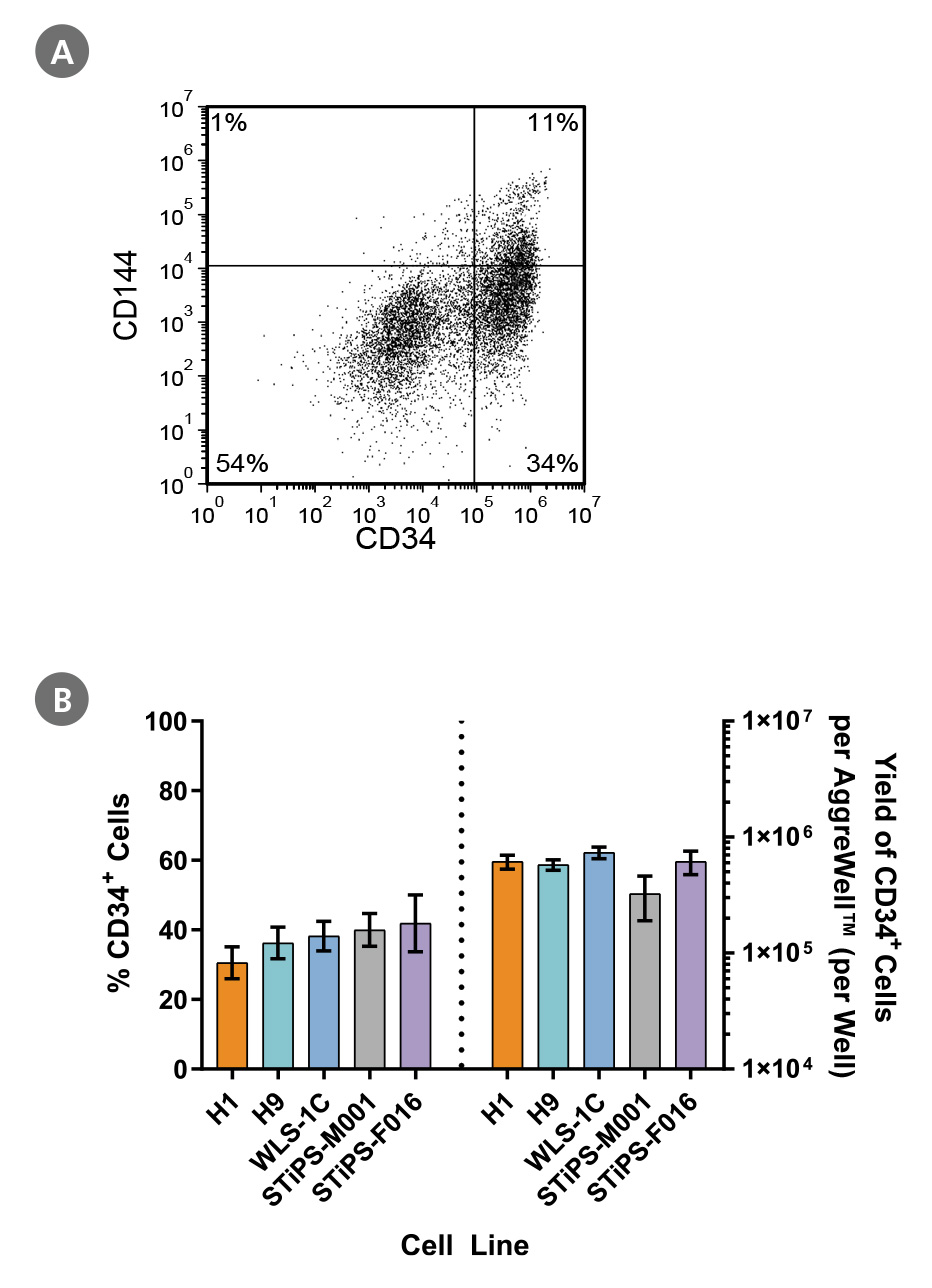
Figure 2. PSCs Differentiate to CD34+ Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells After 12 Days of Culture
Human ES and iPS cells were induced to differentiate to CD34+ cells using a 12-day protocol shown in Figure 1. At the end of the culture period, cells were harvested, dissociated into a single-cell suspension, and analyzed by flow cytometry for CD34 and CD144 expression. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and DRAQ7™ staining. (A) Representative flow cytometry plot for ES (H1)-derived cells analyzed on day 12. (B) The average frequency of viable CD34+ cells on day 12 for two ES cell lines (H1 and H9) and three iPS cell lines (WLS-1C, STiPS-M001, and STiPS-F016) ranged between 31% and 42%. The average yield of CD34+ cells produced per well of a 6-well AggreWell™400 plate ranged between 3.3 x 10^5 and 7.3 x 10^5. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7 - 22).
