STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement Kit
⦁ PSC-derived myotubes display organized sarcomeric proteins and contractility
⦁ Optimized reagents designed to support the entire human PSC-derived myogenic progenitor workflow
- STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement A, 240 μL
- STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement B, 240 μL
- STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement C, 240 μL
- STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement D, 60 mL
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement Kit | 100-0151 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement Kit | 100-0151 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement Kit | 100-0151 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement Kit | 100-0151 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 4 | STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement Kit | 100-0151 | All | English |
Data
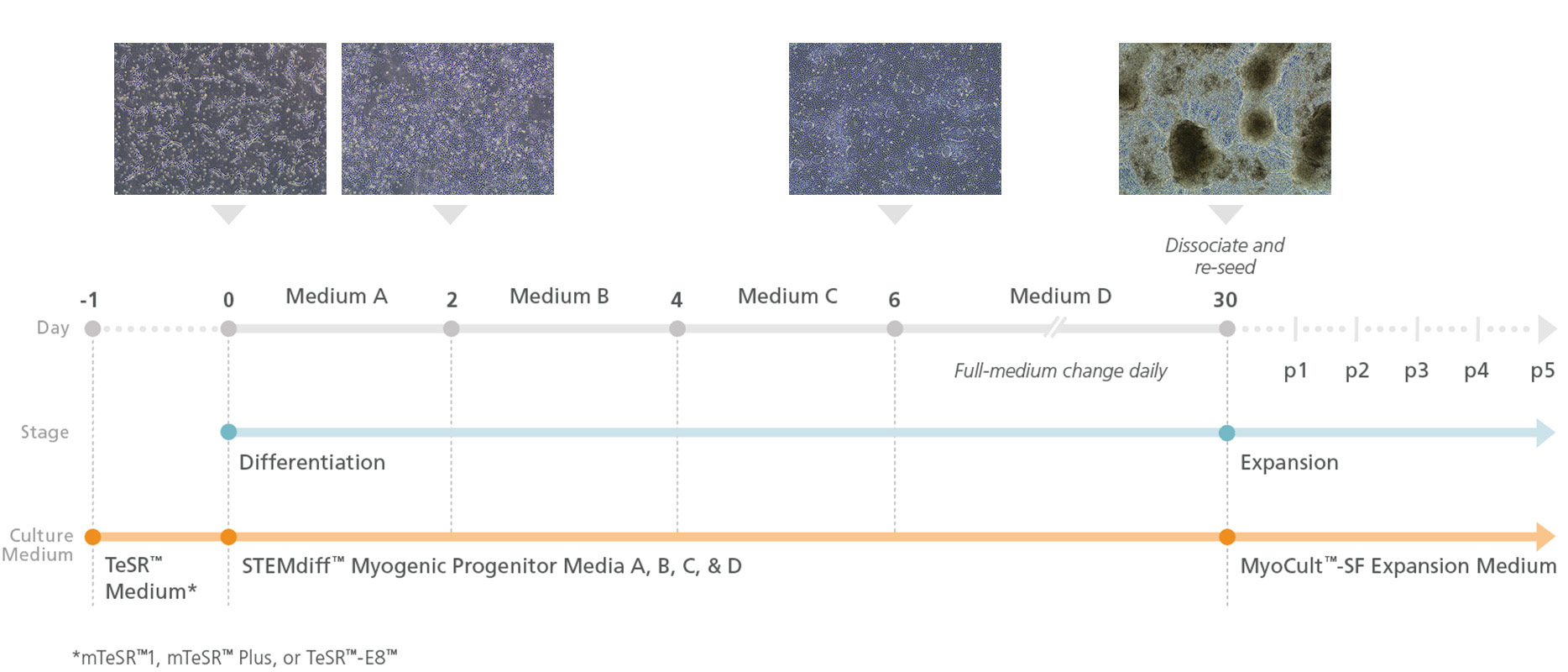
Figure 1. Schematic of Myogenic Induction Using the STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement Kit
Prior to differentiation (Day -1), human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are plated in Corning® Matrigel®-coated plates. On Day 0, differentiation is initiated and continued by performing daily media changes with STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement A at Days 0 - 2, STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement B at Days 2 - 4, STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement C at Days 4 - 6, and STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Supplement D for the remainder of the protocol (Days 6 - 30). Upon completion of the 30-day protocol, the culture contains an abundance of PAX7+MyoD+ myogenic progenitors that can be further expanded using MyoCult™-SF Expansion Supplement Kit (Human; Catalog #05980) for use in downstream applications.
