Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody, Clone Covi-1 (Blocking/Recombinant)
Human monoclonal IgG1 antibody against SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) S protein (HEK293-expressed recombinant)
概要
The Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody, Clone Covi-1 (Blocking/Recombinant) antibody reacts with Spike Protein S1 receptor binding domain (RBD) expressed by SARS-associated coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCoV).
The Spike (S) protein is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein present on the surface of coronaviruses (CoV). Entry of CoV into host cells is mediated by the S protein, where it interacts with the cell-surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). In humans, ACE2 is expressed in several organs and tissues, including intestinal and respiratory epithelium.
The S protein has two subunits, S1 and S2, where S1 primarily consists of the 193 amino acid long RBD and the N-terminal domain (NTD). The S2 domain is responsible for membrane fusion. During CoV infection, the S protein is cleaved into the N-terminal S1 subunit and C-terminal S2 subunit by host proteases, transforming its conformation from the pre-fusion to the post-fusion state. The S protein has been shown to play a key role in the induction of neutralizing antibody and T cell responses, which may lead to protective immunity. The RBD binds to ACE2, while the function of the NTD is not well understood.The Covi-1 antibody can block the S1 subunit from interacting with the ACE2 receptor and binds to a different epitope than the Covi-2 antibody.
The Spike (S) protein is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein present on the surface of coronaviruses (CoV). Entry of CoV into host cells is mediated by the S protein, where it interacts with the cell-surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). In humans, ACE2 is expressed in several organs and tissues, including intestinal and respiratory epithelium.
The S protein has two subunits, S1 and S2, where S1 primarily consists of the 193 amino acid long RBD and the N-terminal domain (NTD). The S2 domain is responsible for membrane fusion. During CoV infection, the S protein is cleaved into the N-terminal S1 subunit and C-terminal S2 subunit by host proteases, transforming its conformation from the pre-fusion to the post-fusion state. The S protein has been shown to play a key role in the induction of neutralizing antibody and T cell responses, which may lead to protective immunity. The RBD binds to ACE2, while the function of the NTD is not well understood.The Covi-1 antibody can block the S1 subunit from interacting with the ACE2 receptor and binds to a different epitope than the Covi-2 antibody.
Subtype
Primary Antibodies
Target Antigen
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Receptor-Binding Domain
Alternative Names
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, SARS-CoV-2 S Protein, SARS-CoV-2 S1 Protein
Conjugation
Unconjugated
Host Species
Human
Application
ELISA, Neutralization and Blocking, Western Blotting
Area of Interest
Immunology, Infectious Diseases, Respiratory Research
Clone
Covi-1
Gene ID
N/A (Uniprot: P0DTC2)
Isotype
IgG1
技术资料
| Document Type | 产品名称 | Catalog # | Lot # | 语言 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Information Sheet | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody, Clone Covi-1 (Blocking/Recombinant) | 100-0583 | All | English |
数据及文献
Data
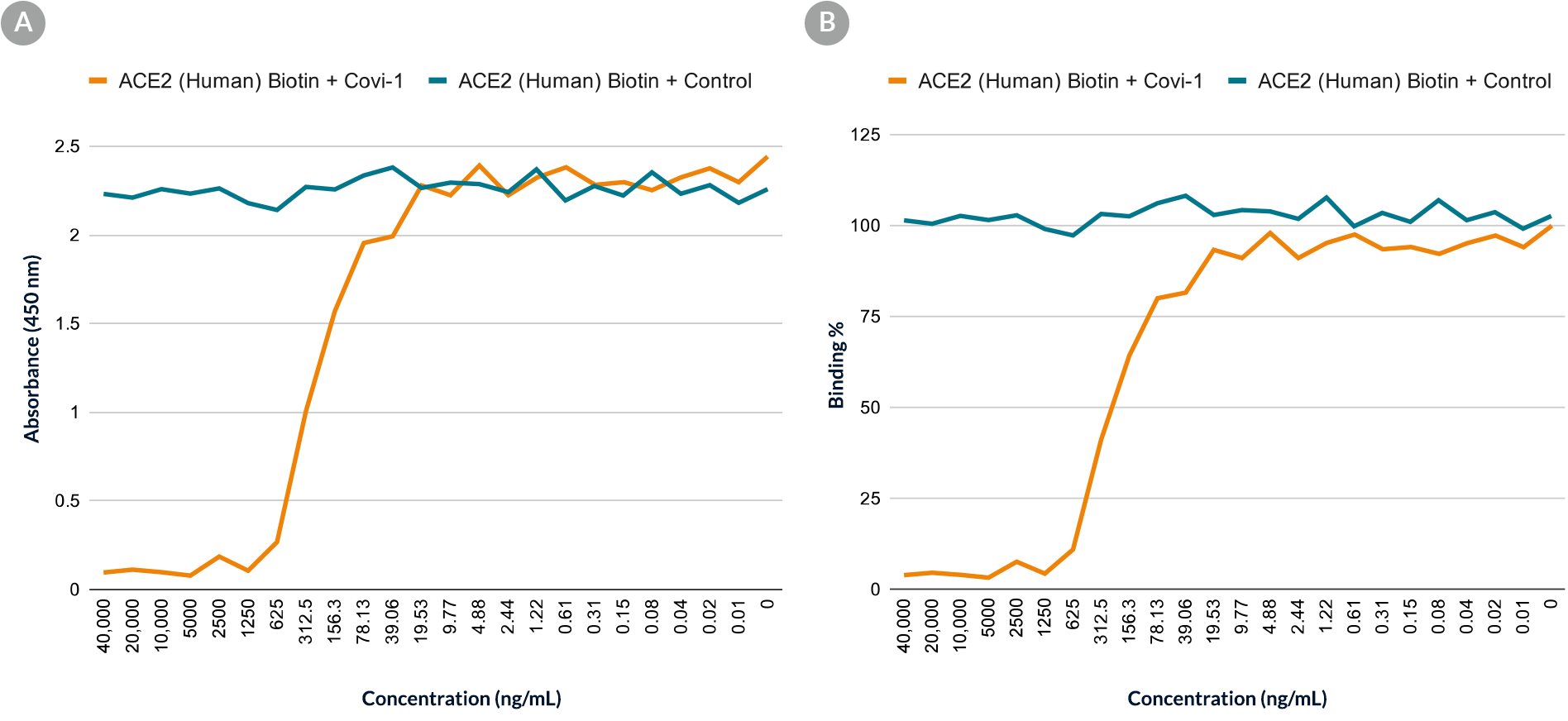
Figure 1. Inhibitory Effect of Covi-1 Antibody on Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain and ACE2 Interaction
ELISA binding assay shows that at high concentrations, Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody, Clone Covi-1 (Blocking/Recombinant) (orange line) blocks biotinylated recombinant human ACE2 from binding to an ELISA plate coated with recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein S1 RBD, in comparison to a negative control antibody (blue line). The binding of biotinylated recombinant human ACE2 to the Spike protein S1 RBD was detected using streptavidin horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The results were plotted as (A) absorbance (450 nm) or (B) binding percentage.