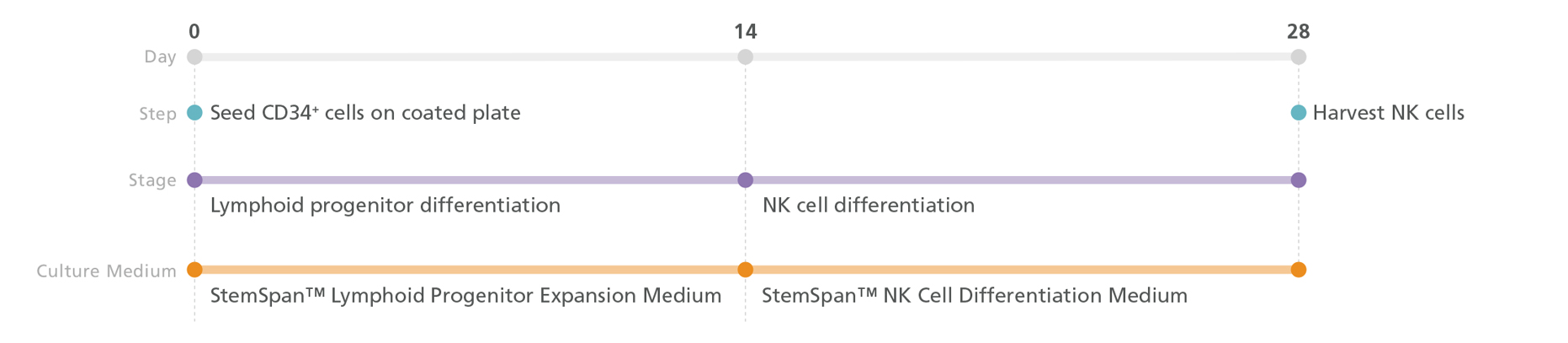
Figure 3. NK Cell Generation Protocol
PSC-derived CD34+ cells are seeded in StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Medium on plates coated with StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material. On day 14, cells at the lymphoid progenitor stage are harvested and reseeded in StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Medium for further differentiation into NK cells. Note: UM729 (not included in the kit) should be added to the StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Medium. NK cells are harvested after 28 days.