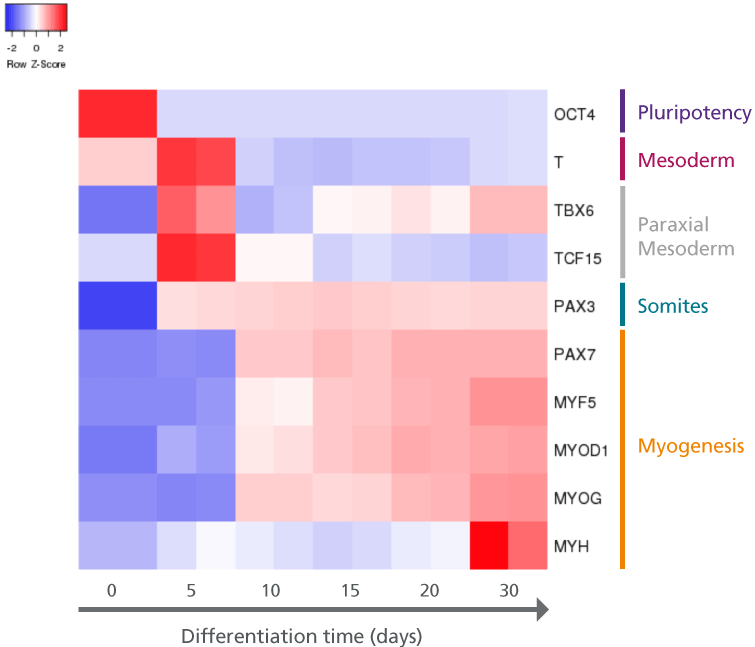
Figure 2. hPSCs Differentiated Using STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit Demonstrate Transcript Patterns of Embryonic Muscle Development
hPSCs (H9 cell line) were differentiated using the STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit and harvested at indicated time points for transcript analysis via qPCR; transcription was normalized against 18s as the housekeeping gene. The resulting heatmap indicates transcriptional changes to genes that mark specific stages of muscle development (mesoderm, paraxial mesoderm, somites, and myogenesis) and demonstrates a cellular trajectory that resembles embryonic muscle development.
