STEMdiff™ Microglia Maturation Kit
Based on the protocol from the laboratory of Mathew Blurton-Jones (Abud et al., 2017), the resulting cells are a highly pure population of microglia (> 80% CD45/CD11b-positive, > 50% TREM2-positive microglia; < 20% morphologically distinct monocytes or macrophages).
Cells derived using these products are versatile tools for modeling neuroinflammation, studying human neurological development and disease, co-culture applications, and toxicity testing.
⦁ Upstream compatibility with HPCs generated using the STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Kit and co-culture with STEMdiff™ neural organoids.
⦁ Allows differentiation to microglia with few contaminating macrophages or monocytes.
⦁ Microglia generated with the kit demonstrate phagocytosis and activation.
⦁ Required materials are provided in a simple, easy-to-use format.
- STEMdiff™ Microglia Maturation Kit (Catalog #100-0020)
- STEMdiff™ Microglia Basal Medium, 90 mL
- STEMdiff™ Microglia Supplement 1, 10 mL
- STEMdiff™ Microglia Supplement 2, 400 uL
- STEMdiff™ Microglia Supplement 3, 400 uL
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | STEMdiff™ Microglia Maturation Kit | 100-0020 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 1 | STEMdiff™ Microglia Maturation Kit | 100-0020 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 2 | STEMdiff™ Microglia Maturation Kit | 100-0020 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 3 | STEMdiff™ Microglia Maturation Kit | 100-0020 | All | English |
| Safety Data Sheet 4 | STEMdiff™ Microglia Maturation Kit | 100-0020 | All | English |
Data

Figure 1. Schematic for the STEMdiff™ Microglia Culture System Protocol
Functional microglia can be generated in 4-10 days from microglial precursors after 24 days in STEMdiff™ Microglia Differentiation Medium. For the differentiation of microglial precursors from hPSC-derived hematopoietic progenitor cells, see the PIS.