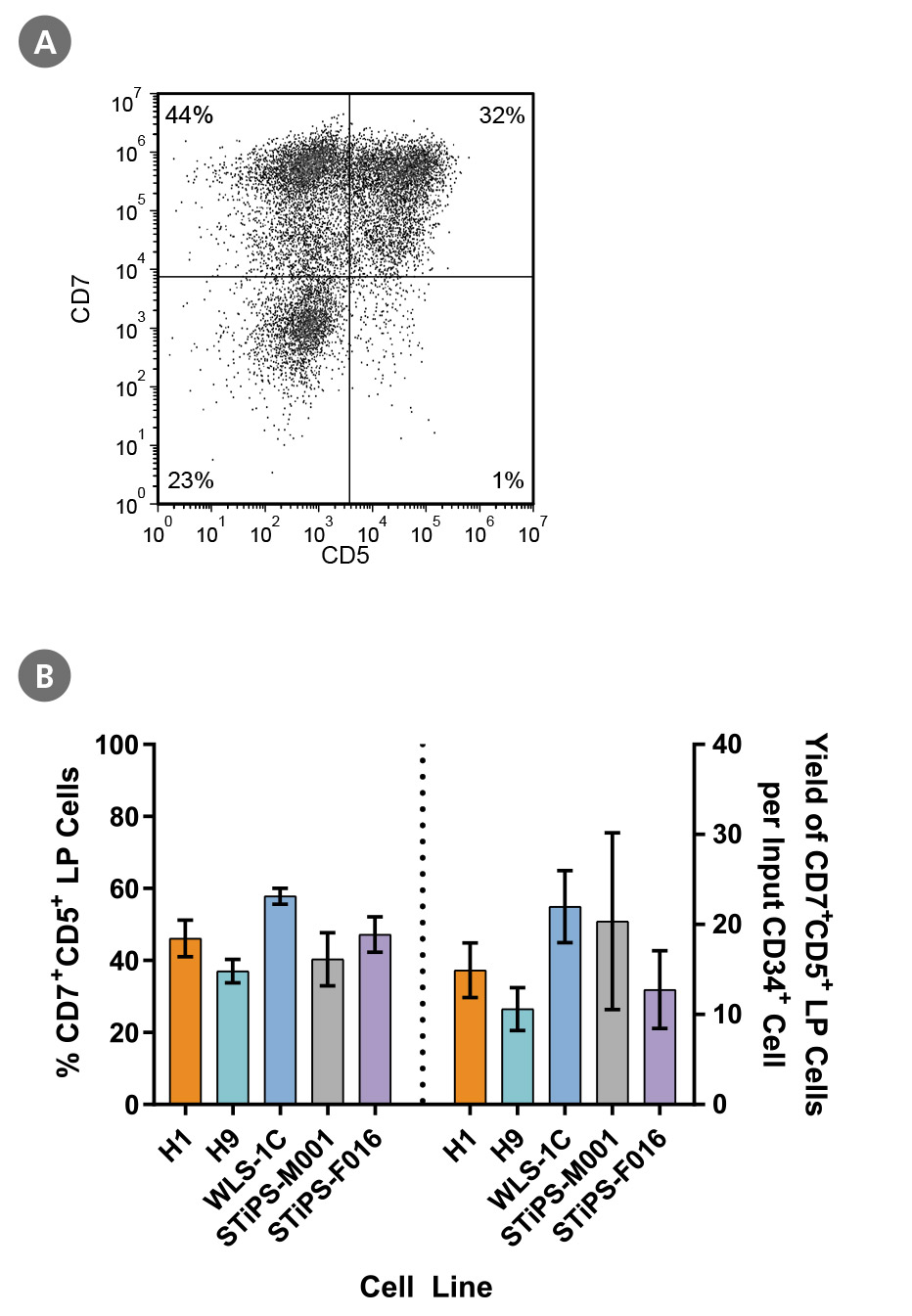
Figure 4. PSC-Derived CD34+ Cells Differentiate to CD5+CD7+ Lymphoid Progenitor Cells Over 14 Days of Culture
PSC-derived CD34+ cells were cultured for 14 days in StemSpan™ SFEM II + StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Supplement on plates coated with StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material (Figure 3). Cells were harvested and analyzed for CD7 and CD5 expression by flow cytometry. (A) Representative flow cytometry plot for ES (H1)-derived cells. (B) The average frequency of viable CD7+CD5+ lymphoid progenitor cells on day 14 ranged between 40% and 58% and the average yield of lymphoid progenitor cells produced per input PSC-derived CD34+ cell was between 11 and 22. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 5 - 21).