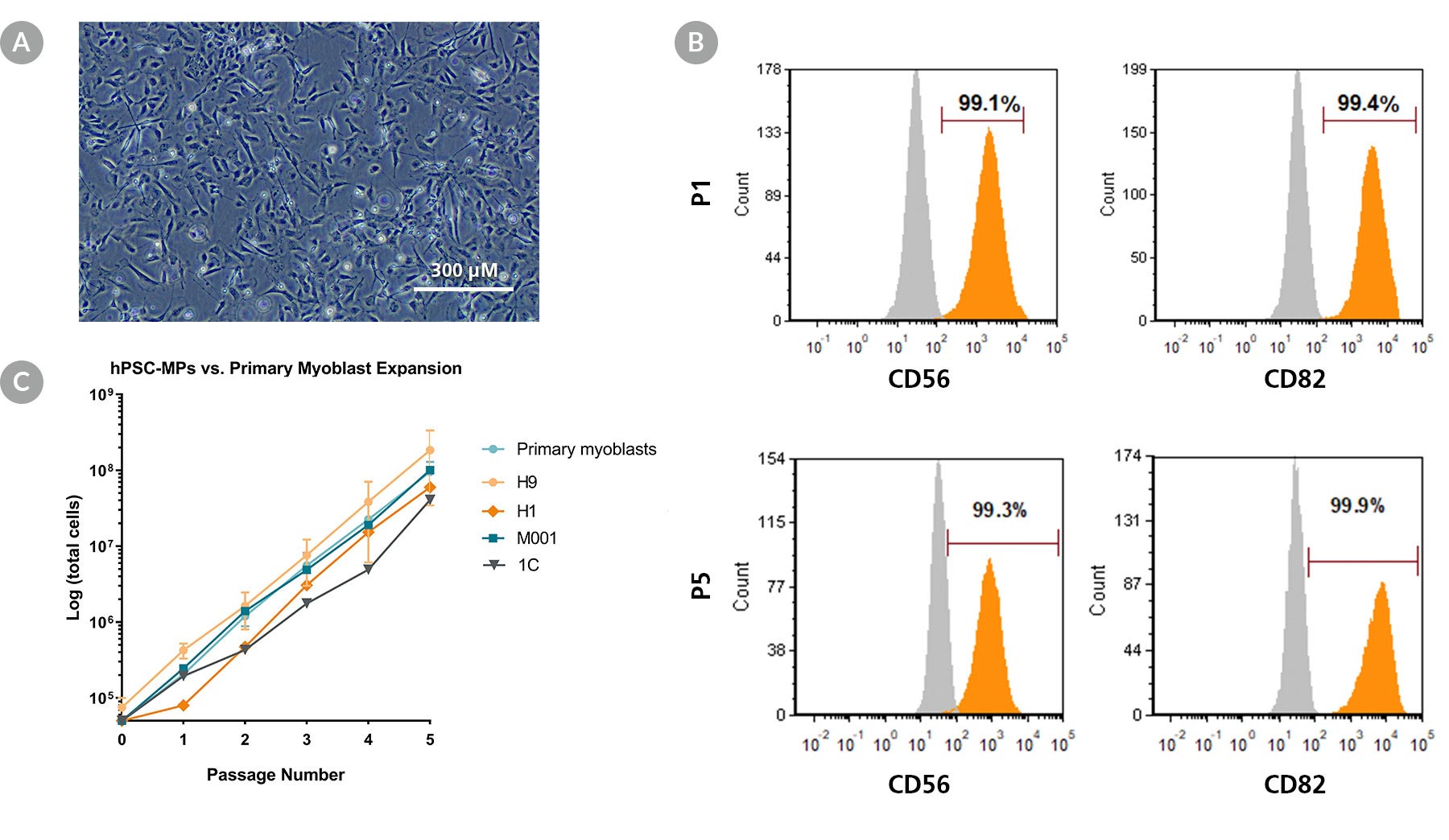
Figure 3. STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit Generates Expandable hPSC-Derived Myogenic Progenitors
(A) Representative image of proliferating sub-cultured hPSC-derived myogenic progenitors generated using the STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit. (B) hPSC-derived myogenic progenitors harvested at passage 1 and 5 expressed human myoblast markers CD56 and CD82. (C) Expansion rates of hPSC-derived myogenic progenitors (hSPC-MP) over 5 passages across multiple hPSC lines are comparable to human primary myoblasts. Error bars represent standard error of mean, n = 3.