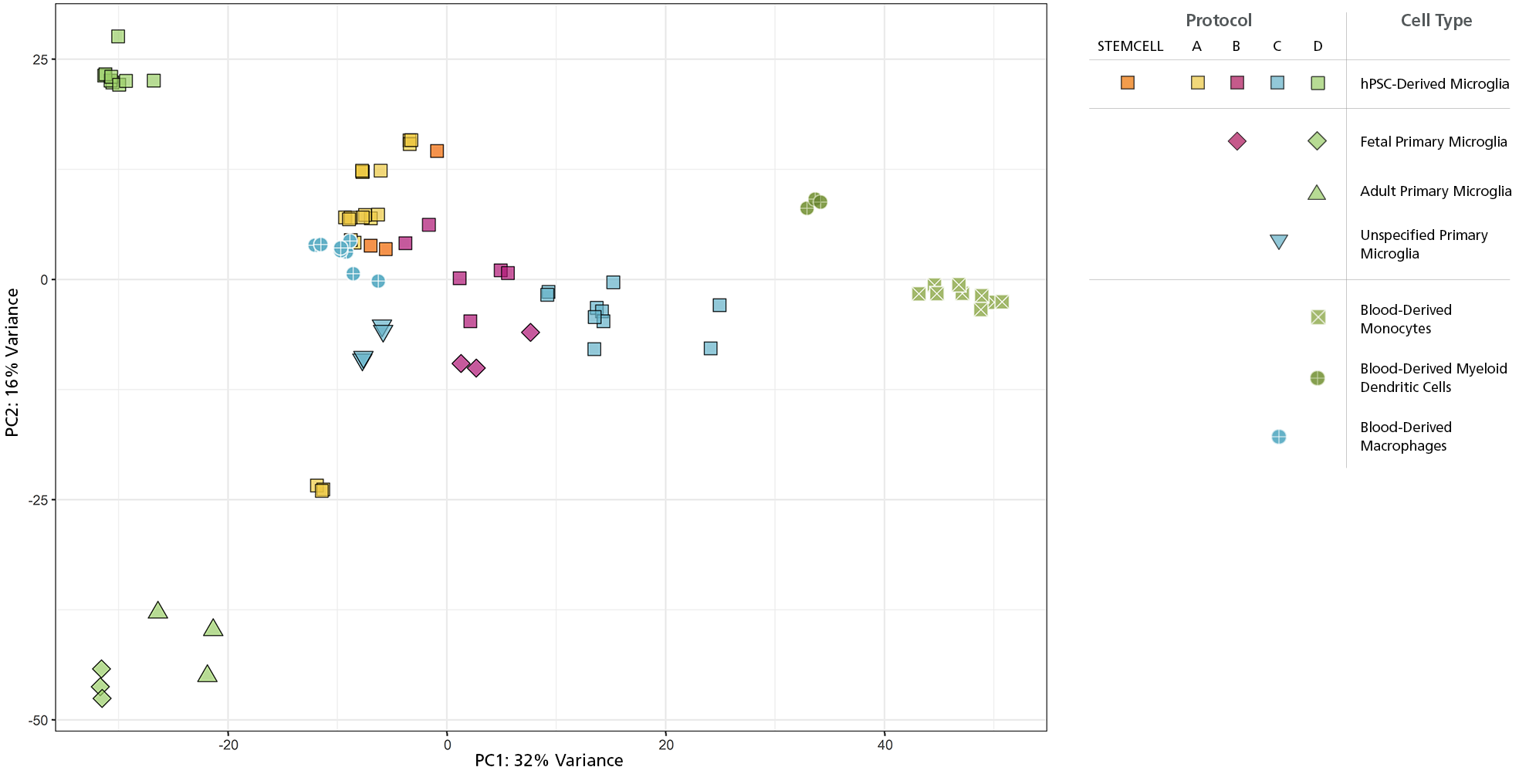
Figure 2. Microglia Generated with STEMdiff™ Microglia Culture System Are Transcriptionally Similar to Those from Published Differentiation and Maturation Protocols
RNA-seq datasets were extracted from 4 different publications (protocols A-D) that generated hPSC-derived microglia and compared their transcriptional profiles to those of other immune cell types (N = 500 genes). Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on these data along with RNA-seq data from microglia generated with STEMdiff™ Microglia Culture System. The hPSC-derived microglia from STEMdiff™ Microglia Culture System plot most closely to those from protocols A and B.
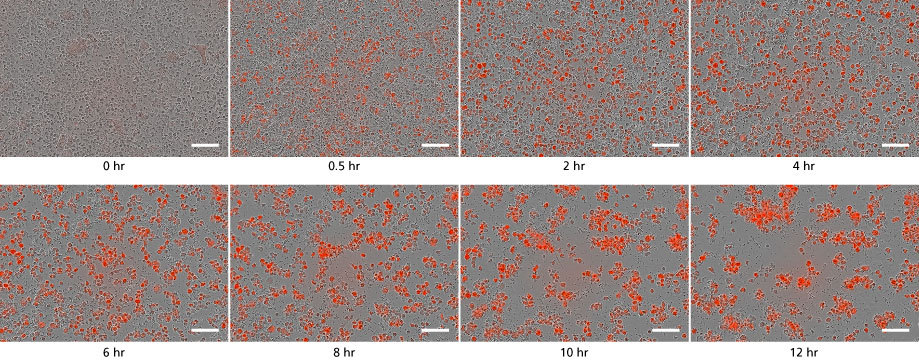
Figure 3. STEMdiff™ Microglia Culture System Generates Functional Microglia Capable of Phagocytosis at Day 34
Microglia taking up pH-sensitive bioindicator particles at a concentration of 250 μg/mL (small dots) were measured over a 12-hour time period with live cell imaging. As the particles are phagocytosed, the cells turn red. Over time, the number of small dots decreased, and the red cells increased in number and aggregated. Scale bar = 100μm.
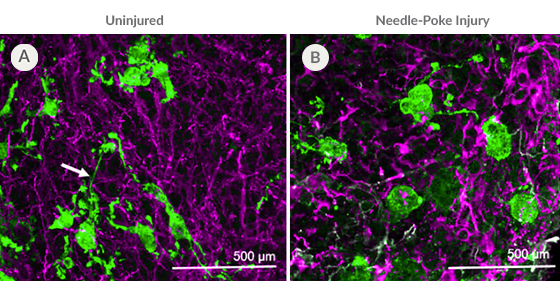
Figure 4. PSC-Derived Microglia Incorporate into Brain Organoids After 10 Days and Display an Activated Morphology upon Injury.
(A) Representative microglia and brain organoid co-cultures after 10 days, stained with IBA1 for microglia (green) and MAP2 for neurons (magenta). The microglia integrate among the neurons and display an unactivated morphology with extended processes (arrow). (B) The microglia display an activated amoeboid morphology upon injury as shown by IBA1 staining.