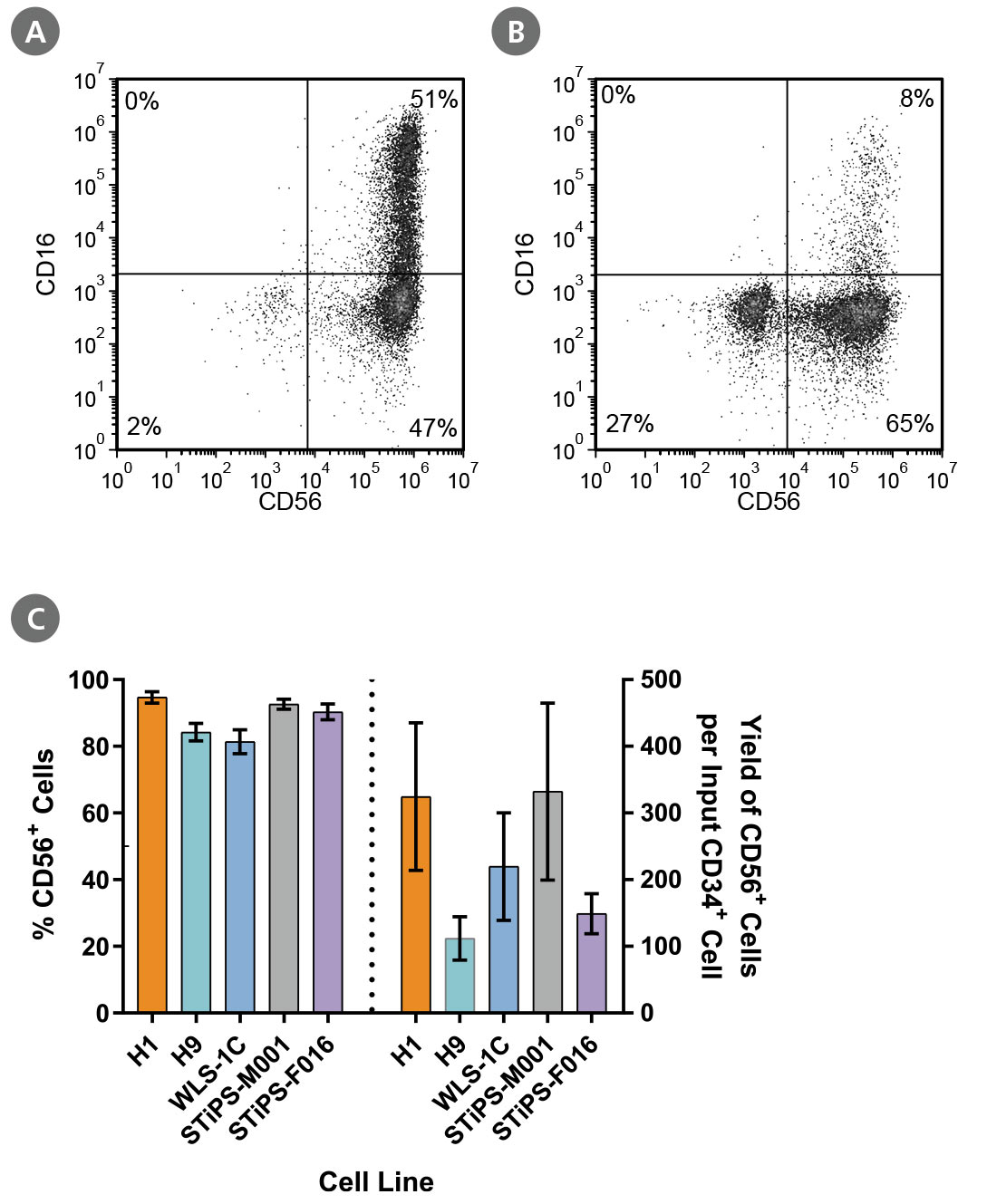
Figure 5. PSC-Derived Lymphoid Progenitor Cells Differentiate to CD56+ NK Cells After 14 Days of Culture
PSC-derived lymphoid progenitor cells were cultured in StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Medium on non-coated plates for 14 days. Cells were harvested and analyzed for expression of CD56 and CD16 by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry plots are shown for both (A) ES (H1)-derived and (B) iPS (WLS-1C)-derived cells. (C) After 28 days of culture, the average frequency of viable CD56+ NK cells from PSC-derived CD34+ cells ranged between 81% and 95%. The average yield of CD56+ cells produced per PSC-derived CD34+ cell was between 112 and 332. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 4 - 13).