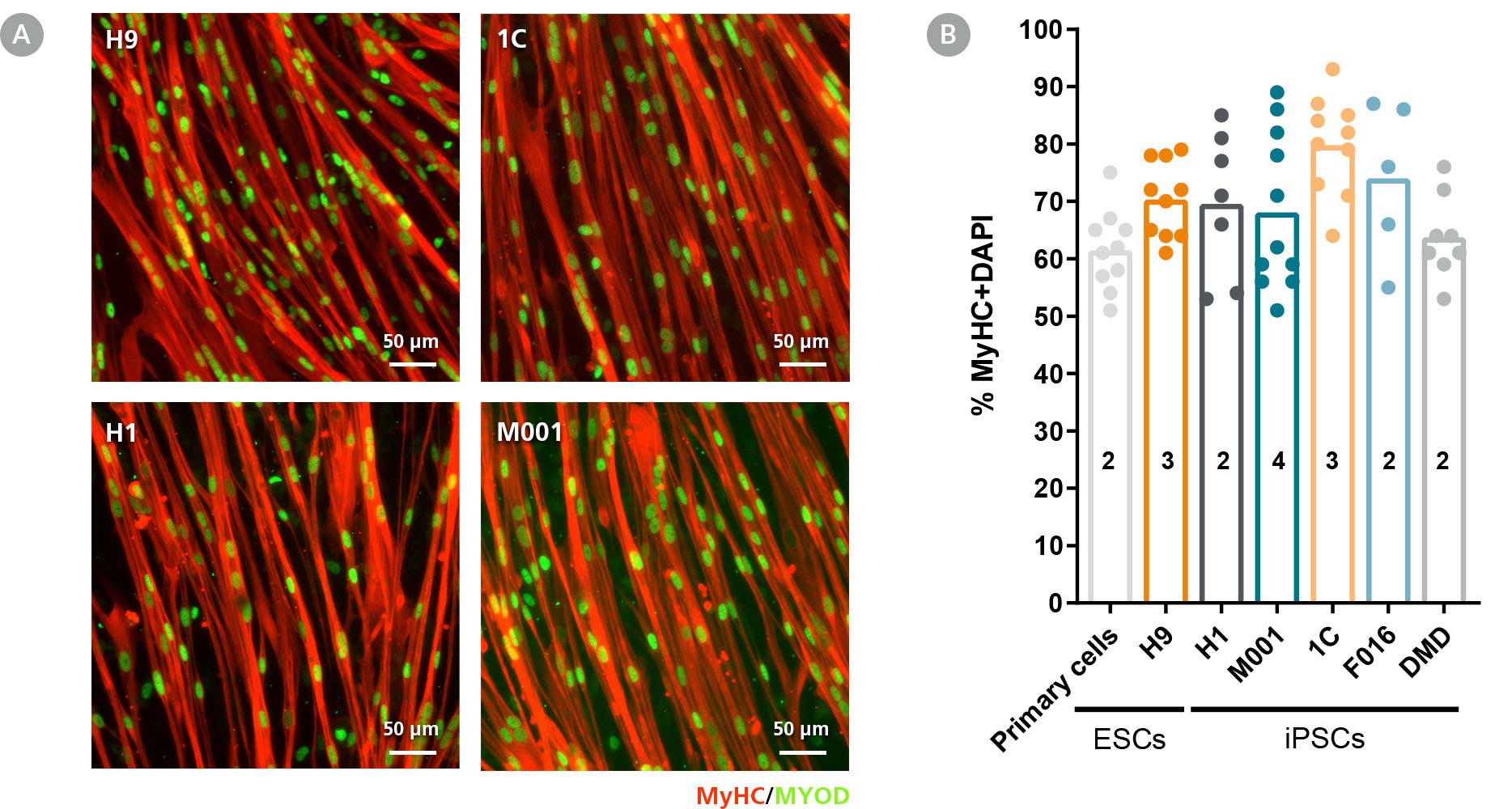
Figure 4. STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit Facilitates Efficient Differentiation of hPSC-Derived Myogenic Progenitors into hPSC-Derived Myotubes
(A) hPSC-derived myogenic progenitors were generated from multiple hPSC lines using the STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit and then induced to differentiate into myotubes using MyoCult™ Differentiation Medium (Human; Catalog #05965). After 8 days, myotubes were fixed and stained for MyHC and MyoD. (B) Multiple hPSC cell lines differentiated and induced using said method exhibited high fusion indices similar to primary human myoblasts (Numbers in bars represent the n number and dots represent technical replicates).
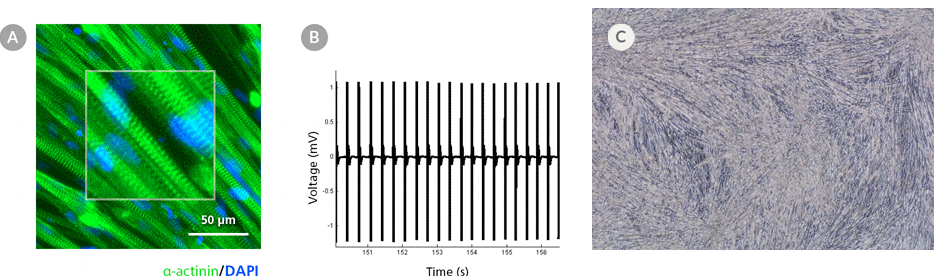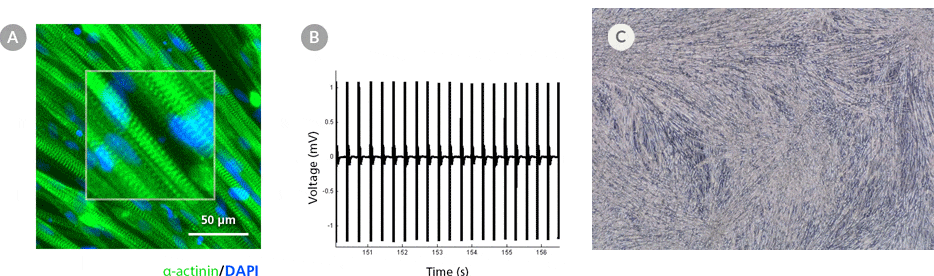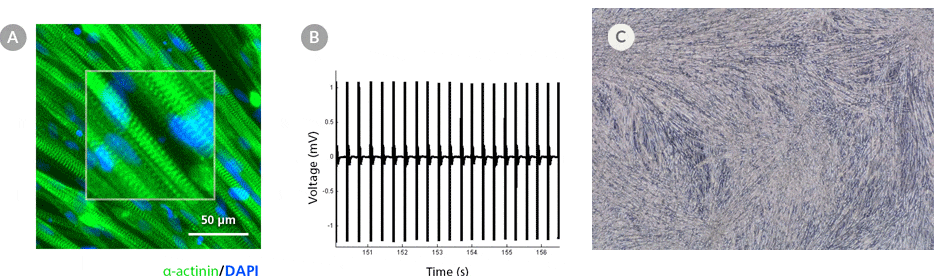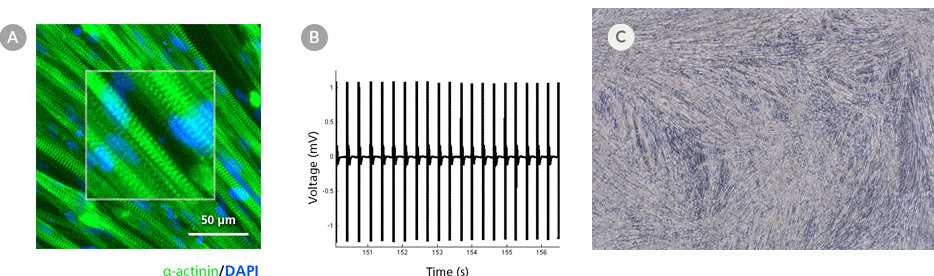
Figure 5. hPSC-Derived Myotubes Generated Using STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit Are Functionally Contractile
hPSC-derived myogenic progenitors were generated using the STEMdiff™ Myogenic Progenitor Kit and then induced to differentiate into myotubes using MyoCult™ Differentiation Medium. (A) hPSC-derived myotubes were stained for alpha-actinin and displayed organized sarcomeric structures as indicated by the zoomed-in area. (B) Spontaneous field potential recordings of hPSC-derived myotubes using microelectrode assay plate indicated that the derived myotubes are contractile. (C) Representative video of contracting hPSC-derived myotubes.