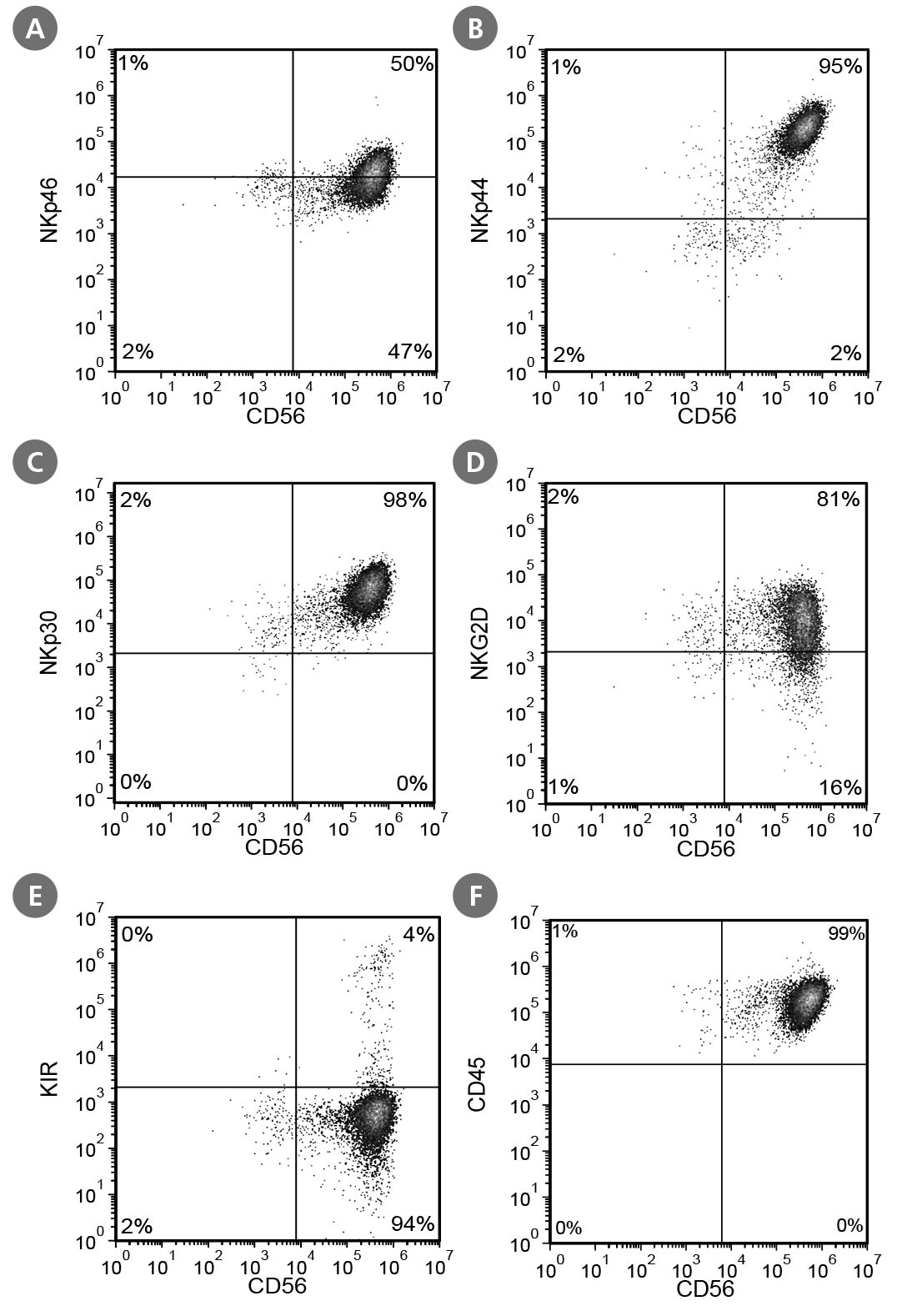
Figure 6. Cell Surface Marker Expression on PSC-Derived CD56+ NK Cells After 28 Days of Culture
PSC-derived CD34+ cells were cultured in StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Medium on plates coated with StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material for 14 days, followed by 14 days of culture in StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Medium on non-coated plates to generate CD56+ NK cells. Cells were harvested and analyzed for CD56, NKp46, NKp44, NKp30, NKG2D, KIR, and CD45 expression by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and DRAQ7™ staining. Data shown are from a representative culture initiated with ES (H1) cells.
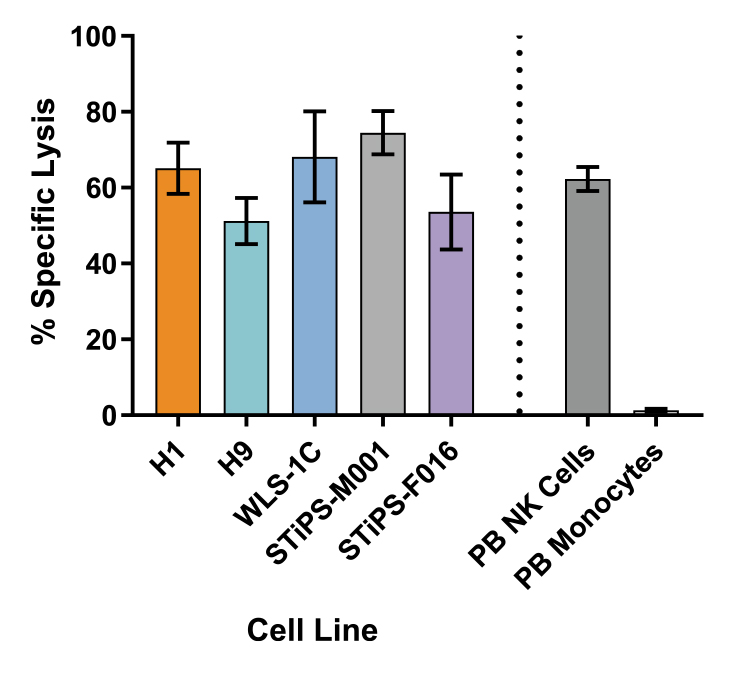
Figure 7. Cultured NK Cells Exhibit Cytotoxicity Toward K562 Cell Line
CD56+ NK cells were generated from PSC-derived CD34+ cells after 28 days of culture and then co-cultured with calcein AM (CAM)-labeled K562 cells at a ratio of 2.5:1 for 4 hours. Isolated peripheral blood (PB) NK cells and monocytes were also co-cultured with labeled K562 cells as positive and negative controls, respectively. Before the co-culture, frozen PB NK cells were thawed and cultured overnight with the NK Cell Differentiation Supplement and StemSpan™ SFEM II, while PB monocytes were cultured overnight in SFEM II only. To measure maximum release, the labeled K562 cells were treated with 1% Triton™ X-100. Culture supernatants were assessed for fluorescence released by dead cells after 4 hours using a SpectraMax® microplate reader (excitation 485 nm / emission 520 nm). The % specific lysis was calculated as follows: [(test release - spontaneous release) / (maximum release - spontaneous release)] X 100%. The average specific lysis by PSC-derived NK cells ranged between 51% and 75% as compared to 62% specific lysis by PB NK cells. Cultures of ES (H1 and H9) and iPS (WLS-1C, STiPS-M001, and STiPS-F016) cells are shown. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 - 7).